Carbon facts for kids

Graphite (left) and diamond (right), two allotropes of carbon
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carbon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allotropes | graphite, diamond and more (see Allotropes of carbon) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | graphite: black diamond: clear |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar, std(C) | [12.0096, 12.0116] conventional: 12.011 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carbon in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 14 (carbon group) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [He] 2s2 2p2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sublimation point | 3915 K (3642 °C, 6588 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | amorphous: 1.8–2.1 g/cm3 graphite: 2.267 g/cm3 diamond: 3.515 g/cm3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Triple point | 4600 K, 10,800 kPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | graphite: 117 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | graphite: 8.517 J/(mol·K) diamond: 6.155 J/(mol·K) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | −4, −3, −2, −1, 0, +1, +2, +3, +4 (a mildly acidic oxide) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 2.55 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | sp3: 77 pm sp2: 73 pm sp: 69 pm |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 170 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectral lines of carbon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
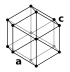
| Crystal structure | graphite: simple hexagonal
(black) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
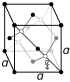
| Crystal structure | diamond: face-centered diamond-cubic
(clear) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | diamond: 18,350 m/s (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | diamond: 0.8 µm/(m⋅K) (at 25 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | graphite: 119–165 W/(m⋅K) diamond: 900–2300 W/(m⋅K) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | graphite: 7.837 µΩ⋅m | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | −5.9·10−6 (graph.) cm3/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | diamond: 1050 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | diamond: 478 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | diamond: 442 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poisson ratio | diamond: 0.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | graphite: 1–2 diamond: 10 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-44-0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Egyptians and Sumerians (3750 BCE) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recognized as an element by | Antoine Lavoisier (1789) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main isotopes of carbon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Carbon is a very important chemical element, with a chemical symbol of C. All known life on Earth needs it. Carbon has atomic mass 12 and atomic number 6. It is a nonmetal, meaning that it is not a metal.
When iron is alloyed with carbon, hard steel is formed. Carbon in the form of coal is an important fuel.
Contents
Chemistry of carbon
A whole type of Chemistry, organic chemistry, is about carbon and its compounds. Carbon makes many types of compounds. Hydrocarbons are molecules with carbon and hydrogen. Methane, Propane, and many other fuels are hydrocarbons. Many of the substances that people use daily are organic compounds.
Carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and some other elements like sulfur and phosphorus together form most life on earth (see List of biologically important elements). Carbon forms a very large number of organic compounds because it can form strong bonds with itself and with other elements. Because of the amounts of carbon living things have, all organic things are considered "carbon-based". Each carbon atom can form four single covalent bonds. These bonds allow carbon to form long chain-shaped molecules, called polymers, such as plastics.
Etymology
The name of carbon comes from Latin carbo, meaning charcoal. In many foreign languages the words for carbon, coal and charcoal are synonyms.
Types of carbon
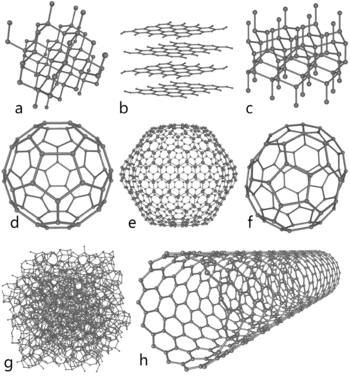
Carbon in nature is found in three forms called allotropes: diamond, graphite, and fullerenes. Graphite, with clay, is in pencils. It is very soft. The carbon atoms in it make rings, which are on top of each other and slide very easily. Diamonds are the hardest natural mineral. Fullerenes are a "soccer ball" shape of carbon. They are mostly of interest to science. A special, man-made, tube-shaped allotrope of carbon is the carbon nanotube. Carbon nanotubes are very hard, so they might be used in armor. Nanotubes might be useful in nanotechnology.
There are 10 million known carbon compounds.
Radiocarbon dating
A radioactive isotope of carbon, carbon-14, can be used to figure out how old some objects are or when something died. As long as something is on the surface of the earth and taking in carbon, the amount of carbon-14 stays the same. When an object stops taking in carbon, the carbon-14 amount goes down. Because the half-life (how long it takes for half of a radioactive isotope to go away) of carbon-14 is 5730 years, scientists can see how old the object is by how much carbon-14 is left.
Where carbon is
Carbon is in many places in the universe. It was first made in old stars. Carbon is the fourth most common element in the sun. The atmospheres of Venus and Mars are mostly carbon dioxide.
Carbon is important to the human body and other living things, and it is the second most common element in the human body, at 23% of all body weight. It is also a key part of many biological molecules (molecules used in life).
Most of the carbon on Earth is coal. Graphite is in many (typically desert) areas, including Sri Lanka, Madagascar, and Russia. Diamonds are rare and are found largely in Africa. Carbon is also in some meteorites.
Related pages
| Periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn | ||||||||||
| Fr | Ra | Ac | Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Uut | Fl | Uup | Lv | Uus | Uuo | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Images for kids
-
Comet C/2014 Q2 (Lovejoy) surrounded by glowing carbon vapor
-
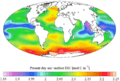
"Present day" (1990s) sea surface dissolved inorganic carbon concentration (from the GLODAP climatology)
-
Correlation between the carbon cycle and formation of organic compounds. In plants, carbon dioxide formed by carbon fixation can join with water in photosynthesis (green) to form organic compounds, which can be used and further converted by both plants and animals.
-
Antoine Lavoisier in his youth
-
Pencil leads for mechanical pencils are made of graphite (often mixed with a clay or synthetic binder).
-
Sticks of vine and compressed charcoal
See also
 In Spanish: Carbono para niños
In Spanish: Carbono para niños