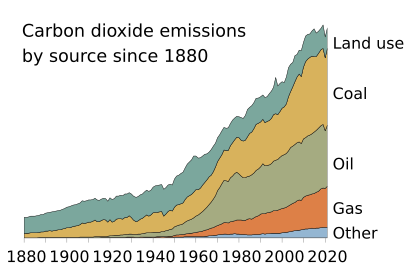
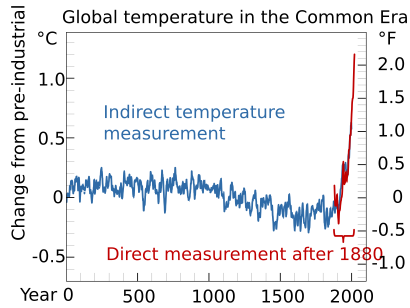
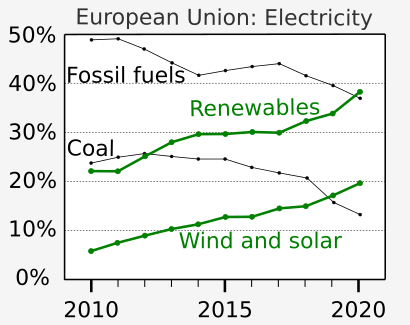
Fossil fuel facts for kids
Fossil fuels are special fuels that come from very old plants and animals. These living things died long, long ago and slowly changed underground over millions of years. The three most important fossil fuels are coal, petroleum (also known as oil), and natural gas.
Oil and gas are made of molecules called hydrocarbons, which only have hydrogen and carbon atoms. Coal is mostly carbon. We call them fossil fuels because they are dug up from deep inside the Earth, just like fossils! Coal mining brings up solid coal, while oil wells bring up liquid oil and gas. People didn't use fossil fuels much until the Middle Ages. Coal became super important during the Industrial Revolution, when many new machines were invented.
Contents
How We Use Fossil Fuels
Most of the fuels people burn today are fossil fuels. A really big use for them is to make electricity.
Making Electricity
In power plants, fossil fuels, usually coal, are burned. This burning heats up water and turns it into steam. The steam then pushes a giant fan-like object called a turbine. As the turbine spins, special magnets inside it create electricity.
Fueling Transportation
Petroleum (crude oil) can be separated into different fuels like gasoline, kerosene, jet fuel, and diesel fuel. This is done in an oil refinery. These fuels are super important for transportation. They are burned to make cars, trucks, ships, airplanes, and even trains move! Without them, getting around would be very different.
Heating Homes and Cooking
People also burn fossil fuels to heat their homes. They use coal less for this now because it can make things dirty. In many homes, people burn natural gas in a stove for cooking their food. Fossil fuels are also used a lot in construction to build things.
Where Fossil Fuels Come From
All fossil fuels come from times in Earth's history when our planet had huge tropical forests and wetlands. During these periods, plants grew and died very quickly. But instead of fully rotting away, much of the dead plant material got buried. Over millions of years, under great heat and pressure, this buried vegetation slowly turned into coal and other similar substances like peat.
Most of the world's coal comes from periods like the Pennsylvanian (part of the Upper Carboniferous), the early Permian, the Jurassic, and the Eocene periods.
Problems with Fossil Fuels

Burning fossil fuels causes a lot of air pollution. This pollution can be reduced by burning the fuels more cleanly and by using special filters. This pollution is also a big reason why the Earth is getting warmer, a problem called global warming.
Another major issue is that fossil fuels are non-renewable resources. This means there's only a limited amount of coal, gas, and oil underground, and we can't make more of it quickly. Eventually, all the fossil fuels will be used up. Some scientists believe that coal might run out by the year 2200 and oil by 2040.
Looking for Solutions
To help with these problems, people are using more Renewable energy sources. These include energy from biomass (like firewood), wind power, tidal energy (from ocean tides), and solar energy (from the sun). Many governments are also helping car makers develop electric cars and hybrid cars that use less oil.
Effects on Our Environment
Burning fossil fuels has several harmful effects on our environment.
Climate Change
When fossil fuels burn, they release greenhouse gases like CO
2 into the air. These gases trap heat and cause climate change. Climate change is negatively affecting ecosystems around the world. Some animal and plant species are becoming extinct, and people are producing less food. This makes the problem of world hunger even worse. The World Health Organization says that climate change is the biggest threat to human health in the 21st century.
Acid Rain
When fossil fuels burn, they also create sulfuric acid and nitric acid. These acids mix with rain and fall to Earth as acid rain. Acid rain can damage buildings and statues, especially those made from marble and limestone, because the acids dissolve these materials.
Radioactive Materials
Fossil fuels also contain tiny amounts of radioactive materials, mainly uranium and thorium. When coal is burned, these materials are released into the air. For example, in 2000, about 12,000 tonnes of thorium and 5,000 tonnes of uranium were released worldwide from burning coal.
Other Environmental Impacts
Getting and moving fossil fuels also affects the environment. Coal mining methods, like mountaintop removal and strip mining, can harm landscapes. Offshore oil drilling can be dangerous for sea creatures. Also, transporting coal and oil often requires burning even more fossil fuels.
How Fossil Fuels Affect Our Health
Air pollution from burning fossil fuels can make people sick and even cause death when they breathe it in. Health problems include early death, serious breathing illnesses, worse asthma, long-lasting bronchitis, and reduced lung function. People who are poor, don't get enough food, are very young or very old, or already have health problems are more at risk. In 2018, over 8 million people died because of air pollution from fossil fuels. That's almost 1 out of every 5 deaths worldwide.
Fossil fuels cause the most greenhouse gas emissions and are the most dangerous for human health. On the other hand, modern renewable energy sources are much safer for human health and cleaner.
Efforts to Reduce Fossil Fuel Use
People are trying to reduce the negative effects of fossil fuels. Governments are making rules to stop waste products, like fly ash, from being released into the air.
There's also a big movement to use other energy sources, especially renewable energy. Data shows that coal, oil, natural gas, and biomass cause higher death rates and more greenhouse gas emissions than hydropower, nuclear energy, wind, and solar power. For example, 1.8 million lives have been saved by using nuclear power instead of fossil fuels.
In December 2020, the UN Secretary General António Guterres said that "Humanity is waging war on nature. [...] Nature always strikes back—and it is already doing so with growing force and fury."
However, Guterres also said there is still hope. He mentioned Joe Biden's plan for the US to join other big countries like China and the EU in aiming for net zero emissions by 2050. This means trying to remove as much greenhouse gas from the air as we put into it.
Images for kids
-
A petrochemical refinery in Grangemouth, Scotland, UK
-
An oil well in the Gulf of Mexico
See also
 In Spanish: Combustible fósil para niños
In Spanish: Combustible fósil para niños