Kingdom of England facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
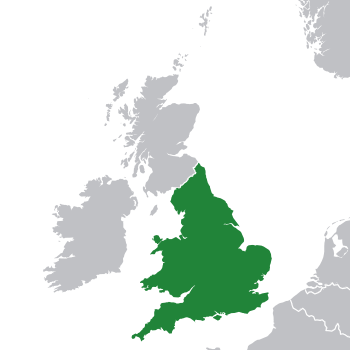
Kingdom of England
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Motto:
"Dieu et mon droit" (French) "God and my right" |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Location of the Kingdom of England in 1700
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Christianity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | English | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Heptarchy (5th century – 10th century) Elective monarchy (10th century – 1066) Absolute monarchy (1066-1215) Unitary parliamentary monarchy (1215-1649) Commonwealth (1649-1660) Unitary parliamentary monarchy (1660-1707) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monarch | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 927–939
|
Æthelstan (first) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1702–1707
|
Anne (last) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Legislature | Parliament | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| House of Lords | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| House of Commons | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 927 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 October 1066 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1277–1283 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1535–1542 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 March 1603 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 December 1688 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 May 1707 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1283–1542 est. | 145,000 km2 (56,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1542–1707 est. | 151,000 km2 (58,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1283
|
2,600,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1542
|
3,000,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1707
|
5,750,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Pound sterling | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | GB-ENG | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Kingdom of England was an independent country on the island of Great Britain. It started in 927 when different Anglo-Saxon kingdoms joined together. It lasted until 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain.
Contents
Early History of England
On July 12, 927, Æthelstan brought together the various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms. This created the Kingdom of England. In 1016, England became part of the North Sea Empire. This empire was ruled by Cnut the Great and included England, Denmark, and Norway.
The Norman conquest of England happened in 1066. After this, the main royal city moved from Winchester to Westminster. The City of London quickly became England's biggest and most important business center.
Ruling Families and Key Events
Historians often divide the Kingdom of England's history by the families who ruled. These periods are:
- Norman (1066–1154)
- Plantagenet (1154–1485)
- Tudor (1485–1603)
- Stuart (1603–1714)
All English monarchs after 1066 were descendants of the Normans.
England and Wales
In 1284, Edward I completed the conquest of Wales by Edward I. This put Wales under the control of the English king. Later, in 1542, England and the Principality of Wales officially became one country. This was done through the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542.
Changes in Government and Power
King Edward III (who ruled from 1327 to 1377) made England one of the strongest military powers in Europe. His reign also saw important changes in laws and how the government worked. The English Parliament became much more important during this time.
From the 1340s, the kings of England also said they should be king of France. However, after the Hundred Years' War and the Wars of the Roses (which started in 1455), England lost most of its land in France. Only Calais remained.
The Tudor Era
After the difficult times of the Wars of the Roses, the Tudor dynasty came to power. This period was known as the English Renaissance. The Tudor monarchs made the English king's power stronger, even outside England.
Henry VIII led a big change in England's religion, known as the English Reformation. His daughter, Elizabeth I (who ruled from 1558 to 1603), created a plan for religion called the Elizabethan Religious Settlement. She also made England a great power and started to build the British Empire by claiming lands in the New World.
The Stuart Dynasty and Civil War
From 1603, the Stuart dynasty ruled England. Their kings also ruled Scotland and Ireland at the same time. This was called a "personal union."
Under the Stuart kings, England had a big civil war. This war ended with Charles I being put to death in 1649. The monarchy returned in 1660, but the Civil War had shown that an English king could not rule without Parliament agreeing. This idea became a law after the Glorious Revolution of 1688.
From this time on, the Kingdom of England, and later the United Kingdom, became a constitutional monarchy. This means the king or queen shares power with a parliament. On May 1, 1707, England and Scotland officially united to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. This happened under the Acts of Union 1707.
Images for kids
-
The lands ruled by Cnut the Great (1014–1035).
-
King John signs Magna Carta in 1215. This illustration is from Cassell's History of England, 1902.
-
A miniature from the 15th century showing the English winning the Battle of Agincourt against France.
-
A portrait of Elizabeth I. It was made to celebrate the defeat of the Spanish Armada in 1588, which you can see in the background. Her hand on the globe shows her international power.
-
Cromwell at Dunbar. Oliver Cromwell brought all of the British Isles under his control by force and created the Commonwealth of England.
See also
 In Spanish: Reino de Inglaterra para niños
In Spanish: Reino de Inglaterra para niños