Peat facts for kids
Peat, also known as turf, is a special kind of soil made from plants that have only partly rotted away. It forms in very wet places like wetlands, bogs, and swamps.
Peat is created when dead plant material, often from marshy areas, doesn't fully rot. This happens because the conditions are very acidic and have little to no oxygen. Peat is mostly made of marsh plants like trees, grasses, and even fungi. Sometimes, you can also find parts of insects and other animals in it.
The wetter the conditions, the faster peat forms and the less it rots. Scientists who study climate can use peat to learn about how the climate has changed over time. By looking at what's inside the peat, they can also figure out what ancient environments were like.
Over millions of years, if peat is buried deep underground and heated, it can turn into coal. This is why peat is sometimes called the first step in coal formation.
Most of the peat bogs we see today formed in cold places after the last ice age ended, about 9,000 years ago. They grow very slowly, usually only about one millimeter each year. The world's peatlands have been forming for 360 million years and hold a huge amount of carbon, about 550 Gigatonnes!
How People Use Peat
Peat is an important source of fuel in some parts of the world. There's a lot of peat on Earth, covering about 2% of all land. That's enough to provide a lot of energy!
Peat is soft and can be easily squeezed. When you press it, water comes out. Once it dries, peat can be burned as a fossil fuel. It's used as a fuel in countries like Ireland and Finland, where it's collected on a large scale. In places like Ireland and Scotland, where trees were scarce, people traditionally used peat for cooking and heating their homes. You can still see stacks of drying peat in some rural areas.
Peat is also good at keeping things warm or cool because of its insulating properties. This makes it useful in some industries.
Did you know peat is used to make Scotch whisky? Peat fires are used to dry the barley, which gives Scotch whisky its special smoky taste. This taste is often called "peatiness."
Challenges with Peat
Even though peat has many uses, it can also cause problems. When peat is dry, it can be a big fire hazard. Peat fires can burn for a very long time, sometimes even underground! They can even start up again after winter if there's still some oxygen around.
Peat deposits also make it hard to build things like roads and railways. This is because peat is very soft and squishes easily, even under small weights. For example, when the West Highland Line railway was built across Rannoch Moor in Scotland, workers had to create a special floating base of tree roots, branches, and tons of earth and ashes to support the tracks.
Images for kids
-
Peat in Lewis, Scotland
-
A peat stack in Ness in the Isle of Lewis (Scotland).
-
Peat stacks in Südmoslesfehn (district of Oldenburg, Germany) in 2013
-
Peat gatherers at Westhay, Somerset Levels in 1905
-
Peat extraction in East Frisia, Germany
-
A worked bank in a blanket bog, near Ulsta, Yell, Shetland Islands
-
Falkland Islanders shovelling peat in the 1950s
-
Industrial peat production in the Bog of Allen in Ireland. The 'turf' in the front is made by machines for home use.
-
Shatura Power Station. Russia has the most power plants that use peat in the world.
-
The Bor Peat Briquette Factory, Russia
-
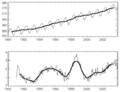
This graph shows how much carbon dioxide is in the air and how it changes each year.
-
Smoke and ozone pollution from Indonesian fires in 1997.
See also
 In Spanish: Turba para niños
In Spanish: Turba para niños
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |