Climate change facts for kids

Climate change means big, long-term shifts in the Earth's weather patterns. These changes can make some places warmer or colder. It includes both global warming, which is a rise in Earth's average temperature, and global cooling.
These changes happen over many years, from decades to millions of years. They can be caused by things happening inside the Earth, like Volcanic eruptions. They can also be caused by outside forces, like changes in how much sunlight reaches Earth. More recently, human activities have become a major cause of climate change. For example, Ice ages are a natural type of climate change that happened long ago.
Climate change is about unusual changes to the climate and how these changes affect our planet. For instance, the melting of ice caps at the South Pole and North Pole is a sign of climate change. These shifts can take a very long time to happen.
Some temperature changes are part of natural cycles, like El Niño–Southern Oscillation, which can last for years. Other changes come from an energy imbalance in Earth's climate system. This can be due to more greenhouse gases in the air, changes in the Sun's brightness, or how Earth orbits the Sun.
Today, when people talk about climate change, they usually mean the changes happening now, especially global warming. Many experts suggest we should try to keep Earth’s temperature from increasing by more than 2 degrees Celsius.
Contents
What Are the Effects of Climate Change?
Effects on Our Planet
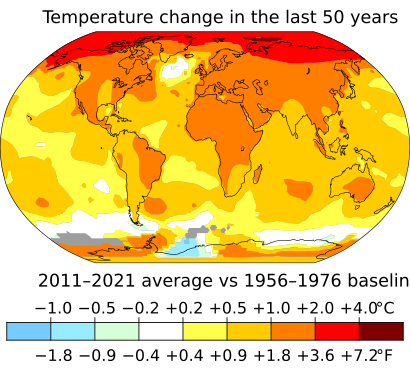
Climate change has wide-ranging effects on our planet. It impacts oceans, ice, and weather patterns. These changes can happen slowly or very quickly. We know about these effects by studying past climate changes, using computer models, and observing what's happening now.
Since the 1950s, we've seen more droughts and heat waves happening at the same time. Very wet or very dry periods during the monsoon season have also increased in places like India and East Asia.
Climate change has caused the Arctic sea ice to shrink and get thinner for decades.
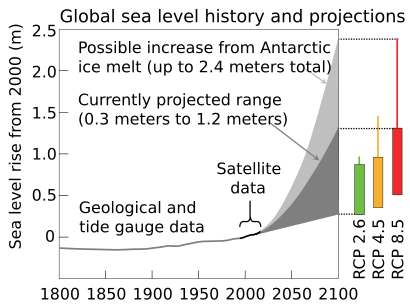
The global sea level is rising. This happens because glaciers and large ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica are melting. Also, warmer water takes up more space, which is called thermal expansion.
Between 1993 and 2017, the sea level rise sped up, going up about 3.1 millimeters each year.
More carbon dioxide (CO2) in the air has also changed ocean chemistry. This extra CO2 makes the ocean more acidic, a process called ocean acidification. This harms sea creatures like corals and shellfish. Also, oxygen levels in the ocean are dropping. This is because oxygen doesn't dissolve as well in warmer water. This leads to hypoxic dead zones where marine life struggles to survive.
Big Changes and Long-Term Impacts
The more the Earth warms, the higher the risk of reaching "tipping points." These are points where certain impacts can no longer be stopped, even if temperatures go down later.
For example, if temperatures rise too much, the West Antarctic and Greenland ice sheets could melt completely. This would cause huge sea level rises.
The long-term effects of climate change include even more ice melting, continued ocean warming, higher sea levels, and more ocean acidification.
Effects on Nature and Wildlife

Recent warming has caused many land and freshwater animals and plants to move. They are heading towards the colder poles or higher altitudes. More CO2 in the air and longer growing seasons have made some parts of the world greener. However, heatwaves and droughts have reduced plant growth in other areas.
Oceans have warmed more slowly than land. But ocean plants and animals have moved towards the colder poles just as fast, or even faster, than land species. Just like on land, heat waves in the ocean are happening more often due to climate change. These harm many organisms like corals, kelp, and seabirds.
Ocean acidification threatens coral reefs, fish populations, and other important natural resources. Harmful algae blooms, made worse by climate change, can cause oxygen shortages in the water. This disrupts food webs and leads to many marine animals dying. Coastal areas are especially at risk. Almost half of the world's wetlands have disappeared due to climate change and other human activities.
- Climate change impacts on the environment
-
Ecological collapse possibilities. Bleaching has damaged the Great Barrier Reef and threatens reefs worldwide.
-
Extreme weather. Drought and high temperatures worsened the 2020 bushfires in Australia.
-
Arctic warming. Permafrost thaws undermine infrastructure and release methane in a positive feedback loop.
-
Habitat destruction. Many arctic animals rely on sea ice, which has been disappearing in a warming Arctic.
-
Pest propagation. Mild winters allow more pine beetles to survive to kill large swaths of forest.
Effects on Humans

The effects of climate change on people are happening all over the world. They are mostly due to warming temperatures and changes in rainfall. The Arctic, Africa, small islands, and large river deltas in Asia are expected to be hit hardest.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that between 2030 and 2050, climate change could cause about 250,000 more deaths each year. These could be from poor nutrition, malaria, diarrhea, and heat stress.
The impacts on humans include direct effects from extreme weather, like injuries and loss of life. There are also indirect effects, such as undernutrition from crop failures.
Some infectious diseases spread more easily in warmer climates. These include dengue fever, which affects children most severely, and malaria. Young children are most at risk from food shortages. Both young children and older people are very vulnerable to extreme heat. The WHO says that climate change is the biggest threat to global health in the 21st century.
Climate change is affecting food security. It has caused a drop in the average global yields of corn, wheat, and soybeans between 1981 and 2010.
Areas that depend on water from glaciers, places that are already dry, and small islands are also at higher risk of water shortages due to climate change.
The economic damage from climate change could be very serious. The World Bank estimates that climate change could push over 120 million people into poverty by 2030.
Existing differences between people, like between men and women, rich and poor, or different ethnic groups, can get worse because of climate change.
Low-lying islands and coastal communities are threatened by rising sea levels. This can cause flooding and even permanent submergence. Up to 1 billion people could be displaced due to climate change by 2050. A common prediction is around 200 million people.
- Climate change impacts on people
-
Environmental migration. Less rainfall leads to desertification that harms farming and can make people move. Shown: Telly, Mali.
-
Tidal flooding. Sea-level rise increases flooding in low-lying coastal areas. Shown: Venice, Italy.
-
Storm intensification. Bangladesh after Cyclone Sidr is an example of huge flooding from more rain.
-
Heat wave intensification. Events like the June 2019 European heat wave are becoming more common.
Related Pages
- Deforestation
- Earth Hour
- Ecology
- Natural disaster
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Cambio climático para niños
In Spanish: Cambio climático para niños
 | John T. Biggers |
 | Thomas Blackshear |
 | Mark Bradford |
 | Beverly Buchanan |