Switzerland facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Swiss Confederation
|
|
|---|---|
|
Anthem: "Swiss Psalm"
|
|
Location of Switzerland (green)
on the European continent (green and dark grey) |
|
| Capital | None (de jure) Bern (de facto) 46°57′N 7°27′E / 46.950°N 7.450°E |
| Largest city | Zürich |
| Official languages | German French Italian Romansh |
| Religion |
|
| Demonym(s) | English: Swiss, German: Schweizer(in), French: Suisse(sse), Italian: svizzero/svizzera, or elvetico/elvetica, Romansh: Svizzer/Svizra |
| Government | Federal semi-direct democracy under a multi-party parliamentary directorial republic |
| Legislature | Federal Assembly |
| Council of States | |
| National Council | |
| History | |
|
• Foundation date
|
c. 1300 (traditionally 1 August 1291) |
| 24 October 1648 | |
|
• Restoration
|
7 August 1815 |
|
• Federal state
|
12 September 1848 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
41,285 km2 (15,940 sq mi) (132nd) |
|
• Water (%)
|
4.2 |
| Population | |
|
• 2019 estimate
|
|
|
• 2015 census
|
8,327,126 |
|
• Density
|
207/km2 (536.1/sq mi) (48th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2020 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$548 billion (38th) |
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2018 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$704 billion (20th) |
|
• Per capita
|
$82,950 (2nd) |
| Gini (2018) | ▼ 29.7 low · 19th |
| HDI (2018) | very high · 2nd |
| Currency | Swiss franc (CHF) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Date format | dd.mm.yyyy (AD) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +41 |
| ISO 3166 code | CH |
| Internet TLD | .ch, .swiss |
Switzerland (German: Schweiz; French: Suisse; Italian: Svizzera; Romansh: Svizra; Swiss German: Schwiz) is a small country in Western Europe. The official name of Switzerland is Confoederatio Helvetica. This is Latin and is not often used except for state documents. Switzerland is a federation of even smaller states - 26 cantons.
Switzerland is known for its neutrality. A country is neutral when it does not take sides among the countries who are at war. Switzerland has been neutral for more than 190 years. Many international organizations are in Switzerland. The United Nations has a main office (but not its headquarters) in Geneva. Its predecessor organization, the League of Nations, was headquartered in Geneva.
There are four official languages in Switzerland: German, French, Italian, and Romansh. Some cantons and even towns have two languages spoken in them, and the largest canton by area, Graubünden, has three. About 2/3 of the population speak German; French is spoken in the west of the country, while Italian is spoken in the canton of Ticino and Romansh in parts of Graubünden.
The capital of Switzerland is Bern. The largest city of Switzerland is Zürich.
To the north of Switzerland is Germany. East of Switzerland are Austria and Liechtenstein. To the south of Switzerland is Italy. To the west of Switzerland is France.
Contents
Geography
The area of Switzerland is 41,285 km². The confederation is divided into 23 full states called cantons. All 26 cantons are: Aargau, Appenzell Innerrhoden, Appenzell Ausserrhoden, Basel-Stadt, Basel-Land, Berne, Fribourg, Geneva, Glarus, Graubünden, Jura, Lucerne, Neuchâtel, Nidwalden, Obwalden, Schaffhausen, Schwyz, Solothurn, St. Gallen, Thurgau, Ticino, Uri, Valais, Vaud, Zug, and Zürich.
The mountains are very tall in the center and south of Switzerland. About 60% of Switzerland is in the Alps area. Only few people live here. The highest mountain is the Dufour Peak at 4,634 m.
Many of the mountains have ice all year. This ice is called glaciers. The rivers Rhine, Rhône, and many other rivers start in the mountains of Switzerland.
There are many lakes in Switzerland. The biggest lakes are all in the north and west: Lake Geneva (Lac Léman), Lake Zürich, Lake Neuchâtel and Lake Constance (Bodensee).
Mountains in the north of Switzerland are fewer and smaller. That is why most Swiss people live in cities and towns in the north. The Jura mountains are in the northwest of Switzerland.
Cities
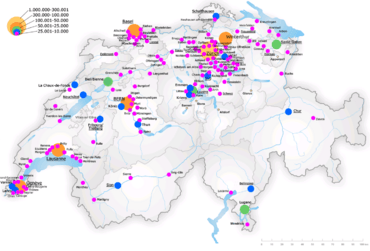
Switzerland has 2,485 villages, towns and cities.
The largest cities are:
- Zurich
- Geneva
- Basel
- Bern
- Lausanne
- Lucerne
- Winterthur
- St. Gallen
- Lugano
- Biel/Bienne
- Thun
- Köniz
- La Chaux-de-Fonds
- Schaffhausen
- Fribourg
- Vernier
- Chur
- Neuchâtel
- Uster
- Sion
People
There are about 8 million people in Switzerland. About 64% of the people speak German as their first language, in northern and central Switzerland. 19% of the people speak French as their first language, in the west of Switzerland. 8% of the people speak Italian, in the south of Switzerland. Only 1% of the people speak Romansh, in the southeastern part of Switzerland. Romansh is an old language that is similar to Latin.
The German-speaking people of Switzerland do not actually speak "German" as their native language. Swiss people speak something called Alemannic which has its own writing language and grammar but still is normally considered a German dialect. Alemannic may be difficult for Germans to understand. Swiss people do write like the people from Germany and also speak standard German very well, especially in the larger cities.
About 23% of the people in Switzerland do not come from Switzerland. They come from other places to usually work in Switzerland.
The religion of most people in Switzerland is Christianity. 43% of the population follow Catholicism. 35% of the population follow Protestantism. 2% follow Eastern Orthodoxy. The religion of 4% of the population is Islam. The rest follow other religions, or they have no religion.
Switzerland is famous for its chocolate, cheese, banking system, watches and mountains.
History
In 1291, people from Uri, Schwyz and Unterwalden wanted to be free. They signed a contract to work together called the Eternal Alliance. Together, they could be free from the people of Habsburg, who were very strong. In 1315 the people from the Eternal Alliance fought the Habsburgs in battles at Morgarten, Sempach and Näfels. The people of the Eternal Alliance won all the battles.
People from other areas signed the contract and joined the Eternal Alliance. More and more people worked together to be free. In 1648, other countries from Europe made an agreement that Switzerland was free. The name of this agreement was the Peace of Westphalia. More areas came to be part of Switzerland.
In 1798, France invaded Switzerland. The ruler of France was Napoleon. He changed many laws. In 1815 Switzerland again became independent from France. Other countries agreed at the Congress of Vienna that Switzerland was free and neutral.
The constitution of Switzerland that was made after a short civil war in 1848 was replaced in 1999. Switzerland did not fight in World War I or World War II. Since 2002, Switzerland is part of the United Nations. It did not join the United Nations for 57 years because of its neutrality.
Government

Switzerland is a republic. Switzerland does not have the same kind of president as the United States or France. Seven people (called ministers) do the job of president. They are called the Federal Council in English, Bundesrat in German, Conseil Fédéral in French, Consiglio Federale in Italian and Cussegl Federal in Romansh. Every year one of these people is made president. The president is not more important than the other six people. At present 3 of the 7 people are women.
There are two parts of parliament in Switzerland. The Council of States and the National Council. Only both together can make laws. There are 46 people in the Council of States. Every full canton of Switzerland can send 2 people. There are 200 people in the National Council. The biggest canton sends most people to the National Council. The smallest 6 cantons can only send one person to the National Council.
The people of Switzerland can collect signatures if they do not like a new law or a law change. This is called a referendum. If enough people sign a referendum, the people vote. The people can also collect signatures to change the constitution. This is called an initiative. The constitution is the basic law of a country.
Economy

Switzerland's most important economic sector is manufacturing. Manufacturing consists largely of the production of specialist chemicals, health and pharmaceutical goods, scientific and precision measuring instruments and musical instruments. The largest exported goods are chemicals (34% of exported goods), machines/electronics (20.9%), and precision instruments/watches (16.9%). Exported services amount to a third of exports. The service sector – especially banking and insurance, tourism, and international organisations – is another important industry for Switzerland.
Tourism is important in Switzerland. There are many places for tourists. Davos, St. Moritz, Pontresina and Flims are in Switzerland. These towns are important both in winter (for skiing) and in summer. Tourists also like the cities of Lucerne, Geneva, and Zürich.
Literature
The literature of Switzerland is divided according to the language used. Most Swiss literature was written in German from 1291 until 1798. French became popular in Bern and elsewhere in the 18th century and many words also in the German speaking parts of Switzerland come from the French and are not known to Germans. Italian language and Romansch-Latin literature are less common in Switzerland.
Heidi, a book for children by Johanna Spyri, is the most famous book of Switzerland. It is located in the mountains in Graubünden.
Sports

Skiing, snowboarding and mountaineering are among the most popular sports in Switzerland. Because of the large mountain range the nature of the country is well suited for such activities. Bobsleigh was invented in St. Moritz. The first world ski championships were held in Mürren (1931) and St. Moritz (1934). St. Moritz hosted the second Winter Olympic Games in 1928 and in 1948. Among the most successful skiers and world champions are Pirmin Zurbriggen and Didier Cuche.
Many Swiss are fans of football. The national team or 'Nati' is widely supported. Switzerland was the joint host, with Austria, of the Euro 2008 tournament. Many Swiss also follow ice hockey. In April 2009, Switzerland hosted the 2009 IIHF World Championship for the 10th time. The National League A is the most attended league in Europe.
The many lakes in the country make Switzerland a good place for sailing. The largest, Lake Geneva, is the home of the sailing team Alinghi. They were the first European team to win the America's Cup in 2003. They also won in 2007. Tennis has become more popular. Swiss players such as Martina Hingis and Roger Federer have won multiple Grand Slams.

Motorsport racecourses and events were banned in Switzerland after the 1955 Le Mans disaster. There were exceptions for events such as Hillclimbing. This ban was overturned in June 2007. During this period, the country still had successful racing drivers such as Clay Regazzoni, Sebastian Buemi, Jo Siffert and successful World Touring Car Championship driver Alain Menu. Switzerland also won the A1GP World Cup of Motorsport in 2007–08 with driver Neel Jani. Swiss motorcycle racer Thomas Lüthi won the 2005 MotoGP World Championship in the 125cc category.
Traditional sports include Swiss wrestling or "Schwingen". It is an old tradition from the rural central cantons and considered the national sport by some. Hornussen is another native Swiss sport. It is like a cross between baseball and golf. Steinstossen is the Swiss version of stone put, a competition in throwing a heavy stone. It is recorded to have taken place in Basel in the 13th century. It is also central to the Unspunnenfest, first held in 1805.
Cuisine

The cuisine of Switzerland is multifaceted. While some dishes such as fondue, raclette or rösti are omnipresent through the country, each region developed its own gastronomy according to the differences of climate and languages. Traditional Swiss cuisine uses ingredients similar to those in other European countries, as well as unique dairy products and cheeses such as Gruyère or Emmental, produced in the valleys of Gruyères and Emmental. The number of fine-dining establishments is high, particularly in western Switzerland.
Chocolate has been made in Switzerland since the 18th century but it gained its reputation at the end of the 19th century with the invention of modern techniques such as conching and tempering which enabled its production on a high quality level. Also a breakthrough was the invention of solid milk chocolate in 1875 by Daniel Peter. The Swiss are the world's largest consumers of chocolate.
Due to the popularisation of processed foods at the end of the 19th century, Swiss health food pioneer Maximilian Bircher-Benner created the first nutrition-based therapy in form of the well-known rolled oats cereal dish, called Birchermüesli.
The most popular alcoholic drink in Switzerland is wine. Switzerland is notable for the variety of grapes grown because of the large variations in terroirs, with their specific mixes of soil, air, altitude and light. Swiss wine is produced mainly in Valais, Vaud (Lavaux), Geneva and Ticino, with a small majority of white wines. Vineyards have been cultivated in Switzerland since the Roman era, even though certain traces can be found of a more ancient origin. The most widespread varieties are the Chasselas (called Fendant in Valais) and Pinot noir. The Merlot is the main variety produced in Ticino.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
General Ulrich Wille, Commander-in-Chief of the Swiss Army during World War I
-
In 2003, by granting the Swiss People's Party a second seat in the governing cabinet, the Parliament altered the coalition which had dominated Swiss politics since 1959.
-
The Swiss Federal Council in 2016 with President Johann Schneider-Ammann (front, centre)
-
The Federal Palace, seat of the Federal Assembly and the Federal Council.
-
The Landsgemeinde is an old form of direct democracy. It is still practised in two cantons.
-
A Swiss Air Force F/A-18 Hornet at Axalp Air Show
-
The Greater Zürich Area, home to 1.5 million inhabitants and 150,000 companies, is one of the most important economic centres in the world.
-
The Engadin Valley. Tourism constitutes an important revenue for the less industrialised alpine regions.
-
Some Swiss scientists who played a key role in their discipline (clockwise):Leonhard Euler (mathematics)Louis Agassiz (glaciology)Auguste Piccard (aeronautics)Albert Einstein (physics)
-
The campus of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich (ETHZ).
-
The LHC tunnel. CERN is the world's largest laboratory and also the birthplace of the World Wide Web.
-
Urbanisation in the Rhone Valley (outskirts of Sion)
-
Alphorn concert in Vals
-
Jean-Jacques Rousseau was not only a writer but also an influential philosopher of the eighteenth century (his statue in Geneva).
-
The Switzerland national football team lining up against Argentina in 2012
See also
 In Spanish: Suiza para niños
In Spanish: Suiza para niños