Munster facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Munster
An Mhumhain
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
 |
|||
| State | Ireland | ||
| Counties | Clare Cork Kerry Limerick Tipperary Waterford |
||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 24,684 km2 (9,527 sq mi) | ||
| Area rank | 1st | ||
| Population
(2022)
|
|||
| • Total | 1,373,346 | ||
| • Rank | 3rd | ||
| • Density | 55.6371/km2 (144.153/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | UTC±0 (WET) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+1 (IST) | ||
| Eircode routing keys |
Beginning with E, H, P, T, V, X (primarily)
|
||
| Telephone area codes | 02x, 05x, 06x (primarily) | ||
| ISO 3166 code | IE-M | ||
| Patron Saint: Ailbe of Emly a. Munster is part of the South constituency; the six Munster counties contain 67.7% of the population of this constituency. | |||
Munster (Irish: an Mhumhain or Cúige Mumhan) is one of the four main regions, called provinces, in the south of Ireland. Long ago, the Kingdom of Munster was a powerful kingdom ruled by a "king of over-kings." After the Normans arrived, the old kingdoms were divided into counties for easier management. Over time, these counties were further split into smaller areas.
Today, Munster does not have an official role in local government. However, it is listed as a region by the ISO (code "IE-M"). Munster covers about 24,684 square kilometers (9,527 sq mi) and has a population of over 1.3 million people. The largest city in Munster is Cork. Other important cities are Limerick and Waterford.
Contents
History of Munster

In ancient times, Munster was home to groups like the Iverni people. In the 5th century, Saint Patrick visited the area. He started Christian churches and made priests there. During the Early Middle Ages, most of Munster was part of a kingdom ruled by the Eóganachta family. Before them, the Dáirine and Corcu Loígde families were in charge.
By the 9th century, Vikings joined the Gaels in Ireland. The Vikings founded important towns like Cork, Waterford, and Limerick. These towns became part of a sea-based empire led by the Dynasty of Ivar. Around this time, a region called Ossory broke away from Munster. The Eóganachta family ruled Munster until the 10th century. Then, the Dalcassian clan rose to power. They took over an area called Thomond, north of the River Shannon. Their leaders were the ancestors of the O'Brien dynasty, which included Brian Boru. He was one of the most famous High Kings of Ireland.
By 1118, Munster had split into three smaller kingdoms:
- The Kingdom of Thomond (ruled by the O'Briens)
- The Kingdom of Desmond (ruled by the MacCarthy dynasty)
- The short-lived Kingdom of Ormond (ruled by the O'Kennedys)
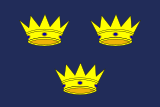
The three crowns on the flag of Munster represent these three kingdoms.
From the 14th century, Norman families like the FitzGeralds and Butlers became important. Some of them created large areas called earldoms. The Earls of Desmond became very powerful and independent. The Earls of Ormond stayed closer to England. In the 1500s, the O'Briens and MacCarthys agreed to be part of the Kingdom of Ireland under the Tudor rulers. However, the Desmond Rebellions, led by the FitzGeralds, soon followed.
In the mid-to-late 16th century, the British started plantations in Munster. This was part of the Tudor conquest of Ireland. The Munster plantation was the biggest colonial project by the English at that time.
In the mid-19th century, the Great Famine severely affected much of Munster, especially the western parts. In the early 20th century, the province was involved in the Irish War of Independence. There was even a short-lived Munster Republic during the Irish Civil War. Famous Irish leaders like Michael Collins and Daniel O'Connell came from old Gaelic families in Munster.
Culture in Munster
Munster is well-known for its Irish folk music traditions. It also has many old castles and monasteries, making it a popular place for tourists. While Saint Patrick founded churches here in the 5th century, a bishop named Ailbe from that same century is the patron saint of Munster.
In Irish mythology, many ancient goddesses are linked to Munster. These include Anann, Áine, Grian, and Clíodhna. The druid-god of Munster is Mug Ruith, and his daughter is Tlachtga. Another legendary figure is Donn.
Munster has always had strong trade and cultural connections with Europe. The Corcu Loígde people had ships that traded along the French coast, bringing wine to Munster. The Eóganachta family had religious ties with Germany. You can see this in the architecture of their special capital at the Rock of Cashel.
Most of the ancient Irish ogham inscriptions (an early form of writing) are found in Munster. Later, the Sanas Cormaic, which was Europe's first dictionary in a language other than Latin or Greek, was created by scholars in Munster. It is believed that King-Bishop Cormac mac Cuilennáin (who died in 908) led this work. The School of Ross in Munster was one of Europe's top learning centers in the Early Middle Ages.
Sports in Munster
Many sports in Munster are organized by province. This includes popular sports like hurling, Gaelic football, rugby union, and soccer. Other sports like cricket and hockey also have provincial groups.
Hurling and Football
Munster is famous for its history in hurling. Three of the four most successful teams in the All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship are from Munster: Cork GAA, Tipperary GAA, and Limerick GAA. The final of the Munster Senior Hurling Championship is a very important day in the Irish GAA calendar. Munster is the only province in Ireland where every single county has won at least one All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship.
In Gaelic football, the strongest teams in Munster are usually Kerry GAA and Cork GAA. However, Tipperary GAA and Limerick GAA have also won All-Ireland Senior Football Championships. Kerry is especially successful and has won more football championships than any other county.
Rugby Union
Rugby is a very popular sport in the cities of Limerick and Cork. Munster Rugby is a team that represents the province. They play in the United Rugby Championship and have won it several times (in 2003, 2009, 2011, and 2023). They also won the Heineken Cup (a European competition) in 2006 and 2008. Until 2016, Munster was the only Irish team to have beaten the famous New Zealand All Blacks rugby team.
Soccer
Soccer is also a popular sport in Munster. The Munster Football Association helps organize the game in the province. In 2024, five clubs from Munster play in the League of Ireland. Waterford FC is in the top division (Premier Division). Cobh Ramblers, Cork City F.C., Treaty United F.C., and Kerry F.C. play in the First Division.
Cricket
In cricket, the Munster Reds team represents the province. They play in the Inter-Provincial Cup (one-day games) and the Inter-Provincial Trophy (Twenty20 games). Cricket Ireland plans to include Munster in the longer first-class cricket tournament in the future.
Irish Language in Munster
The Irish language, specifically the Munster Irish dialect, is spoken as a first language in certain areas called Gaeltachtaí (Irish-speaking areas). These areas include West Kerry (Corca Dhuibhne), South Kerry (Uíbh Ráthach), West Cork (Múscraí), south-west Cork (Oileán Cléire), and parts of Waterford (Gaeltacht na Rinne or Gaeltacht na nDéise).
There are about 35,000 Irish speakers in Munster. About 9,737 of these are native speakers in the Gaeltacht areas of Cork, Kerry, and Waterford. Also, 12,219 students attend 45 Gaelscoils (Irish language primary schools) and 15 Gaelcholáiste (Irish language secondary schools) in the province. In 2011, there were 13,193 people in Munster who spoke Irish daily outside of the education system.
Counties and Cities of Munster
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1981 | 998,315 | — |
| 1986 | 1,020,577 | +2.2% |
| 1991 | 1,009,533 | −1.1% |
| 1996 | 1,033,903 | +2.4% |
| 2002 | 1,100,614 | +6.5% |
| 2006 | 1,173,340 | +6.6% |
| 2011 | 1,246,088 | +6.2% |
| 2016 | 1,280,020 | +2.7% |
| 2022 | 1,373,346 | +7.3% |
Munster is divided into six traditional counties: Clare, Cork, Kerry, Limerick, Tipperary, and Waterford. Munster is the largest of Ireland's four provinces by land area. It is the third largest by population.
| County | Population (2022) |
Area |
|---|---|---|
| Clare (An Clár) | 127,938 | 3,450 km2 (1,330 sq mi) |
| Cork (Corcaigh) | 584,156 | 7,508 km2 (2,899 sq mi) |
| Kerry (Ciarraí) | 156,458 | 4,807 km2 (1,856 sq mi) |
| Limerick (Luimneach) | 209,536 | 2,756 km2 (1,064 sq mi) |
| Tipperary (Tiobraid Árann) | 167,895 | 4,305 km2 (1,662 sq mi) |
| Waterford (Port Láirge) | 127,363 | 1,858 km2 (717 sq mi) |
| Total | 1,373,346 | 24,684 km2 (9,531 sq mi) |
Major Urban Areas
Munster has many large towns and three cities, which is more than any other province in Ireland. Here is a list of the largest urban areas in Munster, based on 2022 census figures. Cities and county towns are shown in bold:
Urban areas with over 10,000 people:
Urban areas with 5,000–10,000 people:
- Nenagh (9,895)
- Youghal (8,564)
- Bandon (8,196)
- Thurles (8,185)
- Newcastle West (7,209)
- Fermoy (6,720)
- Passage West-Monktown (6,051)
- Kinsale (5,991)
- Carrick on Suir (5,752)
- Carrigtwohill (5,568)
- Roscrea (5,542)
- Tipperary (5,387)
- Clonakilty (5,112)
Economy of Munster
Munster's economy is strong. In 2014, the average income per person in Cork and Kerry was about €50,544. In the South Tipperary/Waterford region, it was around €28,094. The money people had to spend (disposable income) in Munster was about €22,000 per person in 2008. This was less than the Dublin area but more than other regions in Ireland.
Agriculture
Munster's farming industry is centered around the Golden Vale. This area has rich pasturelands in counties Cork, Limerick, and Tipperary. Companies like Kerry Group make dairy products from the milk of cows in this region. Glanbia is another food producer with an "innovation center" here. Dawn Meats, a meat producer, also operates from County Waterford.
Retail
The Irish-owned shop chain Dunnes Stores started in Cork. Ireland's largest supermarket group, the Musgrave Group, is also based in Munster.
Employment
Many large companies employ people in Munster. These include AOL, Bausch & Lomb, Dell, Amazon, Motorola, Pfizer, Apple Computer, Intel, and Siemens. The biggest place for jobs in Munster is Metropolitan Cork, where many international companies are located. The Shannon Free Zone in County Clare, near Limerick city, is also a major employment center.
Munster in Media
Several television companies and studios in Munster focus on the region. These include RTÉ Cork (RTÉ's local studio) and others like South Coast TV and Channel South. Channel South used to broadcast local shows to Cork, Limerick, and parts of Kerry, Waterford, Clare, and Tipperary.
Besides local city newspapers, some newspapers focus on the whole province. These include the Avondhu (which covers parts of Cork, Waterford, Limerick, and Tipperary), the Nationalist & Munster Advertiser, and the Munster Express.
See also
 In Spanish: Munster (Irlanda) para niños
In Spanish: Munster (Irlanda) para niños
 | Anna J. Cooper |
 | Mary McLeod Bethune |
 | Lillie Mae Bradford |