Electric motor facts for kids
An electric motor is a cool device that turns electrical energy into movement. Think of it like magic! It makes things spin or move. The opposite of a motor is a generator. A generator takes movement and turns it into electricity. Most electric motors use the power of magnetism to work.
You can find electric motors in many everyday machines. These include fans that keep you cool, washing machines that clean your clothes, fridges that keep food fresh, pumps, and vacuum cleaners.
How Electric Motors Work
To understand electric motors, it's helpful to know about electromagnets. An electromagnet is a temporary magnet created by electricity. It's the main part of an electric motor.
A simple electric motor has a few key parts:
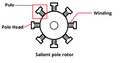
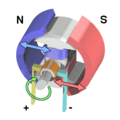
- The rotor (also called the armature) is the part that spins.
- The commutator helps switch the direction of the electric current.
- Brushes connect the power to the commutator.
- An axle is the rod the rotor spins on.
- A field magnet creates a magnetic field around the rotor.
- A power supply (like a battery) provides the electricity.
Electric motors use magnets to create motion. You might know that opposite ends of magnets attract each other (like north and south). Also, similar ends repel each other (like north and north, or south and south). Inside an electric motor, these attracting and repelling forces make the rotor spin around and around.
Electric motors are usually split into two main types:
- DC (direct current) motors use electricity that flows in one direction.
- AC (alternating current) motors use electricity that changes direction.
Each type has different uses that make them perfect for certain jobs.
History of Electric Motors
The first electric motor was made in 1821 by a scientist named Michael Faraday. His motor used the power of magnetism.
Faraday made a simple electromagnet. He wrapped about 100 loops of wire around a nail and connected it to a battery. This made the nail a temporary magnet with a north and south pole. He then put a spindle (a small rod) through a hole in the middle of the nail so it could spin. Next, he placed a horseshoe-shaped magnet around the wire-wrapped nail.
He connected the wire from the north pole of his electromagnet to the negative side of the battery. He connected the wire from the south pole to the positive side. Because of the basic rules of magnetism, the north end of the electromagnet pushed away from the north end of the horseshoe magnet. It also pulled towards the south pole of the horseshoe magnet. The same thing happened on the other side of the nail. This made the nail turn!
At first, Faraday's motor only turned once. But he soon found that by wrapping the wire many times around the nail, he could make the magnetic poles switch back and forth. These extra "turns" made the wire-wrapped nail spin continuously around the spindle, as long as the battery had power. This was a huge step in creating useful electric motors!
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Jedlik's "electromagnetic self-rotor" from 1827. This historic motor still works today!
-
An electric motor given to Kelvin by James Joule in 1842.
See also
 In Spanish: Motor eléctrico para niños
In Spanish: Motor eléctrico para niños
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |