Book facts for kids

A book is a set of printed sheets of paper held together between two covers. The sheets of paper are usually covered with a text, language and illustrations that is the main point of a printed book.
A writer of a book is called an author. Someone who draws pictures in a book is called an illustrator. Books can have multiple authors or illustrators.
A book can also be a text in a larger collection of texts. That way a book is perhaps written by one author, or it only treats one subject area. Books in this sense can often be understood without knowing the whole collection. Examples are the Bible, the Illiad or the Odyssey – all of them consist of a number of books in this sense of the word. Encyclopedias often have separate articles written by different people, and published as separate volumes. Each volume is a book.
Hardcover books have hard covers made of cardboard covered in cloth or leather and are usually sewn together. Paperback books have covers of stiff paper and are usually glued together. The words in books may be read aloud or recorded on tapes (audiobooks) and compact discs.
Books can be borrowed from a library or bought from a bookstore. People can make their own books and fill them with family photos, drawings, or their own writing. Some books are empty inside, like a diary, address book, or photo album. Most of the time, the word "book" means that the pages inside have words printed or written on them.
Some books are written just for children, or for entertainment, while other books are for studying something in school such as math or history. Many books have photographs or drawings.
People who cannot read books, or any type of writing are called illiterate (= 'unlettered').
Contents
Types of books
There are two main kinds of book text: fiction and non-fiction.
Fiction
These books are novels, about stories that did not happen, and have been imagined by the author. Some books are based on real events from history, but the author has created imaginary characters or dialogue for the events.
Non-fiction
Books of non-fiction are about true facts or things that have really happened. Some examples are dictionaries, cookbooks, textbooks for learning in school, or a biography (someone's life story).
Historical

Between the written manuscript and the book lie several inventions. A book is an industrial product, but manuscripts are hand-made.
Manuscripts
A common type of manuscript was the scroll, which was a long sheet rolled up. The sheet could have been made of papyrus (made by the Egyptians, by weaving the inner stems of the papyrus plant and then hammering them together), or parchment or vellum (very thin animal skin, first used by the ancient Greeks), or paper (made from plant fibers, invented by the Chinese). Turning the manuscript into a book required several developments.
The codex
The Romans were the first people to put separate pieces of manuscript between covers, to form a codex. This was more convenient to handle and store than scrolls, but was not yet a book as we understand it.
Printing
Scrolls and codices were written and copied by hand. The Chinese invented woodblock printing, where shapes are carved out of a block of wood, then ink is applied to the carved side, and the block is pressed onto the paper. This way of making books was very slow, and so very few people had these kinds of books.
Johannes Gutenberg was the first to invent a machine for printing, the printing press, in the 15th century. This involved more than just a press, it involved the production of movable metal type suitable for the machine process.
Initially, the machines were slow, and needed a printer to work with them. Fast and automatic machines did not arrive until the 19th century.
Paper and ink
Paper had been invented in the 8th century, but hand-made paper was expensive and in short supply. In the 19th century, automated or semi-automated making of paper from wood pulp was invented. Also, there was the invention of inks for various purposes, and machines driven by electricity.
The common cheap supply of paper fed the faster printing machines, and books became cheaper. Only then could ordinary people afford to buy books. Along with these inventions in the 19th century came the idea of public libraries, so poorer people could get access to the best books. Also, widespread free (or nearly free) education swelled the number of literate people.
Binding
Printing was done on large sheets of paper, which were then folded, guillotined (cut) and sewn in sections, and finally placed into the covers. All these processes became done by machines during the 19th century.
Today
Today some of the technologies have been changed, especially those involving illustration and typography. However, books look much the same as they did, with more illustration in colour, but basically the same. That is because experience has shown that readers need certain things for pleasurable reading. Graphic design and typography are the practical arts used to make books attractive and useful to readers.
Digital printing
Recent developments in book manufacturing include the development of digital printing. Book pages are printed, in much the same way as an office copier works, using toner rather than ink. Each book is printed in one pass, not as separate signatures. Digital printing has permitted the manufacture of much smaller quantities than offset, in part because of the absence of make readies and of spoilage. One might think of a web press as printing quantities over 2000, quantities from 250 to 2000 being printed on sheet-fed presses, and digital presses doing quantities below 250. These numbers are of course only approximate and will vary from supplier to supplier, and from book to book depending on its characteristics. Digital printing has opened up the possibility of print-on-demand, where no books are printed until after an order is received from a customer.
E-book

In the 2000s, due to the rise in availability of affordable handheld computing devices, the opportunity to share texts through electronic means became a more appealing option for media publishers. Thus, the "e-book" was made. The term e-book is a contraction of "electronic book"; it refers to a book-length publication in digital form. An e-book is usually made available through the internet, but also on CD-ROM and other forms. E-Books may be read either via a computer or by means of a portable book display device known as an e-book reader, such as the Sony Reader, Barnes & Noble Nook, Kobo eReader, or the Amazon Kindle. These devices attempt to mimic the experience of reading a print book.
Paper and conservation

Paper was first made in China as early as 200 BC, and reached Europe through Muslim territories. At first made of rags, the industrial revolution changed paper-making practices, allowing for paper to be made out of wood pulp. Papermaking in Europe began in the 11th century, although vellum was also common there as page material up until the beginning of the 16th century, vellum being the more expensive and durable option. Printers or publishers would often issue the same publication on both materials, to cater to more than one market.
Paper made from wood pulp became popular in the early 20th century, because it was cheaper than linen or abaca cloth-based papers. Pulp-based paper made books less expensive to the general public. This paved the way for huge leaps in the rate of literacy in industrialised nations, and enabled the spread of information during the Second Industrial Revolution.
Pulp paper, however, contains acid which eventually destroys the paper from within. Earlier techniques for making paper used limestone rollers, which neutralized the acid in the pulp. Books printed between 1850 and 1950 are primarily at risk; more recent books are often printed on acid-free or alkaline paper. Libraries today have to consider mass deacidification of their older collections in order to prevent decay.
Stability of the climate is critical to the long-term preservation of paper and book material. Good air circulation is important to keep fluctuation in climate stable. The HVAC system should be up to date and functioning efficiently. Light is detrimental to collections. Therefore, care should be given to the collections by implementing light control. General housekeeping issues can be addressed, including pest control. In addition to these helpful solutions, a library must also make an effort to be prepared if a disaster occurs, one that they cannot control. Time and effort should be given to create a concise and effective disaster plan to counteract any damage incurred through "acts of God" therefore an emergency management plan should be in place.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
The Gutenberg Bible, one of the first books to be printed using the printing press.
-
Book of the Dead of Hunefer; c. 1275 BC; ink and pigments on papyrus; 45 × 90.5 cm; British Museum (London)
-
The Codex Amiatinus anachronistically depicts the Biblical Ezra with the kind of books used in the 8th Century AD.
-
Bagh print, a traditional woodblock printing technique that originated in Bagh Madhya Pradesh, India.
-
Selected Teachings of Buddhist Sages and Son Masters, the earliest known book printed with movable metal type, printed in Korea, in 1377, Bibliothèque nationale de France.
-
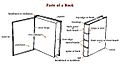
The spine of the book is an important aspect in book design, especially in the cover design. When the books are stacked up or stored in a shelf, the details on the spine is the only visible surface that contains the information about the book. In stores, it is the details on the spine that attract a buyer's attention first.
-
A page from a dictionary
-
An atlas
-
A telephone directory, with business and residence listings.
-
Paperback books
-
The Library of Celsus in Ephesus, Turkey was built in 135 AD, and could house around 12,000 scrolls.
-
Halfbound book with leather and marbled paper.
See also
 In Spanish: Libro para niños
In Spanish: Libro para niños