Solar cell facts for kids
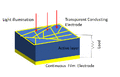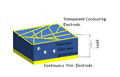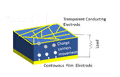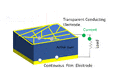
A solar cell is a special device that turns light energy into electricity. Sometimes, people call them photovoltaic cells. The word "solar" usually means they use sunlight. "Photovoltaic" can mean any light source. These cells work by letting light hit a material. This light creates tiny electric particles (called charge carriers). The cell then moves these particles to special contacts. This movement creates electricity. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect. The study of solar cells is called photovoltaics.
Contents
What Solar Cells Are Used For
Solar cells have many important uses. They are great for places where there is no regular electricity grid. For example, they power satellites and space probes far from Earth. They also power small things like calculators and wrist watches. You can find them in remote areas for radiotelephones or to pump water.
More and more, solar cells are used in homes and buildings. Many solar panels are connected to the main electricity grid. They use a device called an inverter to change the electricity. This helps homes use clean energy. Solar cells are a key part of creating a sustainable energy future. This means using energy that does not harm the planet.
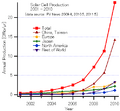
How Solar Cells Developed: Three Stages
Solar cell technology has grown a lot over time. Experts often talk about three main "generations" of solar cells.
First Generation Solar Cells
The first generation of solar cells are the most common type. They are made from a single, large piece of silicon. This silicon is shaped into a thin slice called a wafer. These cells have a special part called a p-n junction. This junction helps turn sunlight into electricity. First generation cells make up over 86% of all solar cells sold today. They are very good at capturing energy from sunlight.
Second Generation Solar Cells
The second generation of solar cells are different. They use very thin layers of special materials called semiconductors. These layers are much thinner than the silicon wafers. This means they use less material to make. Using less material can make them cheaper to produce.
Some materials used for these thin-film cells include amorphous silicon, cadmium telluride, and copper indium selenide. These cells are often not as efficient as first-generation cells. But their lower cost can make them a good choice. Another benefit is that they are lighter. This means they need less support when put on roofs. They can even be made flexible. You can find roll-up solar panels that fit in a backpack. These can charge phones or laptops in remote places.
Third Generation Solar Cells
The third generation of solar cells are very new and exciting. They work differently from the first two types. They do not rely on the traditional p-n junction. Instead, they use new ways to separate the electric particles created by light.
Some examples of these new cells include photoelectrochemical cells and polymer solar cells. These are still being researched and developed. Companies like Xsunx and Konarka Technologies, Inc. are working on them. The USA's National Renewable Energy Laboratory also does a lot of research in this area. These new cells could lead to even more efficient and cheaper solar power in the future.
Images for kids
-
NASA used solar cells on its spacecraft from the very beginning. For Example, Explorer 6, launched in 1959, had four arrays that folded out once in orbit. They provided power for months in space.
-
The Solar Impulse aircraft is powered only by solar cells.
See also
 In Spanish: Célula fotoeléctrica para niños
In Spanish: Célula fotoeléctrica para niños