Ice age facts for kids
An ice age is a period when for a long time the temperature of Earth's climate is very low. This leads to an expansion of the continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and mountain glaciers.
Ice age is a term used in palaeoclimatology for the period of extensive ice sheets in the recent Pleistocene period. We now know that ice ages have happened a number of times in the past, the greatest and longest of which took place in the Proterozoic era, before multi-cellular eukaryotes evolved.
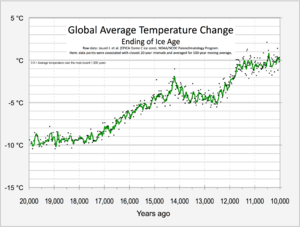
During ice ages the sea level drops as water is held in the great ice sheets at the poles. How much it drops depends on several factors, such as the length of time that a cold period lasts.
Contents
Stages
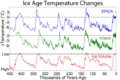
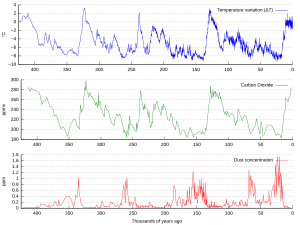
Within an ice age, there are stages. The longer cold stages are called glacials or glacial periods. The shorter warm periods are called interglacials. The last glacial ended about 11,000 years ago when the present interglacial started. The Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets still exist. The last two million years have been the Pleistocene ice age. During glacials, large and thick ice sheets cover much of the North American and Eurasian continents.
Many glacial periods that have occurred during the last few million years are initially at 40,000-year frequency, but more recently ice ages have occurred at 100,000-year frequency.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Haukalivatnet lake (50 meters above sea level) where Jens Esmark in 1823 discovered similarities to moraines near existing glaciers in the high mountains.
-
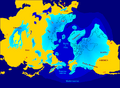
Northern hemisphere glaciation during the last ice ages. The setup of 3 to 4 kilometer thick ice sheets caused a sea level lowering of about 120 m.
-
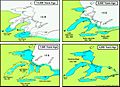
Stages of proglacial lake development in the region of the current North American Great Lakes.
-
Scandinavia exhibits some of the typical effects of ice age glaciation such as fjords and lakes.
See also
 In Spanish: Glaciación para niños
In Spanish: Glaciación para niños