Blindness facts for kids

Blindness is the inability to see anything. Some people are called blind, even though they can see a little bit. This is because they cannot see clearly, but only see unfocused shapes or colours.
In modern countries, few young people are blind. In all the world, blindness is mostly caused by malnutrition and diseases of old people, like cataracts and trachoma. People can become blind because of diseases or accidents, but sometimes people are born blind.
Some people are color blind, which means they can see, but cannot tell certain colours apart.
When people are blind they use such things as the alphabet in braille and guide dogs to do every day life things.
Famous blind people have included Louis Braille, the inventor of the braille alphabet, Stevie Wonder, Ray Charles and Helen Keller.
Contents
Classification
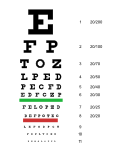
The definition of visual impairment is reduced vision not corrected by glasses or contact lenses. The World Health Organization uses the following classifications of visual impairment. When the vision in the better eye with best possible glasses correction is:
- 20/30 to 20/60 : is considered mild vision loss, or near-normal vision
- 20/70 to 20/160 : is considered moderate visual impairment, or moderate low vision
- 20/200 to 20/400 : is considered severe visual impairment, or severe low vision
- 20/500 to 20/1,000 : is considered profound visual impairment, or profound low vision
- More than 20/1,000 : is considered near-total visual impairment, or near total blindness
- No light perception : is considered total visual impairment, or total blindness
Treatment
Aside from medical help, various sources provide information, rehabilitation, education, and work and social integration.
Mobility
Many people with serious visual impairments can travel independently, using a wide range of tools and techniques. Orientation and mobility specialists are professionals who are specifically trained to teach people with visual impairments how to travel safely, confidently, and independently in the home and the community. These professionals can also help blind people to practice travelling on specific routes which they may use often, such as the route from one's house to a convenience store. Becoming familiar with an environment or route can make it much easier for a blind person to navigate successfully.
Tools such as the white cane with a red tip – the international symbol of blindness – may also be used to improve mobility. A long cane is used to extend the user's range of touch sensation. It is usually swung in a low sweeping motion, across the intended path of travel, to detect obstacles. However, techniques for cane travel can vary depending on the user and/or the situation. Some visually impaired persons do not carry these kinds of canes, opting instead for the shorter, lighter identification (ID) cane. Still others require a support cane. The choice depends on the individual's vision, motivation, and other factors.
A small number of people employ guide dogs to assist in mobility. These dogs are trained to navigate around various obstacles, and to indicate when it becomes necessary to go up or down a step. However, the helpfulness of guide dogs is limited by the inability of dogs to understand complex directions. The human half of the guide dog team does the directing, based upon skills acquired through previous mobility training. In this sense, the handler might be likened to an aircraft's navigator, who must know how to get from one place to another, and the dog to the pilot, who gets them there safely.
GPS devices can also be used as a mobility aid. Such software can assist blind people with orientation and navigation, but it is not a replacement for traditional mobility tools such as white canes and guide dogs.
Some blind people are skilled at echolocating silent objects simply by producing mouth clicks and listening to the returning echoes. It has been shown that blind echolocation experts use what is normally the "visual" part of their brain to process the echoes.
Government actions are sometimes taken to make public places more accessible to blind people. Public transportation is freely available to the blind in many cities. Tactile paving and audible traffic signals can make it easier and safer for visually impaired pedestrians to cross streets. In addition to making rules about who can and cannot use a cane, some governments mandate the right-of-way be given to users of white canes or guide dogs.
Reading and magnification
Most visually impaired people who are not totally blind read print, either of a regular size or enlarged by magnification devices. Many also read large-print, which is easier for them to read without such devices. A variety of magnifying glasses, some handheld, and some on desktops, can make reading easier for them.
Others read Braille (or the infrequently used Moon type), or rely on talking books and readers or reading machines, which convert printed text to speech or Braille. They use computers with special hardware such as scanners and refreshable Braille displays as well as software written specifically for the blind, such as optical character recognition applications and screen readers.
Some people access these materials through agencies for the blind, such as the National Library Service for the Blind and Physically Handicapped in the United States, the National Library for the Blind or the RNIB in the United Kingdom.
Closed-circuit televisions, equipment that enlarges and contrasts textual items, are a more high-tech alternative to traditional magnification devices.
There are also over 100 radio reading services throughout the world that provide people with vision impairments with readings from periodicals over the radio. The International Association of Audio Information Services provides links to all of these organizations.
Computers
Access technology such as screen readers, screen magnifiers and refreshable Braille displays enable the blind to use mainstream computer applications and mobile phones. The availability of assistive technology is increasing, accompanied by concerted efforts to ensure the accessibility of information technology to all potential users, including the blind. Later versions of Microsoft Windows include an Accessibility Wizard & Magnifier for those with partial vision, and Microsoft Narrator, a simple screen reader. Linux distributions (as live CDs) for the blind include Oralux and Adriane Knoppix, the latter developed in part by Adriane Knopper who has a visual impairment. Mac OS also comes with a built-in screen reader, called VoiceOver.
The movement towards greater web accessibility is opening a far wider number of websites to adaptive technology, making the web a more inviting place for visually impaired surfers.
Experimental approaches in sensory substitution are beginning to provide access to arbitrary live views from a camera.
Modified visual output that includes large print and/or clear simple graphics can be of benefit to users with some residual vision.
Other aids and techniques
Blind people may use talking equipment such as thermometers, watches, clocks, scales, calculators, and compasses. They may also enlarge or mark dials on devices such as ovens and thermostats to make them usable. Other techniques used by blind people to assist them in daily activities include:
- Adaptations of coins and banknotes so that the value can be determined by touch. For example:
- In some currencies, such as the euro, the pound sterling and the Indian rupee, the size of a note increases with its value.
- On US coins, pennies and dimes, and nickels and quarters are similar in size. The larger denominations (dimes and quarters) have ridges along the sides (historically used to prevent the "shaving" of precious metals from the coins), which can now be used for identification.
- Some currencies' banknotes have a tactile feature to indicate denomination. For example, the Canadian currency tactile feature is a system of raised dots in one corner, based on Braille cells but not standard Braille.
- It is also possible to fold notes in different ways to assist recognition.
- Labeling and tagging clothing and other personal items
- Placing different types of food at different positions on a dinner plate
- Marking controls of household appliances
Most people, once they have been visually impaired for long enough, devise their own adaptive strategies in all areas of personal and professional management.
For the blind, there are books in braille, audio-books, and text-to-speech computer programs, machines and e-book readers. Low vision people can make use of these tools as well as large-print reading materials and e-book readers that provide large font sizes.
Computers are important tools of integration for the visually impaired person. They allow, using standard or specific programs, screen magnification and conversion of text into sound or touch (Braille line), and are useful for all levels of visual handicap. OCR scanners can, in conjunction with text-to-speech software, read the contents of books and documents aloud via computer. Vendors also build closed-circuit televisions that electronically magnify paper, and even change its contrast and color, for visually impaired users. For more information, consult Assistive technology.
In adults with low vision there is no conclusive evidence supporting one form of reading aid over another. In several studies stand-based closed-circuit television and hand-held closed-circuit television allowed faster reading than optical aids. While electronic aids may allow faster reading for individuals with low vision, portability, ease of use, and affordability must be considered for people.
Children with low vision sometimes have reading delays, but do benefit from phonics-based beginning reading instruction methods. Engaging phonics instruction is multisensory, highly motivating, and hands-on. Typically students are first taught the most frequent sounds of the alphabet letters, especially the so-called short vowel sounds, then taught to blend sounds together with three-letter consonant-vowel-consonant words such as cat, red, sit, hot, sun. Hands-on (or kinesthetically appealing) VERY enlarged print materials such as those found in "The Big Collection of Phonics Flipbooks" by Lynn Gordon (Scholastic, 2010) are helpful for teaching word families and blending skills to beginning readers with low vision. Beginning reading instructional materials should focus primarily on the lower-case letters, not the capital letters (even though they are larger) because reading text requires familiarity (mostly) with lower-case letters. Phonics-based beginning reading should also be supplemented with phonemic awareness lessons, writing opportunities, and lots of read-alouds (literature read to children daily) to stimulate motivation, vocabulary development, concept development, and comprehension skill development. Many children with low vision can be successfully included in regular education environments. Parents may need to be vigilant to ensure that the school provides the teacher and students with appropriate low vision resources, for example technology in the classroom, classroom aide time, modified educational materials, and consultation assistance with low vision experts.
Communication
Communication with the visually impaired can be more difficult than communicating with someone who doesn't have vision loss. However, many people are uncomfortable with communicating with the blind, and this can cause communication barriers. One of the biggest obstacles in communicating with visually impaired individuals comes from face-to-face interactions. There are many factors that can cause the sighted to become uncomfortable while communicating face to face. There are many non-verbal factors that hinder communication between the visually impaired and the sighted, more often than verbal factors do. These factors, which Rivka Bialistock mentions in her article, include:
- Lack of facial expressions, mimics, or body gestures/responses
- Non-verbal gestures that could imply the visually impaired individual not appearing interested
- Speaking when not anticipated or not speaking when anticipated
- Fear of offending the visually impaired
- Standing too close and invading the personal comfort level
- Having to exercise or ignore feelings of pity
- Being uncomfortable with touching objects or people
- A look of detachment or disengagement
- Dependency
- Being reminded of the fear of becoming blind
The blind person sends these signals or types of non-verbal communication without being aware that they are doing so. These factors can all affect the way an individual would feel about communicating with the visually impaired. This leaves the visually impaired feeling rejected and lonely.
Adjusting attitude
In the article Towards better communication, from the interest point of view. Or—skills of sight-glish for the blind and visually impaired, the author, Rivka Bialistock comes up with a method to reduce individuals being uncomfortable with communicating with the visually impaired. This method is called blind-glish or sight-glish, which is a language for the blind, similar to English. For example, babies, who are not born and able to talk right away, communicate through sight-glish, simply seeing everything and communicating non-verbally. This comes naturally to sighted babies, and by teaching this same method to babies with a visual impairment can improve their ability to communicate better, from the very beginning.
To avoid the rejected feeling of the visually impaired, people need to treat the blind the same way they would treat anyone else, rather than treating them like they have a disability, and need special attention. People may feel that it is improper to, for example, tell their blind child to look at them when they are speaking. However, this contributes to the sight-glish method. It is important to disregard any mental fears or uncomfortable feelings people have while communicating (verbally and non-verbally) face-to-face.
Surroundings
Individuals with a visual disability not only have to find ways to communicate effectively with the people around them, but their environment as well. The blind or visually impaired rely largely on their other senses such as hearing, touch, and smell in order to understand their surroundings.
Sound
Sound is one of the most important senses that the blind or visually impaired use in order to locate objects in their surroundings. A form of echolocation is used, similarly to that of a bat. Echolocation from a person's perspective is when the person uses sound waves generated from speech or other forms of noise such as cane tapping, which reflect off of objects and bounce back at the person giving them a rough idea of where the object is. This does not mean they can depict details based on sound but rather where objects are in order to interact, or avoid them. Increases in atmospheric pressure and humidity increase a person's ability to use sound to their advantage as wind or any form of background noise impairs it.
Touch
Touch is also an important aspect of how blind or visually impaired people perceive the world. Touch gives immense amount of information in the persons immediate surrounding. Feeling anything with detail gives off information on shape, size, texture, temperature, and many other qualities. Touch also helps with communication; braille is a form of communication in which people use their fingers to feel elevated bumps on a surface and can understand what is meant to be interpreted. There are some issues and limitations with touch as not all objects are accessible to feel, which makes it difficult to perceive the actual object. Another limiting factor is that the learning process of identifying objects with touch is much slower than identifying objects with sight. This is due to the fact the object needs to be approached and carefully felt until a rough idea can be constructed in the brain.
Smell
Certain smells can be associated with specific areas and help a person with vision problems to remember a familiar area. This way there is a better chance of recognizing an areas layout in order to navigate themselves through. The same can be said for people as well. Some people have their own special odor that a person with a more trained sense of smell can pick up. A person with an impairment of their vision can use this to recognize people within their vicinity without them saying a word.
Images for kids
-
Blind Woman by Diego Velázquez
-
The Sense of Touch by Jusepe de Ribera depicts a blind man holding a marble head in his hands.
See also
 In Spanish: Discapacidad visual para niños
In Spanish: Discapacidad visual para niños