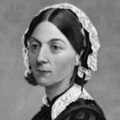King's College London facts for kids

Arms of King's College London
|
|
| Motto | Sancte et Sapienter |
|---|---|
|
Motto in English
|
With Holiness and Wisdom |
| Type | Public |
| Established | 1829 |
| Endowment | £115.23 million |
| Chancellor | HRH The Princess Royal (University of London) |
| Principal | Ed Byrne |
| Chairman of the Council | Lord Charles Wellesley |
| Students | 18,630 |
| Undergraduates | 12,320 |
| Postgraduates | 6,310 |
| Location |
,
51°30′43.00″N 0°06′58.00″W / 51.5119444°N 0.1161111°W |
| Campus | Urban |
| Visitor | The Archbishop of Canterbury ex officio |
| Colours | ______________________ |
| Affiliations | University of London Russell Group Golden Triangle |
| Website | kcl.ac.uk |
 |
|
King's College London (informally King's or KCL) is a public research university located in London, United Kingdom, and a founding constituent college of the federal University of London. King's was established in 1829 by King George IV and Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, when it received its first royal charter (as a university college), and claims to be the fourth oldest university institution in England.
In 1836, King's became one of the two founding colleges of the University of London. In the late 20th century, King's grew through a series of mergers, including with Queen Elizabeth College and Chelsea College of Science and Technology (in 1985), the Institute of Psychiatry (in 1997), the United Medical and Dental Schools of Guy's and St Thomas' Hospitals and the Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery (in 1998). King's has five campuses: its historic Strand Campus in central London, three other Thames-side campuses (Guy's, St Thomas' and Waterloo) and one in Denmark Hill in south London.
King's is generally considered part of the 'golden triangle' of research-intensive English universities alongside the University of Oxford, University of Cambridge, University College London, Imperial College London, and The London School of Economics. King's is home to six Medical Research Council centres. It is the largest European centre for graduate and post-graduate medical teaching and biomedical research, and includes the world's first nursing school, the Florence Nightingale Faculty of Nursing and Midwifery.
One of the most famous pieces of scientific research performed at King's were the crucial contributions to the discovery of the double helix structure of DNA in 1953 by Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin, together with Raymond Gosling, Alex Stokes, Herbert Wilson and other colleagues at the Randall Division of Cell and Molecular Biophysics at King's.
King's alumni and staff include 12 Nobel laureates; contributors to the discovery of DNA structure, Hepatitis C and the Higgs boson; pioneers of in-vitro fertilisation, stem cell/mammal cloning and the modern hospice movement; and key researchers advancing radar, radio, television and mobile phones.
History
King's College, so named to indicate the patronage of King George IV, was founded in 1829 and opened in October 1831 with the cleric William Otter appointed as first principal and lecturer in divinity. The Archbishop of Canterbury presided over the opening ceremony. King's was one of the first of a series of institutions which came about in the early nineteenth century as a result of the Industrial Revolution and great social changes in England following the Napoleonic Wars.
By virtue of its foundation King's has enjoyed the patronage of the monarch, the Archbishop of Canterbury as its visitor and during the nineteenth century counted among its official governors the Lord Chancellor, Speaker of the House of Commons and the Lord Mayor of London.
In 1840, King's opened its own hospital on Portugal Street near Lincoln's Inn Fields. The appointment in 1877 of Joseph Lister as professor of clinical surgery greatly benefited the medical school, and the introduction of Lister's antiseptic surgical methods gained the hospital an international reputation.
In 1845 King's established a Military Department to train officers for the Army and the British East India Company, and in 1846 a Theological Department to train Anglican priests. In 1855, King's pioneered evening classes in London.
In World War II, the buildings of King's College London were used by the Auxiliary Fire Service with a number of King's staff serving as firewatchers. Parts of the Strand building, the quadrangle, and the roof of apse and stained glass windows of the chapel suffered bomb damage in the Blitz. During the post-war reconstruction, the vaults beneath the quadrangle were replaced by a two-storey laboratory, which opened in 1952, for the departments of Physics and Civil and Electrical Engineering.
Images for kids
-
Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington and then prime minister, fought a duel against the Earl of Winchilsea in 1829 over the Duke's support for the rights of Irish Catholics and the independence of the newly established King's College London
-
The Embankment terrace entrance to the Strand Campus overlooking the River Thames, originally designed by Sir William Chambers, was completed by Sir Robert Smirke in 1835
-
Evacuated King's College London students at the University of Bristol during the Second World War
-
The Maughan Library. Following a £35m renovation, it is the largest new university library in the United Kingdom since World War II
-
Bush House, Strand Campus
-
The Grade I listed King's College London Chapel on the Strand Campus seen today was redesigned in 1864 by Sir George Gilbert Scott
-
Life-size wax sculpture of Virginia Woolf, a writer and alumna of King's
-
Florence Nightingale and her class of nurses
-
King's Business School is based in Bush House, Aldwych in Central London
-
King's graduands with academic dress designed by Vivienne Westwood
-
Opening of the King George III Museum by Albert, Prince Consort on 1 July 1843
-
King's traditional rivalry with UCL is nowadays most noted at the yearly varsity rugby match
-
Archbishop Desmond Tutu (BD '65, MTh '66) was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1984
-
Somerset House adjacent to King's College London's East Wing has a yearly ice skating rink from November to January
-
Romantic poet John Keats (Medicine, 1816)
-
Polymath Sir Francis Galton (Medicine, 1839)
-
Dramatist Sir W. S. Gilbert of Gilbert and Sullivan (BA, 1856)
-
1929 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine laureate Sir Frederick Hopkins (Medicine, 1894)
-
1951 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine laureate Max Theiler (Medicine)
-
Science fiction writer Sir Arthur C. Clarke (BSc, 1948)
-
Queen bassist John Deacon (BSc, 1971)
-
Writer and philosopher Alain de Botton (MPhil, 1992)
See also
 In Spanish: King's College de Londres para niños
In Spanish: King's College de Londres para niños