Electric vehicle facts for kids
An electric vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that uses electricity to move. Its wheels are powered by electric motors.
Electric vehicles were some of the first types of vehicles that didn't rely on horse or human power. Electric trains and cars were first built in the 1830s. In the early 1900s, there were actually more electric cars than gasoline-powered cars! However, cars using gasoline or diesel fuel became the most common type for most of the last 100 years.
Electric vehicles have been used for special jobs for a long time. You might have seen them as forklifts inside buildings, golf carts, trolley buses, or vehicles used at airports. In the early 2000s, people started using more electric and hybrid vehicles again. This is a great way to reduce pollution and use less gasoline.
Contents
History of Electric Vehicles
It's not totally clear who invented the first electric car. However, Ányos Jedlik from Hungary built a small working model in 1828. In the 1830s, Robert Anderson of Scotland, Professor Stratingh of Holland, and Thomas Davenport, a blacksmith from Vermont, all built electric vehicles. Davenport is often called the inventor of the DC electric motor.
Later, in 1865, Gaston Plante of France made a much better battery. In 1886, the inventor Frank Sprague of Connecticut made important improvements to the electric motor.
Great Britain and France were early leaders in making better electric cars. In the United States, interest in electric cars grew after 1891. That's when A. L. Ryker built a three-wheeled electric car, and William Morrison built a six-passenger electric wagon.
The years 1899 and 1900 were the best for electric cars in America. They actually sold more than all other types of cars, including steam, gasoline, and diesel cars! For example, the 1902 Phaeton by Woods Motor Vehicle Company of Chicago could travel 18 miles and had a top speed of 14 mph. It cost $2,000. Back then, there weren't many good roads between towns, so most driving was for short trips.
Electric cars could go as far as steam-powered cars and didn't take 30 to 40 minutes to start up. Gasoline engines were also smelly and noisy.
But then, the internal combustion engine (which uses gasoline and diesel) got much better. Cars with these engines could travel much farther and faster than electric cars.
For a long time, no big car company made electric cars. Some people would even build their own electric cars in their garages. They would take out the engine and put in an electric motor and batteries. It wasn't until the late 1990s that big car companies started making electric cars again. The most famous was the GM's EV-1. Now, there's a growing interest in alternative fuel vehicles.
Kinds of Electric Vehicles
Pure Electric Cars
These cars don't have any kind of gasoline engine. They are driven completely by electric motors. The power for these motors comes from different sources:
- A fuel cell makes electricity from hydrogen. Hydrogen is very common, but it's hard to store. It can be made from water, but it's usually made from natural gas. These cars are rare because there aren't many places to fill up with hydrogen. Toyota makes one of the few fuel cell cars, called the Mirai.
- A solar cell uses energy from the sun to make electricity. This electricity then powers the car. However, the sunlight that hits a solar car isn't usually enough to make a full-sized car go very fast. It also can't work at night unless it stores energy. There's a competition every year to see who can make a car that goes the farthest on only solar power.
- A battery-electric vehicle (BEV) stores electrical energy in a big battery inside the car. The batteries get their energy from an electric supply outside the car, usually a regular electrical outlet like those in a house. This is the most common type of electric car you see today. Many governments are encouraging public places to install charging stations. These stations have a plug that can charge most types of plug-in cars. Companies that make BEVs include Nissan (with the Leaf) and Mitsubishi Motors (with the i-MiEV). An American company called Tesla is famous for making BEVs that charge very quickly, like the Roadster (a sports car) and the Model S.
Hybrid Cars
A hybrid is a mix of two things. In cars, it means a combination of an electric motor and another type of power, usually a gasoline engine. Because of this, hybrid vehicles are not considered "pure" electric vehicles.
- A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) has both a gasoline engine and an electric motor that drives the wheels. Usually, the electric motor is used when the car is moving at low speeds. The gasoline engine is used as the car goes faster. The engine gets its power from gasoline or diesel. It can also create electricity, which is stored in batteries for the electric motor to use later. The battery in an HEV is much smaller than in a pure electric vehicle. Even though the car can go a short distance on electric power alone, the battery runs out quickly, and the gasoline engine has to start. The Toyota Prius is the best-selling HEV ever. Many other companies like Honda (with the Clarity) and Ford (with the Focus) also make hybrid cars. Some cars, like the Honda Civic and Toyota Camry, come in both gasoline-only and hybrid versions. The hybrid version is usually more expensive because it has more parts.
- A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) is like a regular hybrid electric vehicle because it has both a gasoline engine and an electric motor. The main difference is that a PHEV has a bigger battery that can be charged by plugging it into an outlet, just like a battery-electric vehicle. This allows the car to go farther on electric power alone than an HEV before the gasoline engine needs to be used. However, the battery is still quite small, so a PHEV usually doesn't go as far on electric power alone as a BEV. The Chevrolet Volt from General Motors and the Sonata by Hyundai are examples of plug-in hybrids. Toyota also makes a plug-in version of its Prius, as does Honda with its Clarity.
- A human electric hybrid vehicle (HEHV) is often a bicycle with a battery and motor added. The Twike is a covered vehicle that can hold two people. It can be pedaled, run from the battery, or use both at the same time.
Other Electric Vehicles
There are many other types of electric vehicles. A trolley bus (also called a trackless trolley) uses overhead electric lines to power it. Many trains use a railway electrification system to get power. A few high-speed rail lines use powerful magnets in the track to move the train. This system is called 'mag-lev' (magnetic levitation). There are also electric bicycles, motorcycles, and some tricycles (trikes) like the Corbin Motors Sparrow.
Most freight trains are diesel-electric. This means the locomotive has a diesel engine that creates electricity, and an electric motor that makes the wheels turn. In recent years, some buses and trains store their power in a battery or use fuel cells. These types of vehicles don't need overhead wires.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Electric vehicles are very quiet because they use an electric motor.
- They don't produce any smell or pollution from exhaust gases. This is why many governments are encouraging their use.
- They can be used indoors, in tunnels, and in mines.
- Oil, which is used for gasoline and diesel, is a limited resource. It won't last forever and is becoming more expensive.
- If the electricity for a battery-electric vehicle comes from a renewable energy source, like a windmill, solar cells, geothermal, or hydroelectric power, then it produces fewer global warming gases.
Disadvantages:
- Batteries don't store a lot of energy, and they are large and heavy. This means electric vehicles usually cannot go very far on a single charge.
- It takes a long time to recharge a battery, sometimes many hours.
- Good batteries can be very expensive. All batteries also need to be replaced after a while.
- Most electricity in some places, like the United States, comes from burning coal or natural gas. So, an electric vehicle powered by electricity from these plants will still add to global warming gases, just not directly from the car itself.
Modern Electric Vehicles
More electric cars are being made every year. Here are a few examples:
- Tesla Roadster (a sports car, no longer sold, replaced by the Model S)
- Tesla Model S
- Nissan Leaf
- Ford Focus Electric
- BMW i3
Records
- Rimac Nevera, an electric sports car, set 23 world speed records in one day.
- Electric Land Speed Record 353 mph (568 km/h).
- Electric Car Distance Record 1,725 miles (2,776 km) in 24 hours by Bjørn Nyland.
- Greatest distance by electric vehicle, single charge 999.5 miles (1,608.5 km).
- Solar-powered EV is fastest EV to go over 1,000 km without stopping to recharge, the Sunswift 7.
- Electric Motorcycle: 1,070 miles (1,720 km) under 24 hours. Michel von Tell on a Harley LiveWire.
- Electric flight: 439.5 miles (707.3 km) without charge.
Images for kids
-
Edison and a 1914 Detroit Electric model 47 (courtesy of the National Museum of American History)
-
This 1973 photo from Seattle shows an AMC Gremlin modified to be electric. It could travel about 50 miles on one charge.
-
A Battery electric bus powered by lithium-ion batteries
-
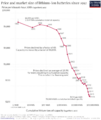
The price of lithium-ion batteries dropped by 97% in thirty years.
-
A streetcar (or tram) getting power from an overhead wire using a pantograph
-
A trolleybus uses two overhead wires for its electric power.
-
Hess Swisstrolley 3 in St. Gallen
See also
 In Spanish: Vehículo eléctrico para niños
In Spanish: Vehículo eléctrico para niños