East Japan Railway Company facts for kids
 |
|

The company headquarters in Shibuya ward, Tokyo
|
|
|
Native name
|
東日本旅客鉄道株式会社
|
|---|---|
|
Romanized name
|
Higashi-Nihon Ryokaku Tetsudō kabushiki gaisha lit. East Japan Passenger Railway Share Company |
| Public (Kabushiki gaisha) | |
| Traded as |
|
| Industry | Rail transport |
| Predecessor | Japanese National Railways (JNR) |
| Founded | 1 April 1987, privatization of JNR |
| Headquarters |
2-2-2 Yoyogi, Shibuya, Tokyo
,
Japan
|
|
Area served
|
Kanto and Tōhoku regions Niigata, Nagano, Yamanashi and Shizuoka prefectures |
|
Key people
|
Tetsuro Tomita (Chairman of the Board) Masaki Ogata (Vice Chairman of the Board) Yuji Fukasawa (President, Representative Director) |
| Products | Suica (a rechargeable contactless smart card) |
| Services | Passenger railways freight services bus transportation other related services |
| Revenue | |
|
Operating income
|
|
|
|
| Total assets |
|
| Total equity |
|
| Owner | JTSB investment trusts (8.21%) Mizuho Bank (4.07%) TMTBJ investment trusts (3.97%) MUFG Bank (2.75%) Repurchased shares (2.67%) (as of 30 September 2018) |
|
Number of employees
|
73,017 (as of 31 March 2013) |
| Divisions | Railway operations Life-style business IT & Suica business |
| Subsidiaries | 83 companies, including Tokyo Monorail and J-TREC |
| East Japan Railway Company | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Line up of JR East Shinkansen trains, October 2009
|
|||||||
| Operation | |||||||
| National railway | Japan Railways Group | ||||||
| Infrastructure company | Japan Railway Construction, Transport and Technology Agency | ||||||
| Statistics | |||||||
| Ridership | 6.169 billion per year | ||||||
| Passenger km | 130.5 billion per year | ||||||
| System length | |||||||
| Total | 7,512.6 km (4,668.1 mi) | ||||||
| Double track | 3,668 km (2,279 mi) (49%) | ||||||
| Electrified | 5,512.7 km (3,425.4 mi) (73.2%) | ||||||
| High-speed | 1,052.9 km (654.2 mi) (14.0%) | ||||||
| Track gauge | |||||||
| Main | 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) | ||||||
| High-speed | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) | ||||||
| Electrification | |||||||
| Main | 1,500 V DC overhead catenary 2,680.3 km (1,665.5 mi) | ||||||
| 20 kV AC, 50 Hz | 1,779.5 km (1,105.7 mi) Conventional lines in Tohoku Joban Line (Fujishiro-Iwanuma) Mito Line |
||||||
| 25 kV AC, 50/60 Hz overhead | 1,052.9 km (654.2 mi) Tohoku Shinkansen (50 Hz) Joetsu Shinkansen (50 Hz) Hokuriku Shinkansen (50/60 Hz) |
||||||
| Features | |||||||
| No. tunnels | 1,263 | ||||||
| Tunnel length | 882 km (548 mi) | ||||||
| Longest tunnel | The Seikan Tunnel 53,850 m (176,670 ft) Hokkaido Shinkansen |
||||||
| No. bridges | 14,865 | ||||||
| Longest bridge | No.1 Kitakami River Bridge 3,868 m (12,690 ft) Tohoku Shinkansen |
||||||
| No. stations | 1,681 | ||||||
|
|||||||
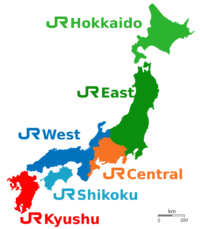
The East Japan Railway Company is a major passenger railway company in Japan, the largest of the seven Japan Railways Group companies. The company name is officially abbreviated as JR-EAST or JR East in English, and as JR Higashi-Nihon (JR東日本, Jeiāru Higashi-Nihon) in Japanese. The company's headquarters are in Yoyogi, Shibuya, Tokyo, next to Shinjuku Station. It is listed in the Tokyo Stock Exchange (it formerly had secondary listings in the Nagoya and Osaka stock exchanges), is a constituent of the TOPIX Large70 index, and is one of three Japan Railways Group constituents of the Nikkei 225 index, the others being JR Central and JR West.




Contents
History
JR East was incorporated on 1 April 1987 after being spun off from the government-run Japanese National Railways (JNR). The spin-off was nominally "privatization", as the company was actually a wholly owned subsidiary of the government-owned JNR Settlement Corporation for several years, and was not completely sold to the public until 2002.
Following the breakup, JR East ran the operations on former JNR lines in the Greater Tokyo Area, the Tōhoku region, and surrounding areas.
Lines
Railway lines of JR East primarily serve the Kanto and Tohoku regions, along with adjacent areas in Kōshin'etsu region (Niigata, Nagano, Yamanashi) and Shizuoka prefectures.
Shinkansen
JR East operates all of the Shinkansen high-speed rail lines north of Tokyo, with the exception of the Hokkaido Shinkansen which is operated by JR Hokkaido.
The Tokyo–Osaka Tōkaidō Shinkansen is owned and operated by the Central Japan Railway Company (JR Central), although it stops at several JR East stations. |
Kanto region
These lines have sections inside the Tokyo suburban area (Japanese: 東京近郊区間) designated by JR East. This does not necessarily mean that the lines are fully inside the Greater Tokyo Area.
|
Koshinetsu region
|
Tohoku region
|
Services
Below is the full list of limited express and express train services operated on JR East lines as of 2022.
Shinkansen
- Asama
- Hakutaka
- Hayabusa
- Hayate
- Kagayaki
- Komachi
- Nasuno
- Tanigawa
- Toki
- Tsubasa
- Yamabiko
Limited express (daytime)
- Kusatzu
- Akagi
- Azusa
- Fuji Excursion
- Hitachi and Tokiwa
- Inaho
- Kaiji/View Kaiji
- Kusatsu
- Narita Express
- Nikkō and Kinugawa
- Saphir Odoriko/Odoriko
- Sazanami
- Shirayuki
- Shiosai
- Shōnan
- Tsugaru
- Wakashio
Limited express (overnight)
- Sunrise Izumo/Sunrise Seto (not operated by JR East, operated by JR Central and JR-West over the Tokaido Main Line, part of which JR East owns between Tokyo and Atami)
Stations
During fiscal 2017, the busiest stations in the JR East network by average daily passenger count were:
- Shinjuku Station (778,618)
- Ikebukuro Station (566,516)
- Tokyo Station (452,549)
- Yokohama Station (420,192)
- Shinagawa Station (378,566)
- Shibuya Station (370,669)
- Shimbashi Station (277,404)
- Omiya Station (255,147)
- Akihabara Station (250,251)
- Kita-Senju Station (217,838)
Subsidiaries

- Higashi-Nihon Kiosk - provides newspapers, drinks and other items in station kiosks and operates the Newdays convenience store chain
- JR Bus Kanto / JR Bus Tohoku - intercity bus operators
- Nippon Restaurant Enterprise - provides bentō box lunches on trains and in train stations
- Tokyo Monorail - (70% ownership stake)
- East Japan Marketing & Communications
Sponsorship
JR East co-sponsors the JEF United Chiba J-League football club , which was formed by a merger between the JR East and Furukawa Electric company teams.
Carbon emission plan
JR East aims to reduce its carbon emissions by half, as measured over the period 1990–2030. This would be achieved by increasing the efficiency of trains and company-owned thermal power stations and by developing hybrid trains.
Alleged revolutionary front
The Tokyo Metropolitan Police Department has stated that JR East's official union is a front for a revolutionary political organization called the Japan Revolutionary Communist League (Revolutionary Marxist Faction). An investigation of this is ongoing.
Culture foundation
The East Japan Railway Culture Foundation is a non-profit organization established by JR East for the purpose of developing a "richer railway culture". The Railway Museum in Saitama is operated by the foundation.
Bids outside Japan
JR East holds a 15% shareholding in West Midlands Trains with Abellio and Mitsui that commenced operating the West Midlands franchise in England in December 2017. The same consortium has also been listed to bid for the South Eastern franchise.
See also
 In Spanish: East Japan Railway Company para niños
In Spanish: East Japan Railway Company para niños