Image: Flagellata 1
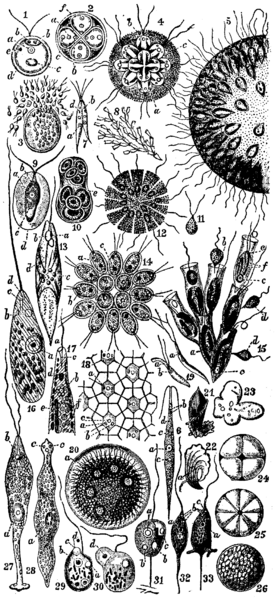
Description: 1. — Chlamydomonas pulvisculus, Ehr. (Chlamydomonadidae) free-swimming individual. a = nucleus. b = contractile vacuole. c = starch corpuscle. d = cellulose investment. e = stigma (eye-spot). 2. Resting stage of the same, with fourfold division of the cell-contents. Letters as before. 3. Breaking up of the cell-contents into minute biflagellate swarm-spores, which escape, and whose history is not further known. 4. Syncrypta volvox, Ehr. (Chrysomonadidae). A colony enclosed by a common gelatinous test c. a = stigma. b = vacuole (non-contractile). 5. Uroglena volvox, Ehr. (Chrysomonadidae). Half of a large colony, the flagellates embedded in a common jelly. 6. Chlorogonium euchlorum, Ehr. (Chlamydomonadidae). a = nucleus. b = contractile vacuole. c = starch grain. d = eye-spot. 7. Chlorogonium euchlorum, Ehr. (Chlamydomonadidae). Copulation of two liberated microgonidia. a = nucleus. b = contractile vacuole. d = eye-spot (so-called). 8. Colony of Dinobryon sertularia, Ehr. (Chrysomonadidae). 9. Haematococcus palustris, Girod (= Chlamydococcus, Braun, Protococcus, Cohn), one of the Chrysomonadidae; ordinary individual with widely separated test. a = nucleus. b = contractile vacuole. c = amylon nucleus (pyrenoid). 10. Dividing resting stage of the same, with eight fission products in the common test e. 11. A microgonidium of the same. 12. Phalansterium consociatum, Cienk. (Choanoflagellata); × 325. Disk-like colony. 13. Euglena viridis, Ehr.; × 300 (Euglenidae). a = pigment spot (stigma). b = clear space. c = paramylum granules. d = chromatophor (endochrome plate). 14. Gonium pectorale, O. F. Müller (Volvocineae). Colony seen from the flat side; × 300. a = nucleus. b = contractile vacuole. c = amylon nucleus. 15. Dinobryon sertularia, Ehr. (Chrysomonadidae). a = nucleus. b = contractile vacuole. c = amylon nucleus. d = free colourless flagellates, probably not belonging to Dinobryon. e = stigma (eye-spot). f = chromatophors. 16. Peranema trichophorum, Ehr. (Peranemidae), creeping individual seen from the back; × 140. c = pharynx. d = mouth. 17. Anterior end of Euglena acus, Ehr., in profile. a = mouth. b = vacuoles. c = pharynx. d = stigma (eye-spot). e = paramylum-body. f = chlorophyll corpuscles. 18. Part of the surface of a colony of Volvox globator, L. (Volvocidae), showing the intercellular connective fibrils. a = nucleus. b = contractile vacuole. c = starch granule. 19. Two microgametes (spermatozoa) of Volvox globator, L. a = nucleus. b = contractile vacuole. 20. Ripe asexually produced daughter-individual of Volvox minor, Stein, still enclosed in the cyst of the partheno-gonidium. a = young, partheno-gonidia. 21, 22. Trypanosoma sanguinis, Gruby (Haematoflagellates), from the blood of Rana esculenta. a = nucleus; × 500. 23—26. Reproduction of Bodo caudatus, Duj. (Bodonidae), after Dallinger and Drysdale:—23, fusion of several individuals (plasmodium); 24, encysted fusion-product dividing into four; 25, later into eight; 26, cyst filled with swarm-spores. 27. Distigma proteus, Ehbg., O.F. Müller (Euglenidae); × 440. Individual with the two flagella, and strongly contracting hinder region of the body. 28. The same devoid of flagella. c, c = the two dark pigment spots (so-called eyes) near the mouth. 29. Oicomonas termo (Monas termo) Ehr. (one of the Oicomonadidae). c = food-ingesting vacuole. d = food-particle; × 440. 30. The food-particle d has now been ingested by the vacuole. 31. Oicomonas mutabilis, Kent (Oicomonadidae), with adherent stalk. a = nucleus. b = contractile vacuole. c = food-particle in food vacuole. 32, 33. Cercomonas crassicauda, Duj. (Oicomonadidae), showing two conditions of the pseudo-podium-protruding tail. a = nucleus. b = contractile vacuoles. c = mouth.
Title: Flagellata 1
Usage Terms: Public domain
License: Public domain
Attribution Required?: No
Image usage
There are no pages that link to this image.

