Image: Newton area law derivation
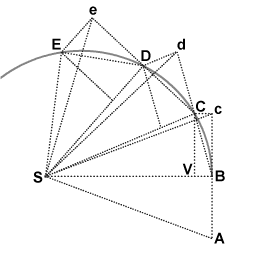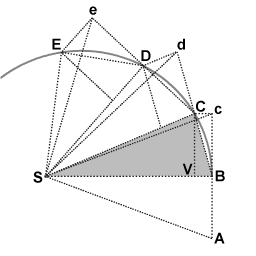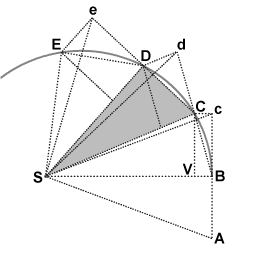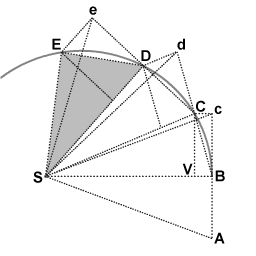
Description: Newton's derivation of the area law from the laws of motion: as an object orbits the Sun it sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. An object (not shown) is in orbit around the Sun (Point S). The effect of the Sun's gravitational attraction is represented as a sequence of impulses, always directed towards point S. In the limit of infinitely many small impulses the representation approaches infinitely close to smooth gravitational attraction. When the object is at point B it receives an impulse towards point S. Without that impulse the object would proceed to point c. The actual displacement BC follows from the rules for velocity composition; the displacement BC is the vector sum of the displacements BV and Bc. The triangles SBc and SBC have the same base and the same height, hence they have the same surface area. At point C the object receives another impulse towards point S. Without that impulse the object would have proceeded to point d in an equal interval of time. The impulse towards point S makes the object proceed to point D. The triangles SBc, SBC, SCd, SCD, SDe, SDE all have the same surface area. In the limit of the time intervals going to infinitisimally small the sequence of lines connecting the points B, C, D, E, etc approaches infinitely close to the actual smooth trajectory.
Title: Newton area law derivation
Credit: self-made
Author: Cleonis
Usage Terms: Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0
License: CC-BY-SA-3.0
License Link: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Attribution Required?: Yes
Image usage
The following page links to this image: