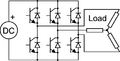
Inverter facts for kids
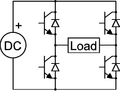
An inverter is an electric device that changes direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). Think of it like a translator for electricity! DC power comes from things like batteries and solar panels. AC power is what usually comes out of wall sockets in your home.
Inverters are super useful because they let you use DC power sources to run everyday household items. For example, if you have solar panels, an inverter helps them power your lights, microwave oven, or other electric machines.
Sometimes, an inverter also makes the electricity's voltage higher. When the voltage goes up, the electric current goes down. This means an inverter might use a lot of current from the DC side (like a battery) to produce a smaller amount of current on the AC side (for your devices).
Inverters come in many different sizes. Some are small, like 150 watts, which is enough for a few small gadgets. Others are huge, like 1 megawatt (that's 1 million watts!), used for big solar farms or industrial needs.
Types of Inverters
There are different kinds of inverters, each producing a slightly different type of AC power:
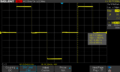
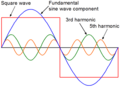
- Sine wave inverters create very smooth and clean AC power. This is similar to the electricity you get from the power grid. These inverters are usually more expensive.
- A modified sine wave inverter produces AC power that isn't as smooth. It's a bit "rougher" and can sometimes cause issues with sensitive electronics. However, these inverters are often cheaper.
Images for kids
-
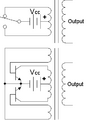
Top: Simple inverter circuit shown with an electromechanical switch and automatic equivalent auto-switching device implemented with two transistors and split winding auto-transformer in place of the mechanical switch.
See also
 In Spanish: Inversor (electrónica) para niños
In Spanish: Inversor (electrónica) para niños