Fuel cell facts for kids
A fuel cell is a device that makes electricity. It does this by mixing a special fuel (usually hydrogen) with air. This reaction creates water and sometimes carbon dioxide.
Fuel cells work a bit like a battery, but they don't run out. As long as you keep giving them fuel, they keep making electricity! The most common fuel is hydrogen. When hydrogen mixes with oxygen from the air, it only produces water. This means it's very clean.
Hydrogen can be found in things like water, natural gas, or plants. To get hydrogen, you need some energy. One way is to separate it from fuels like oil or gas. This process can release carbon dioxide. Another way is to get it from water using electrolysis. If the energy for this comes from clean sources like solar or wind power, then no pollution is released. Hydrogen can also come from biogas, which is also a clean source.
Contents
How Fuel Cells Make Electricity
Water is a molecule made of one oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms. It takes energy to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. When they come back together as water, energy is released. A fuel cell brings hydrogen and oxygen back together in a special way that releases this energy as electricity.
Inside a Fuel Cell
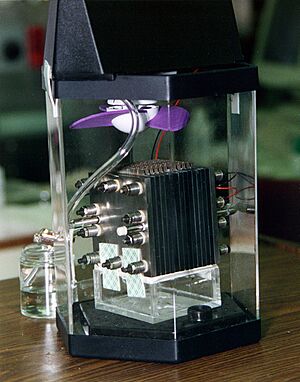
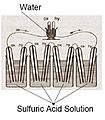
Fuel (usually hydrogen) and air (which has oxygen) go into different sides of the fuel cell. In the middle, there's a "screen" called an electrolyte. This screen is between two metal plates called electrodes. The screen keeps the fuel and air separate. Different types of fuel cells are named after the kind of screen they use.
The screen only lets special charged particles, called ions, pass through. To make these ions, tiny particles called electrons have to move from one side to the other.
Creating Electric Current
The metal plate on the fuel side separates electrons from the fuel. These electrons can't go through the screen. So, they travel through a separate wire to the other metal plate on the air side. This movement of electrons through the wire creates electric current, which is electricity! You can use this electricity to power things, like a light bulb.
Meanwhile, the ions pass through the screen. On the air side, they meet the oxygen and the electrons that came through the wire. They all react to form water. This water then leaves the fuel cell through an exhaust pipe.
How Efficient Are Fuel Cells?
Fuel cells are very good at making electricity. They can turn about 40% to 70% of the fuel's energy into electricity. If they also use the heat they produce, their efficiency can go up to 83%.
Fuel cells can use many different fuels. Besides hydrogen, they can use natural gas, methanol, LPG, naphtha, and kerosene.
Benefits of Fuel Cells
Some fuel cells produce only water as a byproduct, which means no pollution! Most types of fuel cells create much less pollution than traditional power generators.
Less Pollution and More Efficiency
Fuel cells can use the same fuels as regular engines, like diesel. But they are about twice as efficient. This means they can make the same amount of energy using half as much fuel. So, they also create at least half as much pollution.
Also, fuel cells don't burn fuel. This means they are less likely to produce harmful gases like NOx and SOx. These gases cause air pollution and contribute to global warming.
Quiet and Durable
Fuel cells are very quiet. They don't have many moving parts, just some fans and pumps. This means they usually don't need many repairs. However, some very large fuel cells can be delicate.
Because they are so clean and quiet, fuel cells are used in special places.
Where Are Fuel Cells Used?
Fuel cells are used in many different ways:
- Vehicles: Major car companies are making fuel cell cars. There are also fuel cell buses, boats, trains, planes, and even forklifts.
- Portable Devices: Small fuel cells might power cell phones, laptops, and other electronics in the future.
- Buildings: Hospitals, banks, and police stations use fuel cells for reliable power.
- Waste Management: Some wastewater treatment plants and landfills use fuel cells. They turn methane gas (a byproduct of waste) into electricity.
- Space: Fuel cells have been used in outer space for a long time. Spaceships use them to make electricity from hydrogen and oxygen. The water they produce can even be used as drinking water for astronauts!
- Remote Locations: Because they use fuel efficiently, fuel cells can work for a long time without needing more fuel. This makes them great for places that are hard to reach, like weather stations or military bases.
- Telecommunications: Cell phone towers and emergency call centers use fuel cells for backup power.
Types of Fuel Cells
Fuel cells are often grouped by the type of inner screen (electrolyte) they use.
- Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell (PAFC): These cells work at lower temperatures. They are used in things like cell phones and cars that need a lot of electricity. They are also very safe.
- Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEM): These cells work at fairly low temperatures (around 175°F). They can produce a lot of power and change their output quickly. This makes them good for cars, where you need a quick start. Most fuel cell cars use this type. The main challenge is that they need very pure hydrogen, which can be expensive to make.
- Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell (MCFC): These cells work at very high temperatures. This allows them to use more complex fuels, like natural gas, and turn them into hydrogen right inside the cell. They take a long time to start up and shut down. So, they are best for places that need continuous power, like large buildings.
- Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC): These are special fuel cells that use tiny living things (microbes) to turn organic stuff into electricity.
Images for kids
-
Sketch of Sir William Grove's 1839 fuel cell
-
The world's first certified fuel cell boat (HYDRA) in Leipzig, Germany.
See also
 In Spanish: Pila de combustible para niños
In Spanish: Pila de combustible para niños
 | Jessica Watkins |
 | Robert Henry Lawrence Jr. |
 | Mae Jemison |
 | Sian Proctor |
 | Guion Bluford |