Outer space facts for kids


Space, also known as outer space, is the huge, almost empty area between planets, stars, and galaxies. It's where everything in the Universe exists, beyond Earth and its atmosphere.
There isn't one exact point where Earth's atmosphere ends and space begins. However, the Kármán line, which is about 100 km (62 mi) above sea level, is often used as the official start of outer space. This line helps define where space travel begins for treaties and records.
Contents
What is the Environment Like in Space?

Outer space is almost a perfect vacuum, meaning it's mostly empty. Because there's almost no air or friction, planets, stars, and moons can move freely in their paths, called orbits. Even though it seems empty, space isn't completely void. For example, in the vast space between galaxies, there are a few hydrogen atoms in every cubic meter. This is very different from the air we breathe, which has trillions of molecules in the same amount of space!
The low amount of matter in space means that light and other electromagnetic radiation can travel huge distances without being blocked or scattered. This is why we can see distant stars and galaxies.
Planets and stars hold onto their atmospheres with their gravity. An atmosphere doesn't have a sharp edge; it just gets thinner and thinner until it blends into outer space. The entire observable universe is also filled with faint cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB), which is leftover energy from the Big Bang.
Different Regions of Space
Space is so huge that scientists divide it into different regions based on how far they are from Earth and what they contain.
Space Near Earth
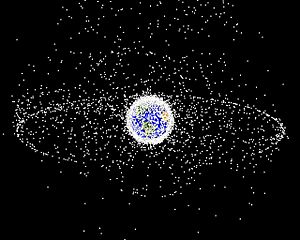
- Near-Earth space is the area from low Earth orbits up to geostationary orbits. This is where most of our artificial satellites orbit, and it's where humans do most of their space activities. Unfortunately, this area has a lot of space debris, which are pieces of old satellites or rockets. This "space pollution" can be dangerous for working satellites.
- Geospace is a region that includes Earth's upper atmosphere and its magnetosphere. The magnetosphere is like a protective bubble around Earth, created by its magnetic field. It shields us from harmful particles from the Sun.

- Cislunar space is the region that includes the Moon's orbit around Earth and other important points called Lagrange points. This area is becoming more important for future space missions.
- Deep space is generally defined as any part of outer space that is farther from Earth than a typical low-Earth orbit. This means the Moon is considered to be in deep space.
Interplanetary Space

Interplanetary space is the space between the planets in our Solar System, and also the space between the planets and the Sun. It extends beyond the orbit of Neptune, where the Sun's influence, called the solar wind, is still strong.
This space is also mostly a vacuum, but it contains cosmic rays (high-energy particles), gas, plasma, and tiny dust particles. It also has the magnetic field created by the Sun.
Interstellar Space

Interstellar space is the space between different stars or stellar systems within a galaxy. Each star creates a "bubble" of plasma around it with its stellar wind. This bubble is called an astrosphere. For our Sun, this bubble is called the heliosphere. Interstellar space is found outside these astrospheres.
This region contains a mix of very thin matter and radiation, known as the interstellar medium. About 70% of this medium is made of single hydrogen atoms, and most of the rest is helium atoms. There are also many different types of molecules and tiny dust particles found here.
Intergalactic Space
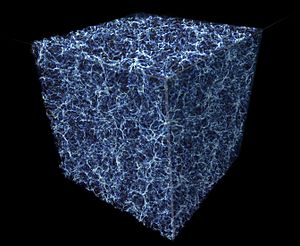
Intergalactic space is the huge physical space between different galaxies. When we look at how galaxies are spread out in the universe, it looks a bit like foam. There are groups and clusters of galaxies that form long, thin structures called filaments. These filaments take up about one-tenth of all space. The rest of the space forms huge, mostly empty areas called cosmic voids.
Even these "empty" voids are not completely empty. They contain a very thin plasma, called the intergalactic medium (IGM), which stretches between galaxies in a filamentary structure.
How Do We Explore Space?
Exploring space is very challenging! There's no air, and it's incredibly vast. Even the fastest spacecraft can only explore a tiny part of it. For example, it takes about three days to travel to the Moon. Reaching the closest star, Proxima Centauri, would take a very long time, even with our fastest ships.
When astronauts travel in space, their spacecraft must be specially designed. They need to keep good air inside and protect the astronauts from the extreme temperatures and the vacuum of space.
Most of what we know about space comes from different kinds of telescopes. Some are space telescopes, which are placed in orbit to get a clearer view without Earth's atmosphere getting in the way. We also use Space probes, which are robotic spacecraft that travel to and explore planets, comets, and other objects that are not too far away.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
This is an artist's concept of the expansion of space, where a volume of the Universe is shown at different times. On the left, you see the rapid expansion from the beginning, followed by steadier expansion to the present day, shown on the right.
-
Part of the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field image showing a typical section of space with galaxies spread out in the deep vacuum. Because light takes time to travel, this view shows us the past 13 billion years of outer space's history.
-
Because of the dangers of a vacuum, astronauts must wear a special pressurized space suit when they are outside their spacecraft in space.
-
Aurora australis (Southern Lights) observed from the Space Shuttle Discovery, in May 1991.
-
SpaceShipOne made the first human private spaceflight in 2004, reaching an altitude of 100.12 km (62.21 mi).
-
A 2008 launch of the SM-3 missile used to destroy an American reconnaissance satellite.
-
The original Magdeburg hemispheres (lower left) used to show how a vacuum pump works.
-
The first image taken by a human of the whole Earth, likely photographed by William Anders of Apollo 8. South is up; South America is in the middle.
See also
 In Spanish: Espacio exterior para niños
In Spanish: Espacio exterior para niños
 | Audre Lorde |
 | John Berry Meachum |
 | Ferdinand Lee Barnett |