Near-Earth object facts for kids
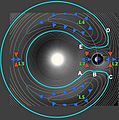
A near-Earth object (NEO) is a space object whose path around the Sun brings it close to Earth. These objects can be asteroids or comets. They travel through our Solar System and sometimes come quite close to our planet.
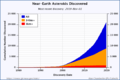
NEOs include thousands of near-Earth asteroids (NEAs) and near-Earth comets. They also include some spacecraft orbiting the Sun and even large meteoroids. Scientists track these objects to see if they might ever hit Earth. In the past, collisions with NEOs have greatly changed Earth's history, affecting its geology and life.

Contents
What are Near-Earth Objects?
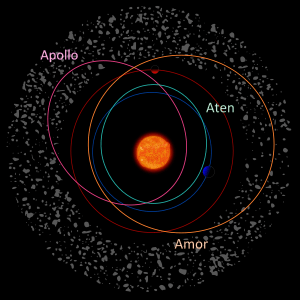
Near-Earth objects are space rocks or icy bodies. Their closest point to the Sun, called their perihelion, is less than 1.3 AU (Astronomical Units). One AU is the average distance from Earth to the Sun. This means NEOs come closer to the Sun than Mars does.
Types of NEOs
There are two main types of near-Earth objects:
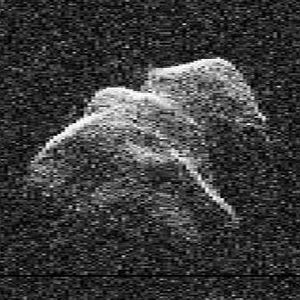
- Near-Earth Asteroids (NEAs): These are rocky objects. Most of them orbit the Sun between Mars and Jupiter. But some have paths that cross Earth's orbit.
- Near-Earth Comets: These are icy bodies that come from the outer Solar System. As they get close to the Sun, their ice turns into gas, forming a tail.
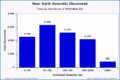
Scientists are always looking for new NEOs. They use telescopes to find and track them. This helps us understand where they are going and how fast.
When NEOs Hit Earth
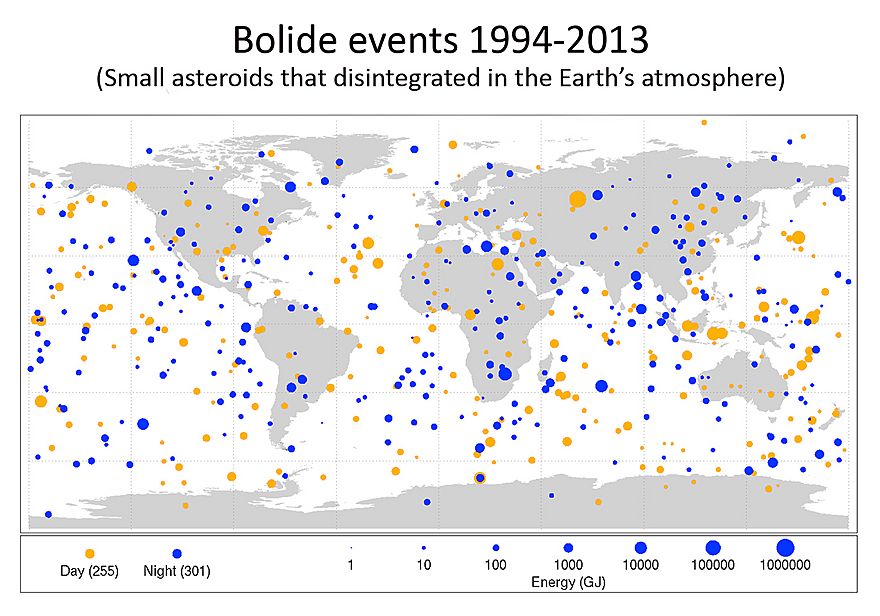
Sometimes, NEOs do hit Earth. Most of the time, smaller ones burn up in our atmosphere. They create bright streaks of light we call meteors or "shooting stars." These usually cause no harm.
However, some NEOs are big enough to be dangerous. Scientists try to predict when one might hit Earth. This is called impact prediction.
The Tunguska Event
On June 30, 1908, a space rock exploded over a remote forest in Siberia, Russia. This event is known as the Tunguska event. The rock was about 45 meters (148 feet) wide. It exploded high in the air, releasing huge amounts of energy. This energy was like a very large nuclear weapon.
The explosion flattened about 2,000 square kilometers (770 square miles) of forest. This area is larger than the city of London. Because the location was so remote, no deaths were recorded. Scientists believe an event like Tunguska happens about two or three times every thousand years.
The Dinosaur Extinction
About 66 million years ago, a much larger asteroid hit Earth. This asteroid was roughly 10 kilometers (6 miles) wide. It caused a massive event known as the K/T extinction event. This event led to the extinction of many types of plants and animals. It included all non-avian dinosaurs. This shows how much a large NEO impact can change life on Earth.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Asteroid Toutatis from Paranal
-
Halley's Comet during its 0.10 AU approach of Earth in May 1910
-
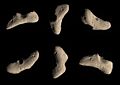
Image mosaic of asteroid 101955 Bennu, target of NASA's OSIRIS-REx probe
See also
 In Spanish: Objeto próximo a la Tierra para niños
In Spanish: Objeto próximo a la Tierra para niños
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |