Ireland facts for kids
|
|
|---|---|
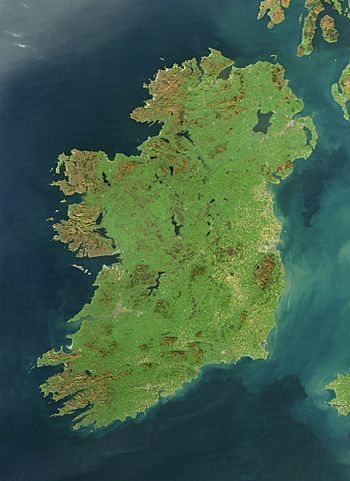
Satellite image, October 2010
|
|
Location of Ireland (dark green)
on the European continent (dark grey) |
|
| Geography | |
| Location | Northwestern Europe |
| Coordinates | 53°26′58″N 07°30′11″W / 53.44944°N 7.50306°W |
| Adjacent bodies of water | Atlantic Ocean |
| Area | 84,421 km2 (32,595 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 20th |
| Coastline | 7,527 km (4,677.1 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 1,041 m (3,415 ft) |
| Highest point | Carrauntoohil |
| Administration | |
|
Republic of Ireland
|
|
| Largest city | Dublin, pop. 1,458,154 Metropolitan Area (2022) |
|
United Kingdom
|
|
| Country | Northern Ireland |
| Largest city | Belfast, pop. 671,559 Metropolitan Area (2011) |
| Demographics | |
| Demonym | Irish |
| Population | 7,185,600 (2023 estimate) |
| Population rank | 19th |
| Pop. density | 82.2 /km2 (212.9 /sq mi) |
| Languages | |
| Ethnic groups | |
| Additional information | |
| Time zone |
|
| • Summer (DST) |
|
| Patron saints |
|
|
|
Ireland ( YRE-lənd; Irish: Éire Ulster-Scots: Airlann) is a large island in the North Atlantic Ocean. It is located in north-western Europe. To its east, it is separated from Great Britain by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the second-largest island in the British Isles. It is also the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest in the world.
The island of Ireland is split into two main parts. Most of the island (about five-sixths) is the Republic of Ireland. This is an independent country. The remaining part is Northern Ireland, which is part of the United Kingdom. In 2022, over 7 million people lived on the island. About 5.1 million live in the Republic of Ireland. Around 1.9 million live in Northern Ireland. This makes Ireland the second-most populated island in Europe, after Great Britain.
Ireland's landscape has low mountains around a flat central area. Many rivers flow inland, and some are good for boats. The island is very green because of its mild, changing climate. Temperatures are not too hot or too cold. A long time ago, much of Ireland was covered in forests. Today, only about 10% of the island is woodland. Most of these trees are not native to Ireland. The weather in Ireland is affected by the Atlantic Ocean. This means winters are milder than you might expect for a northern country. Summers are cooler than in other parts of Europe. It rains often, and there are many cloudy days.
Contents
History of Ireland
Gaelic Ireland developed around the 1st century AD. People on the island became Christian starting in the 5th century. In the 12th century, the Anglo-Normans arrived. After this, England began to claim control over Ireland. However, England did not fully control the whole island until the 16th and 17th centuries. This period, called the Tudor conquest, led to settlers from Britain moving to Ireland.
In the 1690s, a system of Protestant English rule was put in place. This system made it harder for the Catholic majority and other Protestants. It continued through the 18th century. In 1801, the Acts of Union made Ireland part of the United Kingdom.
In the early 1900s, there was a war for independence. This led to the island being divided. The Irish Free State was created, which later became the independent Republic of Ireland. Northern Ireland remained part of the United Kingdom. From the late 1960s to the 1990s, Northern Ireland experienced a lot of civil unrest. This period ended with the Good Friday Agreement in 1998.
In 1973, both the Republic of Ireland and the United Kingdom (including Northern Ireland) joined the European Economic Community. This group later became the European Union (EU). In 2016, the United Kingdom voted to leave the EU. It officially left in 2020. Northern Ireland was given a special status. It can still operate within the EU's single market for goods. This has helped its economy grow faster than the rest of the UK.
What's in a Name?
The names Ireland and Éire come from an Old Irish word. This word is Ériu. Ériu was a goddess in Irish mythology. Her name was first written down in the ninth century. Experts are not sure where the name Ériu comes from. It might be linked to an ancient word meaning "flowing water."
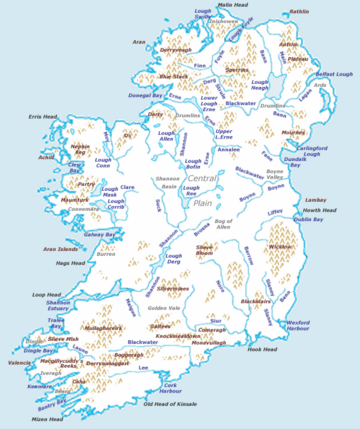
Exploring Ireland's Geography
Ireland is in the north-west of Europe. It lies between 51° and 56° North latitude and 11° and 5° West longitude. The Irish Sea and the North Channel separate it from Great Britain. The narrowest part of the North Channel is about 23 kilometers (14 miles) wide. To the west is the northern Atlantic Ocean. To the south is the Celtic Sea, which is between Ireland and France.
Ireland covers a total area of 84,421 square kilometers (32,595 square miles). The Republic of Ireland takes up 83 percent of this area. Ireland and Great Britain, along with many smaller islands nearby, are sometimes called the British Isles. However, some people find the term British Isles controversial. So, the term Britain and Ireland is sometimes used instead.
A ring of mountains runs along the coast. Low plains are found in the center of the island. The highest mountain is Carrauntoohil (Irish: Corrán Tuathail). It is in County Kerry and is 1,039 meters (3,409 feet) tall. The best farming land is in the province of Leinster. Western areas are mostly mountainous and rocky. They offer beautiful green views. The River Shannon is the island's longest river. It is 360.5 kilometers (224 miles) long. It starts in County Cavan in the north-west and flows through Limerick in the midwest.
Ireland's Land and Rocks
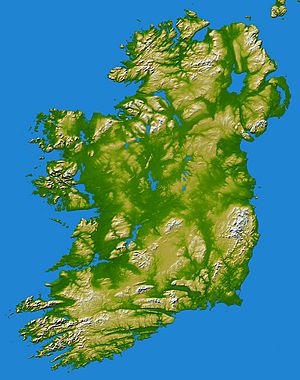
Ireland's land is made up of different types of rocks and soil. In the west, around County Galway and County Donegal, there are old, hard rocks. These rocks are similar to those found in the Scottish Highlands. In the southeast, you can find rocks from the Ordovician and Silurian periods. These are like rocks in the Southern Uplands of Scotland. Further south, near the County Wexford coast, there are granite rocks. These are similar to rocks in Wales.
In the southwest, around Bantry Bay, the rocks are very folded and changed. These rocks are from the Devonian period. This ring of hard rock is covered by a layer of limestone in the center of the country. This limestone makes the land fertile and green. The area called the Burren in the west has interesting karst features. This means the limestone has been shaped by water, creating caves and sinkholes.
People are also looking for oil and gas in Ireland. The first big natural gas discovery was at the Kinsale Head gas field in the 1970s. In 1999, more natural gas was found at the Corrib Gas Field off the County Mayo coast. In 2000, the Helvick oil field was discovered. It was thought to hold over 28 million barrels of oil.
Ireland's Climate
Ireland is known as the Emerald Isle because of its green plants. This greenness comes from its mild climate and frequent rain. Overall, Ireland has a mild but changing oceanic climate. It rarely has extreme temperatures. This is because moist winds usually blow from the southwest Atlantic Ocean.
It rains throughout the year, but the rain is generally light. The west of Ireland tends to be wetter. It often gets Atlantic storms, especially in late autumn and winter. These storms can bring strong winds and heavy rain. Sometimes, they also bring snow and hail. The areas of north County Galway and east County Mayo get the most lightning. Lightning strikes about five to ten days a year there. Munster, in the south, gets the least snow. Ulster, in the north, gets the most.
Inland areas are warmer in summer and colder in winter. Inland weather stations usually have about 40 days below freezing (0 °C or 32 °F) each year. Coastal stations only have about 10 such days. Ireland sometimes has heat waves. Recent ones were in 1995, 2003, 2006, 2013, and 2018. In the winter of 2010–11, Ireland had unusually cold weather. Temperatures dropped to -17.2 °C (1 °F) in County Mayo. Some mountainous areas got up to a meter (3 feet) of snow.
Ireland's Plants and Animals

Ireland has fewer land animals and plants than Great Britain or mainland Europe. This is because Ireland only had an ice bridge to Europe. This bridge melted about 14,000 years ago. There are 55 types of mammals in Ireland. Only 26 of these land mammals are native to the island. Some animals like the red fox, hedgehog, and badger are very common. Others, like the Irish hare, red deer, and pine marten, are less common.
Many sea animals live off the coast. These include sea turtles, sharks, seals, whales, and dolphins. About 400 types of birds have been seen in Ireland. Many of these birds travel long distances, like the barn swallow.
Ireland has many different types of natural places. These include farmland, open woodlands, forests, peat bogs, and coastal areas. However, farming uses a lot of land in Ireland. This limits the natural homes for wild animals. Especially for large wild mammals that need a lot of space. There are no large apex predators in Ireland besides humans and dogs. So, animal populations like deer are controlled by yearly culling.
There are no snakes in Ireland. Only one type of reptile, the common lizard, is native to the island. Some animals that used to live in Ireland are now extinct. These include the Irish elk, the great auk, the brown bear, and the wolf. Some birds, like the golden eagle, have been brought back after disappearing for many years.
Ireland is now one of the least forested countries in Europe. Until the end of the Middle Ages, Ireland had many forests. Native trees include oak, ash, hazel, birch, alder, willow, aspen, rowan, and hawthorn. Evergreen trees like Scots pine, yew, holly, and strawberry trees also grow there. Today, only about 10% of Ireland is woodland. Most of this is non-native conifer plantations. Only 2% is native woodland. The average woodland cover in European countries is over 33%. In the Republic of Ireland, about 3,893.56 square kilometers (1,503.31 square miles) of forest are owned by the state. You can find small parts of native forest around the island. A good example is in Killarney National Park.
Much of the land is now covered with grass for animals. There are also many types of wild-flowers. Gorse (Ulex europaeus), a wild furze, grows commonly in the uplands. Ferns are common in wetter areas, especially in the west. Ireland is home to hundreds of plant species. Some of them are found only on the island. Some new grasses, like Spartina anglica, have also arrived.
The types of algae and seaweed found are those that like cold, mild waters. There are 574 different species. Some new types of algae have also arrived and are now well established.
Because of its mild climate, many different plants can grow in Ireland. This includes sub-tropical plants like palm trees. Ireland is part of the Atlantic European region for plants. The island has two main plant areas: the Celtic broadleaf forests and North Atlantic moist mixed forests.
Images for kids
-
Inisheer (Inis Oírr), Aran Islands.
See also
 In Spanish: Irlanda (isla) para niños
In Spanish: Irlanda (isla) para niños