Space Shuttle Discovery facts for kids
Quick facts for kids DiscoveryOV-103 |
|
|---|---|
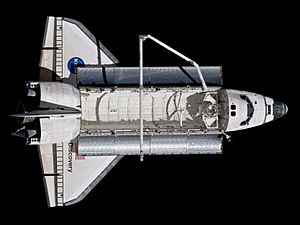
Discovery in orbit in 2011, during STS-133
|
|
| OV designation | OV-103 |
| Country | United States |
| Contract award | January 29, 1979 |
| Named after | Discovery (1602), HMS Discovery (1774), HMS Discovery (1874), RRS Discovery (1901) |
| Status | Retired, on display at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Virginia |
| First flight | STS-41-D August 30, 1984 – September 5, 1984 |
| Last flight | STS-133 February 24, 2011 – March 9, 2011 |
| No. of missions | 39 |
| Crew members | 252 |
| Time spent in space | 1 year (365 days), 22 hours, 39 minutes, 33 seconds |
| Distance travelled | 148,221,675 mi (238,539,663 km) |
| Satellites deployed | 31 (including Hubble Space Telescope) |
| Mir dockings | 1 |
| ISS dockings | 13 |

The Space Shuttle Discovery (also known as OV-103) was a special spacecraft. It was one of the orbiters used by NASA. Discovery was the third of five main orbiters built for the Space Shuttle program.
Its first trip to space, called STS-41-D, happened from August 30 to September 5, 1984. Over 27 years, Discovery flew into space and landed 39 times. This means it had more spaceflights than any other spacecraft at that time!
Like other space shuttles, Discovery had three main parts. These were the Space Shuttle orbiter (the part that looked like a plane), a large fuel tank, and two rocket boosters. The orbiter was covered with nearly 25,000 special heat-resistant tiles. These tiles protected it from the super hot temperatures when it came back into Earth's atmosphere.
Discovery was the third orbiter to start flying. The first two were Columbia and Challenger. Its very last mission, STS-133, began on February 24, 2011. It landed for the final time at Kennedy Space Center on March 9, 2011. In total, Discovery spent almost a full year in space!
Discovery did many important jobs. It carried out scientific research and helped build the International Space Station (ISS). It also famously carried the Hubble Space Telescope into orbit.
Discovery was the first of the operational shuttles to be retired. After it, Endeavour and then Atlantis also stopped flying. Today, you can see Discovery on display. It is at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Virginia.
Contents
Exploring Discovery: Key Missions and Achievements
Discovery played a big role in space exploration. It completed many important missions for NASA.
Launching the Hubble Space Telescope
One of Discovery's most famous missions was STS-31 in 1990. On this mission, Discovery carried the Hubble Space Telescope into space. Hubble is a powerful telescope that takes amazing pictures of the universe. It has helped scientists learn so much about galaxies, stars, and planets far away.
Returning to Flight after Accidents
Discovery was also chosen for very important missions after accidents.
- After the Challenger accident in 1986, Discovery was the first shuttle to fly again. This mission, STS-26 in 1988, showed that the Space Shuttle program was safe to continue.
- Again, after the Columbia accident in 2003, Discovery flew the first "Return to Flight" mission, STS-114, in 2005. These missions were very important for NASA. They helped make sure space travel was as safe as possible.
Building the International Space Station
Discovery made 13 trips to the International Space Station (ISS). The ISS is a huge orbiting laboratory where astronauts from different countries live and work. Discovery helped carry parts and supplies to build and maintain the station. It also brought astronauts to and from the ISS.
Other Important Missions
- Discovery carried many different satellites into orbit. These satellites helped with communication, weather forecasting, and scientific research.
- It also performed research experiments in space. Astronauts on board studied how living in space affects the human body. They also tested new technologies for future space travel.
Images for kids
-
On the maiden voyage of Discovery: Judith Resnik, Henry Hartsfield, Michael L. Coats, Steven A. Hawley, Charles D. Walker, and Richard M. Mullane
See also
 In Spanish: Transbordador espacial Discovery para niños
In Spanish: Transbordador espacial Discovery para niños















