Renewable energy facts for kids
Renewable energy is power that comes from natural sources. These sources refill themselves faster than we use them. Think of sunlight, wind, and flowing water. These are the most common types of renewable energy. Other important types include bioenergy (from plants and animals) and geothermal power (from Earth's heat).
Renewable energy can be used in big power plants or small systems for homes. It works well in cities and the countryside. Often, renewable energy is used to make electricity. This is great because electricity can power heating systems and vehicles very efficiently. It also creates no pollution where it's used.
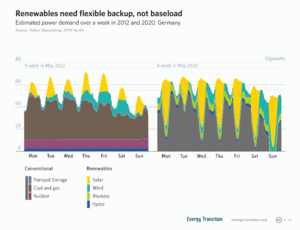
Some renewable sources, like wind and solar, change how much power they make. This depends on the weather. These are called variable renewable energy sources. Others, like hydroelectricity from dams, bioenergy, or geothermal power, can be controlled more easily.
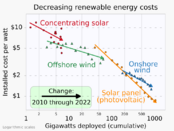
Over the last 30 years, renewable energy systems have become much better and cheaper. Most new electricity plants built around the world now use renewable sources. Solar and wind power costs have dropped a lot. This makes them cheaper than traditional fossil fuels in many places.
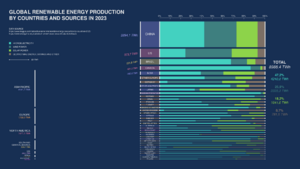
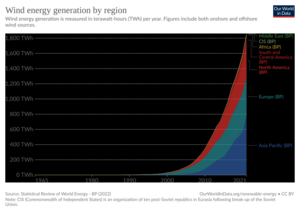
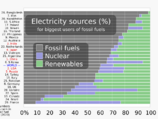
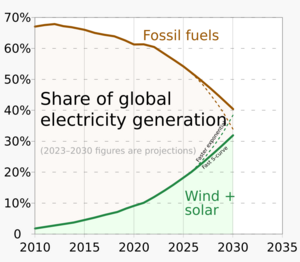
From 2011 to 2021, renewable energy grew from 20% to 28% of the world's electricity. Solar and wind power caused most of this growth. They went from 2% to 10% of the total. By 2024, renewables made over 30% of global electricity. Experts expect this to reach over 45% by 2030. Many countries already get more than 20% of their energy from renewables. Some even get over half or all their electricity this way.
The main reason to use renewable energy is to fight climate change. Burning fossil fuels creates greenhouse gases that warm our planet. Renewable energy sources pollute much less. The International Energy Agency says that by 2050, 90% of global electricity needs to come from renewables. This is needed to reach net zero emissions. Renewables also cause less air pollution and are quieter. This helps public health.
Still, there are challenges to using more renewable energy. These include fossil fuel subsidies, powerful groups who want to keep using old energy sources, and local objections to new power plants. Also, getting the materials for some renewable technologies can harm the environment.
Understanding Renewable Energy
What is Renewable Energy?
Renewable energy comes from natural processes that constantly renew themselves. The International Energy Agency says it's "energy derived from natural processes that are replenished at a faster rate than they are consumed". The main types are solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass.
Renewable energy often replaces fossil fuels in four main areas:
- Making electricity.
- Heating water and buildings.
- Powering transportation.
- Providing energy to rural areas without a main power grid.
Renewable energy sources create much less carbon pollution than fossil fuels. However, "renewable" is not the same as "low-carbon energy". For example, nuclear power creates almost no emissions but uses a non-renewable fuel. Also, burning biomass can create a lot of carbon if new plants are not grown to replace what's burned.
Fighting Climate Change
To slow down climate change, most countries want to reach net zero greenhouse gas emissions. This means stopping the use of fossil fuels and switching to energy sources that produce very little pollution. This change needs to happen much faster to protect our planet.
At the 2023 United Nations Climate Change Conference, about three-quarters of the world's countries agreed to triple renewable energy by 2030. The European Union plans to get 40% of its electricity from renewables by the same year.
Other Benefits of Renewables
Renewable energy sources are found all over the world. Fossil fuels, however, are only in a few countries. This means renewables can make energy supply more fair. They also make people healthier by reducing air pollution from burning fossil fuels. Experts believe this could save trillions of dollars in healthcare costs each year.
Dealing with Changing Power Supply
Solar and wind power are intermittent energy sources. This means they don't produce power all the time. Solar only works during the day, and wind power changes with wind speed. This is different from fossil fuel plants, nuclear plants, or hydropower, which can usually make a steady amount of energy. This changing supply is a challenge when moving away from fossil fuels. Energy demand might be higher or lower than what renewables can provide.
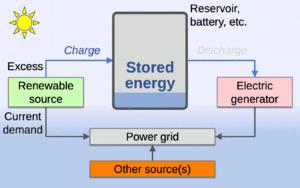
To solve this, we need ways to store energy. Energy storage is very important for dealing with this changing supply. Using different types of renewable energy and smart grids (advanced power grids) can also help balance supply and demand.
We can also connect the power sector with other areas. For example, electric vehicles can charge when there's lots of renewable energy. They could even send power back to the grid if needed. Industries can use hydrogen made with renewable electricity. Buildings can store heat for heating and cooling.
Building more wind and solar farms than needed can help ensure enough electricity. This is true even during bad weather. When the weather is perfect, we might have too much electricity. Then, we might need to stop generating some power if we can't use or store it all.
Storing Electrical Energy
Storing electrical energy means saving it for later. This happens when renewable energy production is high and demand is low. The stored energy is then sent back to the grid when needed. Pumped-storage hydroelectricity is the most common way to store grid power. Batteries are also being used more for homes and the grid. Green hydrogen is another way to store renewable energy for a long time. It can be cheaper than pumped hydro or batteries for large-scale storage.
Keeping Energy Supply Safe
Solar and wind power often use many small power sources spread out. This has good points and bad points. One risk is that most solar panel parts come from one country (China). Also, solar inverters can be controlled remotely. This means cyberattacks could turn off huge amounts of solar power at once. Similar attacks have happened to wind farms. New rules are being made to protect these systems.
Main Renewable Technologies
Solar Energy
| What it is | Details (2023) |
|---|---|
| Global electricity power capacity | 1419.0 GW |
| Yearly growth | 25% (2014-2023) |
| Share of global electricity | 5.5% |
| Cost per megawatt hour | USD 38.343 (2019) |
| Main types | Photovoltaics, concentrated solar power, solar thermal collector |
| Uses | Electricity, water heating, heating, cooling |
Solar power made about 4.6% of the world's electricity in 2022. Most of this growth happened since 2010. Solar energy can be used anywhere the sun shines. But the amount of energy depends on weather, location, and time of day.
There are two main ways to use solar energy:
- Solar thermal turns sunlight into heat.
- Photovoltaics (PV) turns sunlight directly into electricity.
PV is much more common. It makes up about two-thirds of global solar capacity. It's also growing much faster.
Passive solar means designing buildings to use the sun's heat naturally. Examples include special windows, building materials that store heat, and designs that let air move freely.
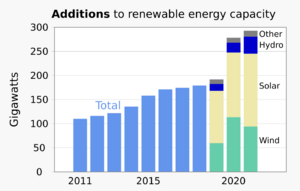
Investments in solar technology almost doubled from 2020 to 2022. This was because solar power became more mature and cheaper. China and the United States received about half of all solar investments. Globally, solar PV and concentrated solar power (CSP) capacity grew by 714 gigawatts (GW) between 2013 and 2021.
Photovoltaics (PV)
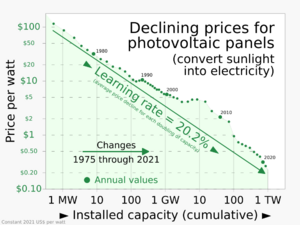
A photovoltaic system uses solar cells in panels to turn light into electricity. PV is the fastest-growing renewable energy because it's cheap, easy to maintain, and can be expanded easily. Its main problem is that it doesn't work as well on cloudy days.
PV systems can be small, like panels on a house roof. Or they can be huge power plants. A home's solar panels can power just that home. If connected to the grid, they can add power for millions of other users.
The first large solar power plant was built in California in 1982. It wasn't profitable then. But over the years, PV cells became much more efficient and cheaper. Global capacity grew from 230 GW in 2015 to 890 GW in 2021. China saw the fastest growth, adding 560 GW between 2016 and 2021. The biggest solar park, Golmud Solar Park, is in China.
Solar panels are recycled to reduce waste and get materials back. This helps avoid mining new materials.
Solar Thermal Energy
Solar thermal systems turn sunlight into heat, not electricity. They use mirrors to focus sunlight onto a receiver. This heats water, which can then be used in homes. The heated water can be stored for later. This means no separate energy storage system is needed. Solar thermal power can also make electricity by using the steam to spin a turbine. But this is more expensive than PV, so it's not common for electricity.
Floating Solar Panels
Floatovoltaics are solar panels that float on water. A good thing about them is that they can be more efficient. Also, using water space can be cheaper than using land. A downside is that building them might cost more.
Solar and Farming Together
Agrivoltaics means using land for both solar energy and farming at the same time. A good point is that it uses land more efficiently. This can lower land costs. A negative point is that the plants grown under the panels need to be ones that like shade. Examples include Polka Dot Plant and Begonia. Agrivoltaics can also help keep the ground cooler, which might save water and help crops grow better.
Wind Power

| What it is | Details (2023) |
|---|---|
| Global electricity power capacity | 1017.2 GW |
| Yearly growth | 13% (2014-2023) |
| Share of global electricity | 7.8% |
| Cost per megawatt hour | USD 30.165 (2019) |
| Main technology | Wind turbine, windmill |
| Uses | Electricity, pumping water |
People have used wind energy for thousands of years. Before the 1900s, it powered ships, windmills, and water pumps. Today, most wind power makes electricity using wind turbines. Modern turbines are very powerful. The stronger the wind, the more power they make. Places with strong, steady winds, like offshore areas, are best for wind farms.
In 2015, wind power made almost 4% of the world's electricity. About 63 GW of new wind power was installed that year. Wind energy was the top new energy source in Europe, the US, and Canada. In Denmark, wind energy met over 40% of its electricity needs.
Experts believe wind energy could make five times the world's current energy production. This would need many turbines in windy areas, especially offshore. Offshore winds are much stronger than land winds.
Investments in wind technology reached USD 161 billion in 2020. Most of this was for onshore wind. Offshore wind investments almost doubled between 2019 and 2020. Global wind capacity grew by 557 GW between 2013 and 2021. It increased by about 19% each year.
Hydropower
| What it is | Details (2023) |
|---|---|
| Global electricity power capacity | 1,267.9 GW |
| Yearly growth | 1.9% (2014-2023) |
| Share of global electricity | 14.3% |
| Cost per megawatt hour | USD 65.581 (2019) |
| Main technology | Dam |
| Uses | Electricity, pumped storage, mechanical power |
Water is much heavier than air. So, even a slow stream or ocean waves can create a lot of energy. Water can turn into electricity with about 90% efficiency. This is the highest rate for renewable energy. There are several ways to use water for energy:
- Large hydroelectric dams and reservoirs have been used for a long time. The biggest are the Three Gorges Dam in China and the Itaipu Dam in Brazil and Paraguay.
- Small hydro systems make up to 50 MW of power. They are used on smaller rivers. China has over 45,000 small hydro plants.
- Run-of-the-river hydroelectricity plants use river flow without a big dam. Water is sent through channels or pipes to a turbine. The Chief Joseph Dam in the United States is an example.
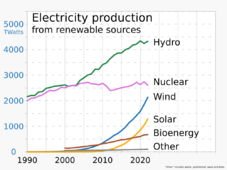
Much hydropower can be controlled. This means it can balance out wind and solar power, which change with the weather. In 2021, the world had 1,360 GW of hydropower capacity. Only about a third of the world's possible hydropower has been built. New hydropower projects can face challenges. They can impact local communities and wildlife. High costs and long approval times are also issues. Many old dams are being updated to make them more efficient. Some are even adding "pump back" systems for pumped-storage hydroelectricity. This helps store energy for peak demand or to support wind and solar.
Bioenergy
| What it is | Details (2023) |
|---|---|
| Global electricity capacity | 150.3 GW |
| Yearly growth | 5.8% (2014-2023) |
| Share of global electricity | 2.4% (2022) |
| Cost per megawatt hour | USD 118.908 (2019) |
| Main types | Biomass, biofuel |
| Uses | Electricity, heating, cooking, transportation fuels |
Biomass is material from living or recently living organisms, usually plants. It can be burned directly for heat. Or it can be turned into a more powerful biofuel like ethanol. Wood is the most common biomass energy source. It often comes from trees cleared for forest management or fire prevention. Waste wood, like sawdust, is also burned for energy. Countries with lots of forests, like Finland and Sweden, produce a lot of wood-based bioenergy.
Bioenergy can harm the environment if old forests are cut down for crops. For example, growing palm oil for biodiesel has led to deforestation in tropical rainforests. Also, burning biomass still creates carbon emissions, though less than fossil fuels. Some biomass sources are not sustainable if used too quickly.

Biofuel
Biofuels are mostly used for transportation. In 2022, they provided 3.5% of the world's transport energy. Biojet fuel is expected to help reduce carbon from long flights.
Besides wood, the main biofuels are bioethanol and biodiesel. Bioethanol comes from fermenting sugars in crops like sugarcane and maize. Biodiesel is made from plant oils like soybean oil and corn oil. Most crops for biofuels are grown just for that purpose. Used cooking oil also makes some biodiesel. The type of biomass used varies by region. Maize is big in the US, sugarcane in Brazil. In Europe, rapeseed oil and palm oil are common for biodiesel. Many countries support biofuels with money or rules.

There are other, less common, bioenergy sources. For example, bioethanol could be made from all parts of a crop, not just the seeds. Sweet sorghum might be a good source because it grows in many climates. Cow dung can be turned into methane. There's also research on algal fuel. Algae grows fast, doesn't need food crops, and can grow almost anywhere.

Geothermal Energy


| What it is | Details (2023) |
|---|---|
| Global electricity power capacity | 14.9 GW |
| Yearly growth | 3.4% (2014-2023) |
| Share of global electricity | <1% (2018) |
| Cost per megawatt hour | USD 58.257 (2019) |
| Main types | Dry steam, flash steam, and binary cycle power stations |
| Uses | Electricity, heating |
Geothermal energy is heat from inside the Earth's crust. This heat comes from slow radioactive decay of minerals and leftover heat from Earth's formation. Some heat is near the surface, but some comes from deep inside the Earth. Geothermal energy works best in countries on tectonic plate edges. Here, Earth's hot interior is closer to the surface. As of 2023, the United States has the most geothermal power. Indonesia and the Philippines are also big users. Global capacity in 2022 was 15 GW.
Geothermal energy can directly heat homes. This is common in Iceland, where almost all energy is renewable. It can also make electricity. Iceland is a world leader in renewable energy. It uses its geothermal and hydroelectric resources from volcanoes and glaciers. For smaller uses, geothermal heat pumps can get heat from shallow ground. To make electricity, large plants need ground temperatures of at least 150 degrees Celsius (302 degrees Fahrenheit). In Kenya and Indonesia, geothermal energy makes up a large part of their electricity.
New technologies might make geothermal power more common. For example, enhanced geothermal systems drill deep into the Earth. They break hot rocks and use water to get the heat. In theory, this could be done anywhere on Earth.
New Technologies
Other renewable energy technologies are still being developed. These include enhanced geothermal systems, concentrated solar power, and marine energy. These technologies are not yet widely used. Some might have great potential but need more research and development.
Enhanced Geothermal Systems
Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) are a new type of geothermal power. They don't need natural hot water or steam. Most underground heat is in solid rocks. EGS uses hydraulic fracturing to break these rocks and release the heat. Water is then pumped in to collect the heat. This is sometimes called "hot dry rock" (HDR). Unlike regular geothermal, EGS might work anywhere. But it's expensive because of the deep drilling. So far, EGS projects are mostly test plants.
Sand Battery
Sand batteries are big tanks filled with soapstone that soak up heat. Extra heat from renewable energy is piped into the tank. Then, the energy is released as boiling water, steam, or hot air. Finland is using this technology. A 1MW sand battery in Pornainen can store up to 100 MWh. It started working in 2025.
Marine Energy
Marine energy is the power from ocean waves, tides, and ocean temperature differences. Technologies to use this energy include wave power, marine current power, and tidal power. Most marine energy technologies are still new and not used on a large scale. Tidal energy is considered the most developed. But it hasn't been used widely. The world's largest tidal power station is on Sihwa Lake, South Korea. It makes about 550 gigawatt-hours of electricity each year.
Market and Industry Trends
Most new renewable energy comes from solar, then wind, then hydro, then bioenergy. Investing in renewables, especially solar, creates more jobs than coal, gas, or oil. In 2020, renewables employed about 12 million people worldwide. Solar PV alone employed almost 4 million. However, as of early 2024, there aren't enough workers for solar energy. Universities still train more people for fossil fuel jobs.
In 2021, China was responsible for almost half of the world's increase in renewable electricity. There are 3,146 gigawatts of renewable energy installed in 135 countries. Also, 156 countries have laws about renewable energy.
Globally, over 10 million jobs were linked to renewable energy in 2020. Solar photovoltaics was the biggest employer. Clean energy jobs grew by about 4.7 million between 2019 and 2022. This brought the total to 35 million jobs by 2022.
How Renewables are Used
Some studies say that switching to 100% renewable energy for everything – power, heat, transport, and industry – is possible and affordable.
One way to make transportation cleaner is to use more electric vehicles (EVs). Even with EVs and biofuels, less than 4% of transport energy comes from renewables. Sometimes hydrogen fuel cells are used for heavy transport. In the future, electrofuels might help clean up aviation and shipping.
Solar water heating is important for renewable heat in many countries, especially China. China has 70% of the world's total solar water heating. Most systems are on apartment buildings. They help heat water for 50-60 million homes in China. Worldwide, over 70 million homes use solar water heating.
Heat pumps provide both heating and cooling. They also help balance electricity demand. So, they are becoming more important. Renewable thermal energy is also growing fast. About 10% of heating and cooling energy comes from renewables.
Cost of Renewable Energy
The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) said that about 86% of new renewable energy added in 2022 was cheaper than electricity from fossil fuels. IRENA also said that renewable energy built since 2000 saved at least $520 billion on electricity bills in 2022. In non-OECD countries, new renewable capacity in 2022 will save up to $580 billion over its lifetime.
| Installed TWp |
Growth TW/yr |
Production per installed capacity* |
Energy TWh/yr* |
Growth TWh/yr* |
Levelized cost US¢/kWh |
Av. auction prices US¢/kWh |
Cost development 2010–2019 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
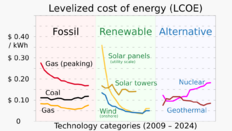
| Solar PV | 0.580 | 0.098 | 13% | 549 | 123 | 6.8 | 3.9 | −82% |
| Solar CSP | 0.006 | 0.0006 | 13% | 6.3 | 0.5 | 18.2 | 7.5 | −47% |
| Wind Offshore | 0.028 | 0.0045 | 33% | 68 | 11.5 | 11.5 | 8.2 | −30% |
| Wind Onshore | 0.594 | 0.05 | 25% | 1194 | 118 | 5.3 | 4.3 | −38% |
| Hydro | 1.310 | 0.013 | 38% | 4267 | 90 | 4.7 | +27% | |
| Bioenergy | 0.12 | 0.006 | 51% | 522 | 27 | 6.6 | −13% | |
| Geothermal | 0.014 | 0.00007 | 74% | 13.9 | 0.7 | 7.3 | +49% |
* = 2018. All other values for 2019.
Growth of Renewables
Levelized cost of energy (LCOE) is a measure of the average net present cost of electricity generation for a generating plant over its lifetime.
A recent study found that if companies have to pay for damages from greenhouse gas emissions, they will have strong reasons to use more renewable energy.
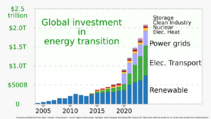
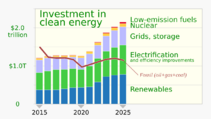
From 2010 to 2019, countries invested $2.7 trillion in renewable energy. China invested $818 billion, the United States $392.3 billion, and Japan $210.9 billion. This was much more than in the previous decade.
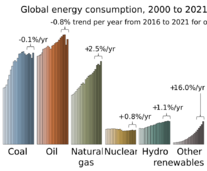
As of 2022, about 28% of the world's electricity came from renewables. This is up from 19% in 1990.
Future Plans
The IEA (International Energy Agency) predicted in December 2022 that renewables would grow by almost 2,400 GW between 2022 and 2027. This is like adding all of China's power capacity from 2021. This growth is 85% faster than the previous five years. Renewables are expected to make up over 90% of new electricity capacity during this time. To reach net zero emissions by 2050, the IEA believes 90% of global electricity needs to be renewable.
In June 2022, IEA Executive Director Fatih Birol said countries should invest more in renewables. This would help people with high fossil fuel prices. It would also make energy systems safer and help reach climate goals.
China's plan for 2021–2025 includes more direct heating from renewables like geothermal and solar thermal. The EU's REPowerEU plan aims for more green hydrogen to reduce reliance on Russian gas.
Experts expect renewable energy to make up most of the world's energy production after a transition period. By 2050, the world's energy mix might be half fossil fuels and half non-fossil sources.
Middle Eastern countries also plan to use less fossil fuel. Many green projects aim for 26% of the region's energy supply to be renewable by 2050. This would cut emissions by 1.1 Gt CO2 per year.
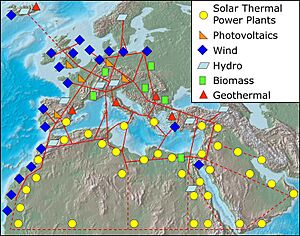
Big Renewable Energy Projects in the Middle East:
- Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park in Dubai, UAE
- Shuaibah Two (2) Solar Facility in Mecca Province, Saudi Arabia
- NEOM Green Hydrogen Project in NEOM, Saudi Arabia
- Gulf of Suez Wind Power Project in Suez, Egypt
- Al-Ajban Solar Park in Abu Dhabi, UAE
Demand for Renewables
In July 2014, WWF and the World Resources Institute talked with major US companies. These companies wanted to use more renewable energy. They agreed on important points for the renewable energy market. These included having choices, fair prices, long-term fixed prices, and help with financing.
UK statistics from September 2020 showed that renewables met 3.4% of transport demand (mostly biofuels). But they met over 20% for "other final users," like businesses that use a lot of electricity.
In some places, homes can choose to buy renewable energy through special programs.
Cost Comparison
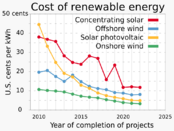
The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA)'s 2023 report shows steady growth in renewable energy investment since 2018. This trend is due to more people seeing renewables as key to fighting climate change and making energy safer. Investors are also interested in alternatives to fossil fuels. Policies like feed-in tariffs in China and Vietnam have greatly increased renewable use. Also, from 2013 to 2022, installation costs for solar PV, onshore wind, and offshore wind dropped a lot. This made renewables more affordable.
Between 2013 and 2022, investment in solar and wind energy grew a lot. But investment in other renewable technologies like hydropower, biomass, biofuels, geothermal, and marine energy went down. From 2017 to 2022, investment in these other renewables dropped by 45%.
In 2023, renewable energy saw a big jump in investments, especially for solar and wind. This totaled about $200 billion, a 75% increase from the year before. These investments added 1% to 4% to the GDP in key regions like the United States, China, the European Union, and India.
The energy sector gets about $3 trillion in investments each year. About $1.9 trillion goes to clean energy technologies. To reach the Net Zero Emissions goal by 2035, this investment needs to increase to $5.3 trillion per year.
Policies for Renewable Energy
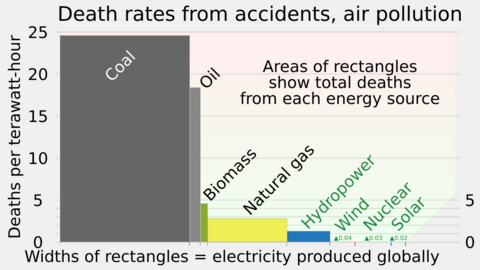
Government policies have been very important for the growth of renewable energy. In the early 2000s, Europe led the way in creating energy policies. Now, most countries worldwide have some form of energy policy.
The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) is a group that helps countries use more renewable energy. It gives advice and helps share technology. IRENA started in 2009 with 75 countries. By April 2019, it had 160 member states. The former UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon said renewable energy can help poorer nations become richer. In 2011, he started the UN Sustainable Energy for All plan. This plan aims to improve energy access, efficiency, and renewable energy use.
The 2015 Paris Agreement on climate change encouraged many countries to create or improve renewable energy policies. In 2017, 121 countries had some renewable energy policy. 176 countries had national goals for renewables. There are also many policies at local levels. Some public utilities help plan or install home energy upgrades.
Many governments have created green banks. A green bank is a special financial group. It uses public money to encourage private investment in clean energy. Green banks use different financial tools to help fill gaps in the market for clean energy.
Global and national policies for renewable energy can be grouped by sector. These include agriculture, transport, buildings, and industry.
The main goal of the European Green Deal is climate neutrality (net zero emissions) by 2050. To reach this, the European Union wants to make its energy system "net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050."
Debates and Challenges
Geopolitics and Energy
The impact of renewable energy on global politics is a big topic. Many countries that produce fossil fuels, like Qatar and Russia, have a lot of power because of their oil wealth. Most of these countries might lose influence as the world switches to renewable energy. However, some, like Norway, also produce and export renewable energy. Fossil fuels and their infrastructure might become less valuable over time. Some think countries that rely on fossil fuels might try to sell them off quickly.
On the other hand, countries with lots of renewable resources or minerals for renewable technology are expected to gain power. China is a leader in making solar panels, wind turbines, and lithium-ion batteries. Countries with lots of sun and wind could become major energy exporters. Some might produce and export green hydrogen. Electricity is expected to be the main way energy is carried by 2050. Countries with large empty areas, like Australia and many African countries, could build huge renewable energy plants. Making renewable energy technologies needs rare-earth elements, which means new supply chains.
Countries with weak governments that depend on fossil fuel money might face more political problems. Nigeria and Sudan are examples of countries at risk.
A study found that switching to renewable energy reduces risks from mining, trade, and political dependence. This is because renewable energy systems don't need fuel once built. They only need materials for construction.
In October 2021, European Commissioner for Climate Action Frans Timmermans said the best way to solve the 2021 global energy crisis was to use less fossil fuels. He said those blaming the European Green Deal were doing so for their own reasons. European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen said Europe relies too much on natural gas imports. She said the answer is to get gas from different places and speed up the switch to clean energy.
Metals and Minerals Needed
The switch to renewable energy needs more mining of certain metals and minerals. Like all mining, this can harm the environment and cause conflicts. For example, lithium mining uses a lot of water in some deserts. This forces farmers and herders to leave their homes. In Africa, the green energy change has led to a mining boom. This causes deforestation and threatens endangered animals. Wind power needs a lot of copper and zinc, plus some rarer metals. Solar power needs less, but still a lot of aluminum. Expanding power grids needs copper and aluminum. Batteries, which store renewable energy, use a lot of copper, nickel, aluminum, and graphite. Demand for lithium is expected to grow 42 times from 2020 to 2040. Demand for nickel, cobalt, and graphite is expected to grow 20-25 times. For most of these minerals, one country controls most of the mining. China controls most of the processing for all of them.
Recycling these metals from old devices is important. This creates a circular economy and makes renewable energy more sustainable. By 2040, recycled copper, lithium, cobalt, and nickel from old batteries could reduce the need for new mining by about 10%.
A debated idea is deep sea mining. Minerals can be collected from the ocean floor. This would harm local sea life. But supporters say there's less life on the deep seabed than in mining areas on land. Land mining often happens in sensitive places like rainforests.
Rare-earth mining can also produce low-level radioactive waste. This is because rare-earth elements are often found with radioactive elements.
Protecting Nature Areas
Renewable energy plants for wind, solar, and hydropower are an increasing threat to important nature areas. They are built in places set aside for nature or other sensitive environments. These plants are often much larger than fossil fuel plants. They need up to 10 times more land to make the same amount of energy. Over 2000 renewable energy facilities are built or being built in important environmental areas. They threaten plants and animals worldwide. The researchers who found this stress that they are not against renewables. Renewable energy is vital for cutting carbon emissions. The key is to build them where they don't harm nature.
In 2020, scientists made a world map showing areas with renewable energy materials. They also estimated how much these areas overlap with "Key Biodiversity Areas," "Remaining Wilderness," and "Protected Areas." The authors said careful planning is needed.
Climate Change Impact on Renewables
Climate change makes weather less predictable. This can make it harder to use renewable energy. For example, in 2023, hydropower production in Sudan and Namibia dropped by more than half due to much less rainfall. In China, India, and parts of Africa, unusual weather reduced wind energy. Heatwaves and clouds make solar panels less effective. Melting glaciers also cause problems for hydropower. Even nuclear energy is affected. Droughts can mean nuclear power plants don't have enough water for cooling.
Society and Culture
Public Support
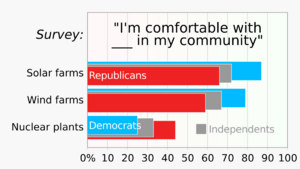
Solar power plants can take up farmland. Onshore wind farms sometimes face opposition because of how they look or the noise they make. People who object are sometimes called NIMBYs ("not in my back yard"). Some environmentalists worry about birds and bats hitting wind turbines. While protests happen, surveys usually show strong public support for both solar and wind power.
Community-owned wind energy is one way to get more local support. A 2011 UK government document said projects are more likely to succeed with public support. This means giving communities a say and a stake in the project. In the 2000s and early 2010s, many renewable projects in Germany, Sweden, and Denmark were owned by local communities.
History of Renewable Energy
Before coal became widely used in the mid-1800s, almost all energy came from renewable sources. The oldest known use of renewable energy is burning biomass for fire, over a million years ago. Using wind to power ships dates back about 7000 years. Geothermal energy from hot springs has been used for bathing since ancient times. In recorded history, the main renewable energy sources were human and animal labor, water power, wind (in windmills), and firewood.
In 1885, Werner Siemens talked about the discovery of the photovoltaic effect. He said solar energy is unlimited and free. He believed it would be used long after all coal was gone.
Max Weber wrote about the end of fossil fuels in 1905. Solar engines were developed until World War I. A 1911 Scientific American article said solar power would be the only way for humans to survive after natural fuels ran out.
The idea of peak oil (when oil production reaches its highest point) was published in 1956. In the 1970s, environmentalists pushed for renewable energy. They saw it as a replacement for oil and a way to be free from oil dependence. The first electricity-generating wind turbines appeared then. Solar had been used for heating, but solar panels were too expensive for large farms until 1980.
New government spending and policies helped the renewables industry grow. In 2022, renewables made 30% of global electricity, up from 21% in 1985.
Ancient Examples of Renewable Energy
Here are some old ways people used renewable energy:
- Windmills in Europe and Asia, like those in the Netherlands and Iran. The earliest windmills were in Iran around 700-900 CE.
- Water mills in ancient China and Persia.
- Archimedes' burning lens to focus sunlight.
- Traditional cooling systems using windcatchers and solar chimneys.
- Buildings designed to use natural heat and air flow.
- Gravity-based fountains.
- Using animal biomass in ancient fuel bricks.
- Solar ovens and furnaces in ancient China, India, Egypt, and Persia.
- Using solar energy for drying crops, hardening pottery, and disinfecting things.
- Long-distance water transport using ancient qanat technology.
- Moving cargo and people using sails on boats.
- Using natural water currents for transport.
- Burning renewable plants like desert shrubs or farm waste for light and heat.
- Using renewable oils (from plants or animals) for light and heat.
- Designing buildings to use natural sunlight and moonlight for lighting and telling time.
See also
 In Spanish: Energía renovable para niños
In Spanish: Energía renovable para niños
- Distributed generation
- Efficient energy use
- Fossil fuel phase-out
- Thermal energy storage
- List of countries by renewable electricity production
- List of renewable energy topics by country and territory
- Renewable heat