Heat pump facts for kids

A heat pump is a special machine that can move heat from one place to another. It's like a heat taxi! It takes heat from a cooler spot and moves it to a warmer spot. This might sound strange because heat usually moves from hot to cold all by itself. But a heat pump makes it go the other way, using a bit of energy.
Contents
How We Use Heat Pumps
- Refrigerators are common heat pumps. They take heat out of the food inside to keep it cold and fresh. The heat then goes into the air outside the fridge.
- Air conditioners are also heat pumps. In summer, they move heat from inside your house to the outside. This keeps your home cool and comfy.
- Some buildings use heat pumps for heating in winter. They can take heat from the cold outside air or ground and bring it inside. This can be a very energy-efficient way to warm a building.
- A Peltier device is a tiny heat pump that uses electricity to move heat. It's often found in small coolers or electronic devices.
How a Heat Pump Works
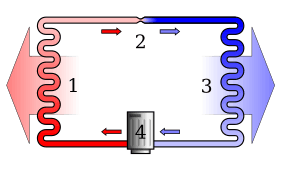
Most heat pumps work using a special process called the refrigeration cycle. This cycle uses a special liquid called a refrigerant. The refrigerant moves through tubes inside the heat pump. As it moves, it changes from a liquid to a gas and back again. This change helps it carry heat.
The Refrigerant's Journey
When the refrigerant changes from a liquid to a gas, it needs heat. So, it absorbs heat from its surroundings, making that area cooler. Think of it like boiling water; it takes heat to turn water into steam.
When the refrigerant changes back from a gas to a liquid, it releases heat. This means it gives off heat to its surroundings, making that area warmer.
Moving the Heat
The heat pump is designed so that the refrigerant picks up heat from the place you want to cool down. Then, it moves that heat to another place where you want to warm things up.
A part called a compressor helps this happen. The compressor squeezes the refrigerant gas, which makes it turn back into a liquid. When it does this, it also releases the heat it was carrying. An electric motor usually powers this compressor.
At the other end of the cycle, the refrigerant boils again. It changes from a liquid to a gas. To do this, it takes heat from its surroundings, making that area feel cooler.
The Complete Cycle
Here's how the full cycle works:
- On the cooling side, the refrigerant changes from a liquid to a gas, absorbing heat and making that area cold.
- The refrigerant then moves to the heating side.
- There, the compressor squeezes the refrigerant, turning it back into a liquid. This makes it release the heat it picked up.
- So, heat has moved from the cooling side to the heating side.
- The cycle then repeats, continuously moving heat.
- If the cooling side is the inside of a refrigerator, your food stays cold.
- If the cooling side is the inside of a building, and the warming side is the outside, it works like an air conditioner to cool your home.
- If the cooling side is the outside of the building, and the warming side is the inside, it works like a heater to warm your home in winter.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Bomba de calor para niños
In Spanish: Bomba de calor para niños