Renewable energy facts for kids
Renewable energy, green energy, or low-carbon energy is energy from renewable resources that are naturally replenished. Renewable resources include sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy sources are sustainable, some are not. For example, some biomass sources are considered unsustainable at current rates of exploitation. Renewable energy is often used for electricity generation, heating and cooling. Renewable energy projects are typically large-scale, but they are also suited to rural and remote areas and developing countries, where energy is often crucial in human development.
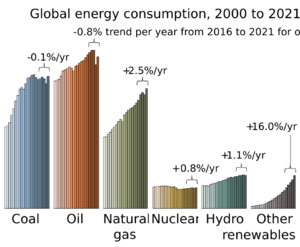
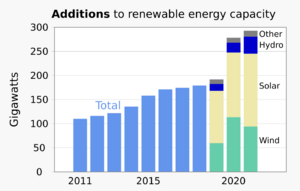
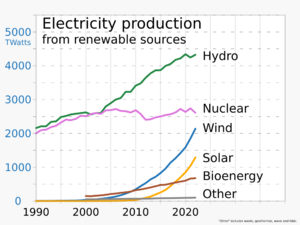
Renewable energy is often deployed together with further electrification, which has several benefits: electricity can move heat or objects efficiently, and is clean at the point of consumption. From 2011 to 2021, renewable energy grew from 20% to 28% of global electricity supply. Use of fossil energy shrank from 68% to 62%, and nuclear from 12% to 10%. The share of hydropower decreased from 16% to 15% while power from sun and wind increased from 2% to 10%. Biomass and geothermal energy grew from 2% to 3%. There are 3,146 gigawatts installed in 135 countries, while 156 countries have laws regulating the renewable energy sector. In 2021, China accounted for almost half of the global increase in renewable electricity.
Globally there are over 10 million jobs associated with the renewable energy industries, with solar photovoltaics being the largest renewable employer. Renewable energy systems are rapidly becoming more efficient and cheaper and their share of total energy consumption is increasing, with a large majority of worldwide newly installed electricity capacity being renewable. In most countries, photovoltaic solar or onshore wind are the cheapest new-build electricity.
Many nations around the world already have renewable energy contributing more than 20% of their total energy supply, with some generating over half their electricity from renewables. A few countries generate all their electricity using renewable energy. National renewable energy markets are projected to continue to grow strongly in the 2020s and beyond. According to the IEA, to achieve net zero emissions by 2050, 90% of global electricity generation will need to be produced from renewable sources. Some studies say that a global transition to 100% renewable energy across all sectors – power, heat, transport and industry – is feasible and economically viable.
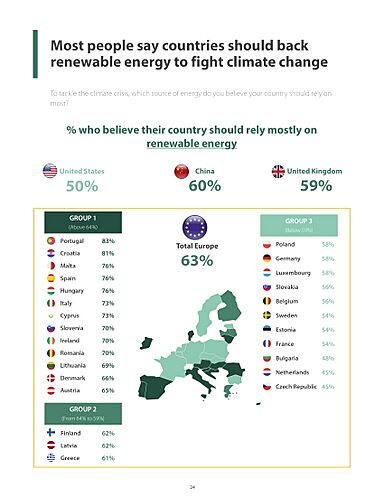
Renewable energy resources exist over wide geographical areas, in contrast to fossil fuels, which are concentrated in a limited number of countries. Deployment of renewable energy and energy efficiency technologies is resulting in significant energy security, climate change mitigation, and economic benefits. However renewables are being hindered by hundreds of billions of dollars of fossil fuel subsidies. In international public opinion surveys there is strong support for renewables such as solar power and wind power. In 2022 the International Energy Agency asked countries to solve policy, regulatory, permitting and financing obstacles to adding more renewables, to have a better chance of reaching net zero carbon emissions by 2050.
Role in addressing climate change
As part of the global effort to address climate change, most of the world's countries have committed substantially reducing their greenhouse gas emissions. In practice, this means phasing out fossil fuels and replacing them with low-emissions energy sources. At the 2023 United Nations Climate Change Conference, around three-quarters of the world's countries set a goal of tripling renewable energy capacity by 2030. The European Union aims to generate 40% of its electricity from renewables by the same year.
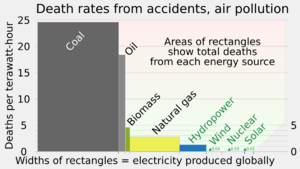
Renewable energy is also more evenly distributed around the world than fossil fuels, which are concentrated in a limited number of countries. It also brings health benefits by reducing air pollution caused by the burning of fossil fuels. The potential worldwide savings in health care costs have been estimated at trillions of dollars annually.
History
New government spending, regulation and policies helped the renewables industry weather the global financial crisis better than many other sectors. In 2022, renewables accounted for 30% of global electricity generation, up from 21% in 1985.
Mainstream technologies
Solar energy
| Global electricity power generation capacity | 1419.0 GW (2023) |
| Global electricity power generation capacity annual growth rate | 25% (2014-2023) |
| Share of global electricity generation | 4.5% (2022) |
| Levelized cost per megawatt hour | Utility-scale photovoltaics: USD 38.343 (2019) |
| Primary technologies | Photovoltaics, concentrated solar power, solar thermal collector |
| Other energy applications | Water heating; heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC); cooking; process heat; water treatment |


Solar power produced around 1.3 terrawatt-hours (TWh) worldwide in 2022, representing 4.6% of the world's electricity. Almost all of this growth has happened since 2010. Solar energy can be harnessed anywhere that receives sunlight; however, the amount of solar energy that can be harnessed for electricity generation is influenced by weather conditions, geographic location and time of day.
There are two mainstream ways of harnessing solar energy: solar thermal, which converts solar energy into heat; and photovoltaics (PV), which converts it into electricity. PV is far more widespread, accounting for around two thirds of the global solar energy capacity as of 2022. It is also growing at a much faster rate, with 170 GW newly installed capacity in 2021, compared to 25 GW of solar thermal.
Passive solar refers to a range of construction strategies and technologies that aim to optimize the distribution of solar heat in a building. Examples include solar chimneys, orienting a building to the sun, using construction materials that can store heat, and designing spaces that naturally circulate air.
Photovoltaic development
A photovoltaic system, consisting of solar cells assembled into panels, converts light into electrical direct current via the photoelectric effect. Almost all commercial PV cells consist of crystalline silicon, with a market share of 95%. Cadmium telluride thin-film solar cells account for the remainder. PV has several advantages that make it by far the fastest-growing renewable energy technology. It is cheap, low-maintenance and scalable; adding to an existing PV installation as demanded arises is simple. Its main disadvantage is its poor performance in cloudy weather.
PV systems range from small, residential and commercial rooftop or building integrated installations, to large utility-scale photovoltaic power station. Building-integrated PV uses existing land and structures to generate power close to where it is consumed. A household's solar panels, and batteries if they have them, can often either be used for just that household or if connected to an electrical grid can be aggregated with millions of others. As of 2022, around 25 million households rely on rooftop solar power worldwide. Australia has by far the most rooftop solar capacity per capita.
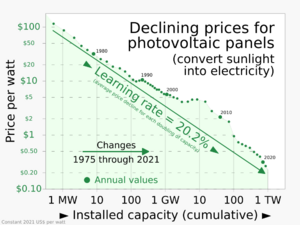
The first utility-scale solar power plant was built in 1982 in Hesperia, California by ARCO. The plant was not profitable and was sold eight years later. However, over the following decades, PV technology significantly improved its electricity generating efficiency, reduced the installation cost per watt as well as its energy payback time, and reached grid parity. As a result, PV adoption has grown exponentially since 2010. Global capacity increased from 230 GW at the end of 2015 to 890 GW in 2021. PV grew fastest in China between 2016 and 2021, adding 560 GW, more than all advanced economies combined. Four of the ten biggest solar power stations are in China, including the biggest, Golmud Solar Park in China. Many utility-scale PV systems use tracking systems that follow the sun's daily path across the sky to generate more electricity than fixed-mounted systems.
Solar thermal
Solar thermal energy (STE) is a form of energy and a technology for harnessing solar energy to generate thermal energy for use in industry, and in the residential and commercial sectors.
Solar thermal collectors are classified by the United States Energy Information Administration as low-, medium-, or high-temperature collectors. Low-temperature collectors are generally unglazed and used to heat swimming pools or to heat ventilation air. Medium-temperature collectors are also usually flat plates but are used for heating water or air for residential and commercial use.
High-temperature collectors concentrate sunlight using mirrors or lenses and are generally used for fulfilling heat requirements up to 300 deg C / 20 bar pressure in industries, and for electric power production. Two categories include Concentrated Solar Thermal (CST) for fulfilling heat requirements in industries, and Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) when the heat collected is used for electric power generation. CST and CSP are not replaceable in terms of application.
The largest facilities are located in the American Mojave Desert of California and Nevada. These plants employ a variety of different technologies. The largest examples include, Ivanpah Solar Power Facility (377 MW), Solar Energy Generating Systems installation (354 MW), and Crescent Dunes (110 MW). Spain is the other major developer of solar thermal power plant. The largest examples include, Solnova Solar Power Station (150 MW), the Andasol solar power station (150 MW), and Extresol Solar Power Station (100 MW).Wind power

| Global electricity power generation capacity | 1017.2 GW (2023) |
| Global electricity power generation capacity annual growth rate | 13% (2014-2023) |
| Share of global electricity generation | 7.6% (2022) |
| Levelized cost per megawatt hour | Land-based wind: USD 30.165 (2019) |
| Primary technology | Wind turbine |
| Other energy applications | Windmill, windpump |
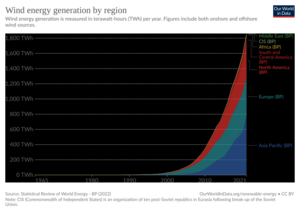
Wind-generated electricity met nearly 4% of global electricity demand in 2015, with nearly 63 GW of new wind power capacity installed. Wind energy was the leading source of new capacity in Europe, the US and Canada, and the second largest in China. In Denmark, wind energy met more than 40% of its electricity demand while Ireland, Portugal and Spain each met nearly 20%.
Globally, the long-term technical potential of wind energy is believed to be five times total current global energy production, or 40 times current electricity demand, assuming all practical barriers needed were overcome. This would require wind turbines to be installed over large areas, particularly in areas of higher wind resources, such as offshore, and likely also industrial use of new types of VAWT turbines in addition to the horizontal axis units currently in use. As offshore wind speeds average ~90% greater than that of land, offshore resources can contribute substantially more energy than land-stationed turbines.
Hydropower
| Global electricity power generation capacity | 1,267.9 GW (2023) |
| Global electricity power generation capacity annual growth rate | 1.9% (2014-2023) |
| Share of global electricity generation | 15% (2022) |
| Levelized cost per megawatt hour | USD 65.581 (2019) |
| Primary technology | Dam |
| Other energy applications | Pumped storage, mechanical power |
Since water is about 800 times denser than air, even a slow flowing stream of water, or moderate sea swell, can yield considerable amounts of energy. Water can generate electricity with a conversion efficiency of about 90%, which is the highest rate in renewable energy. There are many forms of water energy:
- Historically, hydroelectric power came from constructing large hydroelectric dams and reservoirs, which are still popular in developing countries. The largest of them are the Three Gorges Dam (2003) in China and the Itaipu Dam (1984) built by Brazil and Paraguay.
- Small hydro systems are hydroelectric power installations that typically produce up to 50 MW of power. They are often used on small rivers or as a low-impact development on larger rivers. China is the largest producer of hydroelectricity in the world and has more than 45,000 small hydro installations.
- Run-of-the-river hydroelectricity plants derive energy from rivers without the creation of a large reservoir. The water is typically conveyed along the side of the river valley (using channels, pipes and/or tunnels) until it is high above the valley floor, whereupon it can be allowed to fall through a penstock to drive a turbine. A run-of-river plant may still produce a large amount of electricity, such as the Chief Joseph Dam on the Columbia River in the United States. However many run-of-the-river hydro power plants are micro hydro or pico hydro plants.
Hydropower is produced in 150 countries, with the Asia-Pacific region generating 32 percent of global hydropower in 2010. Of the top 50 countries by percentage of electricity generated from renewables, 46 are primarily hydroelectric. There are now seven hydroelectricity stations larger than 10 GW (10,000 MW) worldwide, see table below.
| Rank | Station | Country | Location | Capacity (MW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Three Gorges Dam | 30°49′15″N 111°00′08″E / 30.82083°N 111.00222°E | 22,500 | |
| 2. | Baihetan Dam | 27°13′23″N 102°54′11″E / 27.22306°N 102.90306°E | 16,000 | |
| 3. | Itaipu Dam | 25°24′31″S 54°35′21″W / 25.40861°S 54.58917°W | 14,000 | |
| 4. | Xiluodu Dam | 28°15′35″N 103°38′58″E / 28.25972°N 103.64944°E | 13,860 | |
| 5. | Belo Monte Dam | 03°06′57″S 51°47′45″W / 3.11583°S 51.79583°W | 11,233 | |
| 6. | Guri Dam | 07°45′59″N 62°59′57″W / 7.76639°N 62.99917°W | 10,235 | |
| 7. | Wudongde Dam | 26°20′2″N 102°37′48″E / 26.33389°N 102.63000°E | 10,200 |
Much hydropower is flexible, thus complementing wind and solar. In 2021, the world renewable hydropower capacity was 1,360 GW. Only a third of the world's estimated hydroelectric potential of 14,000 TWh/year has been developed. New hydropower projects face opposition from local communities due to their large impact, including relocation of communities and flooding of wildlife habitats and farming land. High cost and lead times from permission process, including environmental and risk assessments, with lack of environmental and social acceptance are therefore the primary challenges for new developments. It is popular to repower old dams thereby increasing their efficiency and capacity as well as quicker responsiveness on the grid. Where circumstances permit existing dams such as the Russell Dam built in 1985 may be updated with "pump back" facilities for pumped-storage which is useful for peak loads or to support intermittent wind and solar power. Because dispatchable power is more valuable than VRE countries with large hydroelectric developments such as Canada and Norway are spending billions to expand their grids to trade with neighboring countries having limited hydro.
Bioenergy
| Global electricity power generation capacity | 150.3 GW (2023) |
| Global electricity power generation capacity annual growth rate | 5.8% (2014-2023) |
| Share of global electricity generation | 2.4% (2022) |
| Levelized cost per megawatt hour | USD 118.908 (2019) |
| Primary technologies | biomass, biofuel |
| Other energy applications | Heating, cooking, transportation fuels |
Biomass is biological material derived from living, or recently living organisms. It commonly refers to plants or plant-derived materials. As an energy source, biomass can either be used directly via combustion to produce heat, or indirectly after converting it to various forms of biofuel in solid, liquid or gaseous form. Conversion of biomass to biofuel can be achieved by different methods which are broadly classified into: thermal, chemical, and biochemical methods. Wood was the largest biomass energy source as of 2012; examples include forest residues – such as dead trees, branches and tree stumps, yard clippings, wood chips and even municipal solid waste. Industrial biomass can be grown from numerous types of plants, including miscanthus, switchgrass, hemp, corn, poplar, willow, sorghum, sugarcane, bamboo, and a variety of tree species, ranging from eucalyptus to oil palm (palm oil).
Plant energy is produced by crops specifically grown for use as fuel that offer high biomass output per hectare with low input energy. The grain can be used for liquid transportation fuels while the straw can be burned to produce heat or electricity. Plant biomass can also be degraded from cellulose to glucose through a series of chemical treatments, and the resulting sugar can then be used as a first-generation biofuel.
Biomass can be converted to other usable forms of energy such as methane gas or transportation fuels such as ethanol and biodiesel. Rotting garbage, and agricultural and human waste, all release methane gas – also called landfill gas or biogas. Crops, such as corn and sugarcane, can be fermented to produce the transportation fuel, ethanol. Biodiesel, another transportation fuel, can be produced from left-over food products such as vegetable oils and animal fats. There is a great deal of research involving algal fuel or algae-derived biomass due to the fact that it is a non-food resource, grows around 20 times faster than other types of food crops, such as corn and soy, and can be grown almost anywhere. Once harvested, it can be fermented to produce biofuels such as ethanol, butanol, and methane, as well as biodiesel and hydrogen. The biomass used for electricity generation varies by region. Forest by-products, such as wood residues, are common in the United States. Agricultural waste is common in Mauritius (sugar cane residue) and Southeast Asia (rice husks).
Biomass, biogas and biofuels are burned to produce heat/power and in doing so can harm the environment. Pollutants such as sulphurous oxides (SOx), nitrous oxides (NOx), and particulate matter (PM) are produced from the combustion of biomass. With regards to traditional use of biomass for heating and cooking, the World Health Organization estimates that 3.7 million prematurely died from outdoor air pollution in 2012 while indoor pollution from biomass burning effects over 3 billion people worldwide.
Bioenergy global capacity in 2021 was 158 GW. Biofuels avoided 4.4% of global transport fuel demand in 2021.
Biofuel


Biofuels include a wide range of fuels which are derived from biomass. The term covers solid, liquid, and gaseous fuels. Liquid biofuels include bioalcohols, such as bioethanol, and oils, such as biodiesel. Gaseous biofuels include biogas, landfill gas and synthetic gas. Bioethanol is an alcohol made by fermenting the sugar components of plant materials and it is made mostly from sugar and starch crops. These include maize, sugarcane and, more recently, sweet sorghum. The latter crop is particularly suitable for growing in dryland conditions, and is being investigated by International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics for its potential to provide fuel, along with food and animal feed, in arid parts of Asia and Africa.
With advanced technology being developed, cellulosic biomass, such as trees and grasses, are also used as feedstocks for ethanol production. Ethanol can be used as a fuel for vehicles in its pure form, but it is usually used as a gasoline additive to increase octane and improve vehicle emissions. Bioethanol is widely used in the United States and in Brazil. The energy costs for producing bio-ethanol are almost equal to, the energy yields from bio-ethanol. However, according to the European Environment Agency, biofuels do not address global warming concerns. Biodiesel is made from vegetable oils, animal fats or recycled greases. It can be used as a fuel for vehicles in its pure form, or more commonly as a diesel additive to reduce levels of particulates, carbon monoxide, and hydrocarbons from diesel-powered vehicles. Biodiesel is produced from oils or fats using transesterification and is the most common biofuel in Europe. Biofuels provided 2.7% of the world's transport fuel in 2010.
Policies in more than 80 countries support biofuels demand.
Since the 1970s, Brazil has had an ethanol fuel program which has allowed the country to become the world's second largest producer of ethanol (after the United States) and the world's largest exporter. Brazil's ethanol fuel program uses modern equipment and cheap sugarcane as feedstock, and the residual cane-waste (bagasse) is used to produce heat and power. There are no longer light vehicles in Brazil running on pure gasoline.
Biojet is expected to be important for short-term reduction of carbon dioxide emissions from long-haul flights.
Geothermal energy


| Global electricity power generation capacity | 14.9 GW (2023) |
| Global electricity power generation capacity annual growth rate | 3.4% (2014-2023) |
| Share of global electricity generation | <1% (2018) |
| Levelized cost per megawatt hour | USD 58.257 (2019) |
| Primary technologies | Dry steam, flash steam, and binary cycle power stations |
| Other energy applications | Heating |
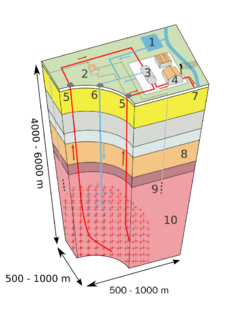
High temperature geothermal energy is from thermal energy generated and stored in the Earth. Thermal energy is the energy that determines the temperature of matter. Earth's geothermal energy originates from the original formation of the planet and from radioactive decay of minerals (in currently uncertain but possibly roughly equal proportions). The geothermal gradient, which is the difference in temperature between the core of the planet and its surface, drives a continuous conduction of thermal energy in the form of heat from the core to the surface. The adjective geothermal originates from the Greek roots geo, meaning earth, and thermos, meaning heat.
The heat that is used for geothermal energy can be from deep within the Earth, all the way down to Earth's core – 6,400 kilometres (4,000 mi) down. At the core, temperatures may reach over 5,000 °C (9,030 °F). Heat conducts from the core to the surrounding rock. Extremely high temperature and pressure cause some rock to melt, which is commonly known as magma. Magma convects upward since it is lighter than the solid rock. This magma then heats rock and water in the crust, sometimes up to 371 °C (700 °F).
Low temperature geothermal refers to the use of the outer crust of the Earth as a thermal battery to facilitate renewable thermal energy for heating and cooling buildings, and other refrigeration and industrial uses. In this form of geothermal, a geothermal heat pump and ground-coupled heat exchanger are used together to move heat energy into the Earth (for cooling) and out of the Earth (for heating) on a varying seasonal basis. Low-temperature geothermal (generally referred to as "GHP") is an increasingly important renewable technology because it both reduces total annual energy loads associated with heating and cooling, and it also flattens the electric demand curve eliminating the extreme summer and winter peak electric supply requirements. Thus low temperature geothermal/GHP is becoming an increasing national priority with multiple tax credit support and focus as part of the ongoing movement toward net zero energy.
Geothermal power is cost effective, reliable, sustainable, and environmentally friendly, but has historically been limited to areas near tectonic plate boundaries. Recent technological advances have expanded the range and size of viable resources, especially for applications such as home heating, opening a potential for widespread exploitation. Geothermal wells release greenhouse gases trapped deep within the earth, but these emissions are usually much lower per energy unit than those of fossil fuels.
In 2017, the United States led the world in geothermal electricity production with 12.9 GW of installed capacity. The largest group of geothermal power plants in the world is located at The Geysers, a geothermal field in California. The Philippines follows the US as the second highest producer of geothermal power in the world, with 1.9 GW of capacity online.
Global geothermal capacity in 2021 was 15 GW.
Emerging technologies
There are also other renewable energy technologies that are still under development, including concentrated solar power, cellulosic ethanol, hot-dry-rock geothermal power, and marine energy. These technologies are not yet widely demonstrated or have limited commercialization. Many are on the horizon and may have potential comparable to other renewable energy technologies, but still depend on attracting sufficient attention and research, development and demonstration (RD&D) funding.
There are numerous organizations within the academic, federal, and commercial sectors conducting large-scale advanced research in the field of renewable energy. This research spans several areas of focus across the renewable energy spectrum. Most of the research is targeted at improving efficiency and increasing overall energy yields. Multiple government supported research organizations have focused on renewable energy in recent years. Two of the most prominent of these labs are Sandia National Laboratories and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), both of which are funded by the United States Department of Energy and supported by various corporate partners.
Enhanced geothermal system
Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) are a new type of geothermal power technology that does not require natural convective hydrothermal resources. The vast majority of geothermal energy within drilling reach is in dry and non-porous rock. EGS technologies "enhance" and/or create geothermal resources in this "hot dry rock (HDR)" through hydraulic fracturing. EGS and HDR technologies, such as hydrothermal geothermal, are expected to be baseload resources that produce power 24 hours a day like a fossil plant. Distinct from hydrothermal, HDR and EGS may be feasible anywhere in the world, depending on the economic limits of drill depth. Good locations are over deep granite covered by a thick (3–5 km or 1.9–3.1 mi) layer of insulating sediments which slow heat loss. There are HDR and EGS systems currently being developed and tested in France, Australia, Japan, Germany, the U.S., and Switzerland. The largest EGS project in the world is a 25 megawatt demonstration plant currently being developed in the Cooper Basin, Australia. The Cooper Basin has the potential to generate 5,000–10,000 MW.
Hydrogen
Marine energy
Marine energy (also sometimes referred to as ocean energy) is the energy carried by ocean waves, tides, salinity, and ocean temperature differences. The movement of water in the world's oceans creates a vast store of kinetic energy, or energy in motion. This energy can be harnessed to generate electricity to power homes, transport and industries. The term marine energy encompasses wave power – power from surface waves, marine current power - power from marine hydrokinetic streams (e.g., the Gulf Stream), and tidal power – obtained from the kinetic energy of large bodies of moving water. Reverse electrodialysis (RED) is a technology for generating electricity by mixing fresh river water and salty sea water in large power cells designed for this purpose; as of 2016, it is being tested at a small scale (50 kW). Offshore wind power is not a form of marine energy, as wind power is derived from the wind, even if the wind turbines are placed over water. The oceans have a tremendous amount of energy and are close to many if not most concentrated populations. Ocean energy has the potential of providing a substantial amount of new renewable energy around the world.
| # | Station | Country | Location | Capacity | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Sihwa Lake Tidal Power Station | South Korea | 37°18′47″N 126°36′46″E / 37.31306°N 126.61278°E | 254 MW | |
| 2. | Rance Tidal Power Station | France | 48°37′05″N 02°01′24″W / 48.61806°N 2.02333°W | 240 MW | |
| 3. | Annapolis Royal Generating Station | Canada | 44°45′07″N 65°30′40″W / 44.75194°N 65.51111°W | 20 MW |
Passive daytime radiative cooling
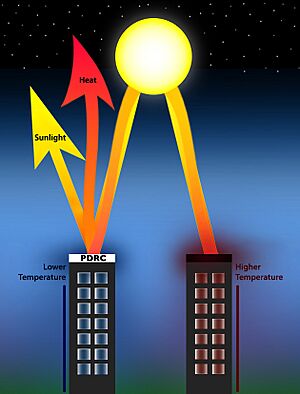
Passive daytime radiative cooling (PDRC) uses the coldness of outer space as a renewable energy source to achieve daytime cooling that can be used in many applications, such as indoor space cooling, outdoor urban heat island mitigation, and solar cell efficiency. PDRC surfaces are designed to be high in solar reflectance to minimize heat gain and strong in longwave infrared (LWIR) thermal radiation heat transfer. On a planetary scale, it has been proposed as a way to slow and reverse global warming. PDRC applications are deployed as sky-facing surfaces, similar to other renewable energy sources such as photovoltaic systems and solar thermal collectors. PDRC became possible with the ability to suppress solar heating using photonic metamaterials, first published in a study by Raman et al. to the scientific community in 2014. PDRC applications for indoor space cooling is growing with an estimated "market size of ~$27 billion in 2025."
Earth infrared thermal radiation
Earth emits roughly 1017 W of infrared thermal radiation that flows toward the cold outer space. Solar energy hits the surface and atmosphere of the earth and produces heat. Using various theorized devices like emissive energy harvester (EEH) or thermoradiative diode, this energy flow can be converted into electricity. In theory, this technology can be used during nighttime.
Others
Algae fuels
Producing liquid fuels from oil-rich (fat-rich) varieties of algae is an ongoing research topic. Various microalgae grown in open or closed systems are being tried including some systems that can be set up in brownfield and desert lands.
Water vapor
Collection of static electricity charges from water droplets on metal surfaces is an experimental technology that would be especially useful in low-income countries with relative air humidity over 60%.
Nuclear energy
Breeder reactors could, in principle, extract almost all of the energy contained in uranium or thorium, decreasing fuel requirements by a factor of 100 compared to widely used once-through light water reactors, which extract less than 1% of the energy in the actinide metal (uranium or thorium) mined from the earth. The high fuel-efficiency of breeder reactors could greatly reduce concerns about fuel supply, energy used in mining, and storage of radioactive waste. With seawater uranium extraction (currently too expensive to be economical), there is enough fuel for breeder reactors to satisfy the world's energy needs for 5 billion years at 1983's total energy consumption rate, thus making nuclear energy effectively a renewable energy. In addition to seawater the average crustal granite rocks contain significant quantities of uranium and thorium that with breeder reactors can supply abundant energy for the remaining lifespan of the sun on the main sequence of stellar evolution.
Artificial photosynthesis
Artificial photosynthesis uses techniques including nanotechnology to store solar electromagnetic energy in chemical bonds by splitting water to produce hydrogen and then using carbon dioxide to make methanol. Researchers in this field strived to design molecular mimics of photosynthesis that use a wider region of the solar spectrum, employ catalytic systems made from abundant, inexpensive materials that are robust, readily repaired, non-toxic, stable in a variety of environmental conditions and perform more efficiently allowing a greater proportion of photon energy to end up in the storage compounds, i.e., carbohydrates (rather than building and sustaining living cells). However, prominent research faces hurdles, Sun Catalytix a MIT spin-off stopped scaling up their prototype fuel-cell in 2012 because it offers few savings over other ways to make hydrogen from sunlight.
Cost comparison
The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) stated that ~86% (187 GW) of renewable capacity added in 2022 had lower costs than electricity generated from fossil fuels. IRENA also stated that capacity added since 2000 reduced electricity bills in 2022 by at least $520 billion, and that in non-OECD countries, the lifetime savings of 2022 capacity additions will reduce costs by up to $580 billion.
| Installed TWp |
Growth TW/yr |
Production per installed capacity* |
Energy TWh/yr* |
Growth TWh/yr* |
Levelized cost US¢/kWh |
Av. auction prices US¢/kWh |
Cost development 2010–2019 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solar PV | 0.580 | 0.098 | 13% | 549 | 123 | 6.8 | 3.9 | −82% |
| Solar CSP | 0.006 | 0.0006 | 13% | 6.3 | 0.5 | 18.2 | 7.5 | −47% |
| Wind Offshore | 0.028 | 0.0045 | 33% | 68 | 11.5 | 11.5 | 8.2 | −30% |
| Wind Onshore | 0.594 | 0.05 | 25% | 1194 | 118 | 5.3 | 4.3 | −38% |
| Hydro | 1.310 | 0.013 | 38% | 4267 | 90 | 4.7 | +27% | |
| Bioenergy | 0.12 | 0.006 | 51% | 522 | 27 | 6.6 | −13% | |
| Geothermal | 0.014 | 0.00007 | 74% | 13.9 | 0.7 | 7.3 | +49% |
* = 2018. All other values for 2019.
Growth of renewables
The results of a recent review of the literature concluded that as greenhouse gas (GHG) emitters begin to be held liable for damages resulting from GHG emissions resulting in climate change, a high value for liability mitigation would provide powerful incentives for deployment of renewable energy technologies.
In the decade of 2010–2019, worldwide investment in renewable energy capacity excluding large hydropower amounted to US$2.7 trillion, of which the top countries China contributed US$818 billion, the United States contributed US$392.3 billion, Japan contributed US$210.9 billion, Germany contributed US$183.4 billion, and the United Kingdom contributed US$126.5 billion. This was an increase of over three and possibly four times the equivalent amount invested in the decade of 2000–2009 (no data is available for 2000–2003).
As of 2022, an estimated 28% of the world's electricity was generated by renewables. This is up from 19% in 1990.
Debates
Renewable electricity generation by wind and solar is variable. This results in reduced capacity factor and may require keeping some gas-fired power plants or other dispatchable generation on standby until there is enough energy storage, demand response, grid improvement, and/or base load power from non-intermittent sources like hydropower, nuclear power or bioenergy.
The market for renewable energy technologies has continued to grow. Climate change concerns and increasing in green jobs, coupled with high oil prices, peak oil, oil wars, oil spills, promotion of electric vehicles and renewable electricity, nuclear disasters and increasing government support, are driving increasing renewable energy legislation, incentives and commercialization.
The International Energy Agency has stated that deployment of renewable technologies usually increases the diversity of electricity sources and, through local generation, contributes to the flexibility of the system and its resistance to central shocks.
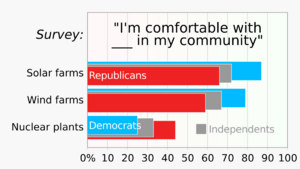
Public support
Solar power plants may compete with arable land, while on-shore wind farms face opposition due to aesthetic concerns and noise, which is impacting both humans and wildlife.In the United States, the Massachusetts Cape Wind project was delayed for years partly because of aesthetic concerns. However, residents in other areas have been more positive. According to a town councilor, the overwhelming majority of locals believe that the Ardrossan Wind Farm in Scotland has enhanced the area. These concerns, when directed against renewable energy, are sometimes described as "not in my back yard" attitude (NIMBY).
A 2011 UK Government document states that "projects are generally more likely to succeed if they have broad public support and the consent of local communities. This means giving communities both a say and a stake". In countries such as Germany and Denmark many renewable projects are owned by communities, particularly through cooperative structures, and contribute significantly to overall levels of renewable energy deployment.
Health and environmental impact
Moving to modern renewable energy has very large health benefits due to reducing air pollution from fossil fuels.
Renewable sources other than biomass such as wind power, photovoltaics, and hydroelectricity have the advantage of being able to conserve water, lower pollution and reduce CO2 emissions.
Solar panels change the albedo of the surface, so if used on a very large scale (such as covering 20% of the Sahara Desert), could change global weather patterns.
See also
- Distributed generation
- Efficient energy use
- Energy harvesting
- Energy security
- Energy storage
- Energy poverty
- Fuel efficiency
- Fossil fuel phase-out
- Mass production in renewable energy sector
- Energy transition
- Thermal energy storage
- List of countries by renewable electricity production
- List of renewable energy topics by country and territory
- Renewable heat
See also
 In Spanish: Energía renovable para niños
In Spanish: Energía renovable para niños