Photovoltaics facts for kids
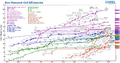
| Solar Power Growth worldwide (GWp) |
|
|---|---|
| 2000 | 1 |
| 2005 | 5 |
| 2010 | 40 |
| 2011 | 70 |
| 2012 | 99 |
| 2013 | 136 |
| Power at year end | |

Photovoltaics (PVs) is a cool way to make electricity directly from sunlight. It uses special materials that turn light energy into an electric current. Think of it like a magic trick where sunshine becomes power!
Because more and more people want renewable energy (energy that won't run out), making solar cells and panels has gotten much better and cheaper recently. Solar power is growing super fast! By the end of 2013, the world had enough solar panels to make 130,000 MW of power. Over 100 countries now use solar PV. You can find solar panels on the ground, sometimes even mixed with farms, or built right into the roofs and walls of buildings.
Contents
Solar Panels: How They Work
Solar panels come in different voltages, which is like their electrical "strength." The most common are 12, 24, and 48 volts. Just like batteries, you can connect many solar panels together to make even higher voltages. For example, two 48-volt panels connected would make 96 volts.
The parts of a solar system, like the inverter, batteries, and solar panels, usually all have the same voltage. Higher voltage systems can use thinner wires, which saves money and is easier to install. However, higher voltages can be more dangerous if not handled properly. That's why systems above 48 volts are usually only found in big solar power plants or large buildings.
A typical solar power setup includes:
- A group of solar panels (called an array).
- An inverter (this changes the electricity from the panels into power your home can use).
- Rechargeable batteries (to store power for when the sun isn't shining, like at night).
- A charge controller (this stops the batteries from getting too full).
- Safety devices called GFCI circuit breakers.
- All the wiring to connect everything.
Sometimes, there's also a transformer after the inverter. This can power bigger appliances like clothes dryers or ovens. Often, this transformer is hidden inside the inverter itself. Everything after the inverter works just like a normal house's electrical system. If there's no transformer, you can only use 120-volt devices. Some solar setups even have special direct current (DC) lights or appliances. This saves energy because the power doesn't need to be changed by the inverter. For safety, DC wires and outlets are kept separate from AC wires and outlets.
Big Solar Power Plants
The world has some really huge solar power stations! These are massive areas covered in solar panels, making lots of clean energy. Here are a few of the biggest ones:
- The Topaz Solar Farm and Desert Sunlight Solar Farm in the USA are both huge, aiming for 550 MW of power.
- The Longyangxia Dam Solar Park in China was completed in 2013 and can make 320 MW.
- The Agua Caliente Solar Project in the USA makes 290 MW and was finished in 2014.
- The Charanka Solar Park in India is a collection of many power plants that together make 224 MW.
- Photovoltaic power plants
-
President Barack Obama at the DeSoto Next Generation Solar Energy Center.
Solar Cells: The Tiny Power Makers

A solar cell, also called a photovoltaic cell, is a small device that turns light energy into electricity. It's the basic building block of a solar panel! This amazing effect, called the photovoltaic effect, was first noticed by a scientist named Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel way back in 1839. Most solar cells are a type of photodiode.
Solar cells can power small tools or recharge batteries. The very first time photovoltaics were used was to power orbiting satellites and other spacecrafts in space. But today, most solar cells are used to create power for homes and businesses connected to the main electricity grid. For this, an inverter is needed to change the direct current (DC) from the cells into alternating current (AC) that homes use.
Solar cells need protection from the weather, so they are usually sealed tightly behind a sheet of glass. When you need more power than one cell can make, many cells are connected together to form photovoltaic modules, which we call solar panels. One solar module might be enough to power an emergency phone. But for a whole house or a big power station, many modules are arranged together to form large solar arrays.
Images for kids
-
The Solar Settlement, a green housing project in Freiburg, Germany.
See also
 In Spanish: Energía solar fotovoltaica para niños
In Spanish: Energía solar fotovoltaica para niños