Habitat destruction facts for kids
Habitat destruction happens when a natural home for plants and animals, called a habitat, can no longer support the living things that belong there. This means the animals and plants that once lived there have to move or they might not survive. This leads to fewer types of plants and animals, which is called a decrease in biodiversity. In fact, losing habitats is the main reason why many species are disappearing from our planet.
People cause habitat destruction in many ways. This includes using too many natural resources, farming, making products in factories, and building more cities. Other activities like digging for minerals (mining), cutting down trees (logging), and certain fishing methods (trawling) also harm habitats. Sometimes, natural events like climate change, new species moving in (invasive species), or different kinds of pollution can also damage habitats. When a large habitat is broken into smaller pieces, it's called habitat fragmentation. Both habitat loss and fragmentation are big problems for endangered species today.
Contents
Where Habitat Loss is Happening
Hotspots Around the World
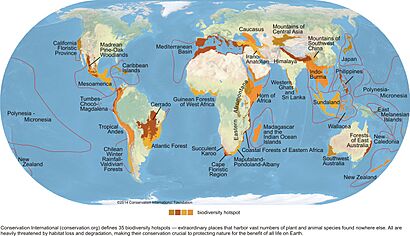
Some places on Earth are called biodiversity hotspots. These are special areas, often in warm, tropical regions, where many unique species live. More than half of all land animals might live in these hotspots! Sadly, these important places are losing their natural homes very quickly.
Many islands and places with lots of people have already lost most of their natural habitats. For example, islands like New Zealand, Madagascar, the Philippines, and Japan have seen a lot of habitat destruction. Countries in South and East Asia, like China, India, Malaysia, and Indonesia, also have huge populations, leaving little space for nature. Even ocean areas near big cities are suffering, with damage to coral reefs and other sea habitats.
Places where farming methods are not sustainable often have high rates of habitat destruction. This includes regions like South Asia, Central America, and the Amazonian tropical rainforest in South America. In these areas, forests are often cleared for farms or ranches.
In the U.S., less than a quarter of the original plant life remains in many eastern and midwestern areas. In Europe, only about 15% of the land is still untouched by human activities. This shows how much our world has changed.
Different Types of Habitats Affected
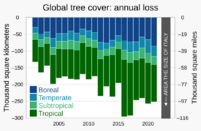
Tropical rainforests are often talked about when we discuss habitat loss. Originally, there were about 16 million square kilometers of rainforests. Today, less than 9 million square kilometers remain. Every year, about 160,000 square kilometers are lost, which is like losing 1% of these forests each year.
Other types of forests have also suffered greatly. For example, over 94% of temperate forests have been disturbed by farming and logging. Many very old forests have lost more than 98% of their original size. Dry forests are even easier to clear for farms and ranches. Because of this, very little of these dry forests remain in places like Central America and Madagascar.
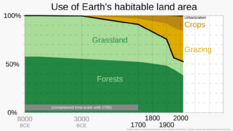
Plains and desert areas have also been affected, but perhaps a bit less. About 10-20% of the world's drylands, which include grasslands and scrublands, have been damaged. This includes about 9 million square kilometers of dry land that humans have turned into deserts through a process called desertification. In North America, less than 3% of the original tallgrass prairies are left; most have become farmland.
Wetlands and ocean areas have also faced a lot of destruction. In the U.S., over half of all wetlands have been destroyed in the last 200 years. Europe has lost 60-70% of its wetlands. In the UK, more homes and tourism along the coast have harmed marine habitats. Rising sea levels and temperatures have caused soil erosion and coastal flooding. About 20% of coastal areas in the ocean have been changed a lot by humans. Also, one-fifth of coral reefs have been destroyed, and another fifth are badly damaged by overfishing and pollution. For example, 90% of the Philippines' coral reefs are gone. More than 35% of mangrove ecosystems worldwide have also been destroyed.
Natural Ways Habitats Change
Sometimes, habitats are destroyed by natural events. Things like volcanoes erupting, fires, and changes in Earth's climate have always shaped habitats. For example, millions of years ago, when rainforests broke into smaller pieces, many amphibians disappeared. But at the same time, the drier climate helped new types of reptiles to appear.
Very powerful bursts of energy from space, called Gamma ray bursts, could also harm habitats by damaging the Earth's protective ozone layer.
How People Cause Habitat Loss
When people cause habitat destruction, it often involves changing land. This includes turning forests into farmland, expanding cities (called urban sprawl), and building roads or other structures. Even without completely destroying a habitat, human actions can damage it. This damage is called habitat degradation. Breaking habitats into smaller pieces is habitat fragmentation, and pollution also harms them. These actions can lead to a habitat collapsing.
Specific types of habitat destruction include desertification (when land turns into desert), deforestation (cutting down forests), and coral reef damage. All these actions reduce the number of different species on Earth.
Main Reasons Behind Human Actions
The reasons why people destroy habitats are called drivers. These drivers can be about how many people there are, how the economy works, how governments are set up, new technologies, and even culture.
One big driver is the growing human population. Most of this growth is happening in or near biodiversity hotspots, which are places with many different species. This means more people are living in areas where nature is most at risk. This growth makes it harder to protect these areas and can cause problems with local communities.
Studies have looked at why tropical forests are being cut down. The main reasons include economic factors (like making money from timber), government policies, new technologies, and cultural habits. For example, the demand for wood and other products drives a lot of forest clearing.
Turning Forests into Farms
Turning forests into farms is a major reason for tropical deforestation. Building new roads also plays a big part, as it opens up areas for more logging and farming.
The size of a habitat is directly linked to how many species can live there. Larger animals and those living in forests or oceans are more sensitive to losing their habitat. When diverse ecosystems are replaced by simple farms, many species lose their homes. Even basic farming changes the environment by clearing land, removing unwanted plants, and focusing on only a few types of crops and animals.
Sometimes, different causes of deforestation work together, making the problem worse. For instance, building new roads can lead to new towns and more people moving in. This increases the demand for wood and food, which then leads to more commercial farming and logging. These bigger operations often use machines that cause even more damage to habitats.
Climate Change and Habitats
Climate change is also destroying some habitats and putting many species in danger. For example:
- Rising sea levels, caused by climate change, threaten natural habitats and species around the world.
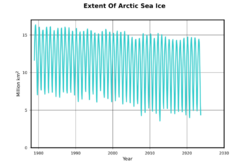
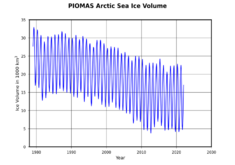
- Melting sea ice destroys the homes of some animals. The amount of sea ice in the Arctic has decreased by over 50% since satellites started recording it. A well-known example is the polar bear, whose Arctic habitat is shrinking.
- Warm-water coral reefs are very sensitive to global warming and changes in ocean chemistry. Coral reefs are home to thousands of species and protect coastlines. However, 70-90% of these reefs are expected to disappear even if global warming is limited. For example, Caribbean coral reefs, which are biodiversity hotspots, could be lost within this century if warming continues at the current rate.
Habitat Fragmentation
When a large habitat is broken into smaller, isolated pieces, it's called habitat fragmentation. This can happen when roads are built through a forest or when parts of a natural area are cleared for development. These smaller pieces of habitat can make it harder for animals to find food, mates, and safe places to live.
Impacts of Habitat Loss
On Animals and Plants
When a habitat is destroyed, it can no longer support the plants and animals that live there. This causes their numbers to drop, sometimes leading to extinction.
Habitat loss is one of the biggest threats to living things and biodiversity. For example, a study found that 82% of endangered bird species were greatly threatened by losing their homes. Many amphibian species are also at risk. Species that only live in one specific area are most affected because they have nowhere else to go.
Extinction can happen long after a habitat is destroyed, a process called extinction debt. Habitat destruction can also reduce the area where certain animal groups live. This can lead to less variety in their genes and make it harder for them to have healthy offspring. A famous example is the giant panda in China. It once lived in many areas but is now found only in small, separate regions due to widespread deforestation.
When habitats are destroyed, the types of species change. Animals and plants that can live in many different places (generalists) tend to survive, while those needing very specific conditions (specialists) often disappear. Invasive species are often generalists that can adapt to new habitats.
On People

Habitat destruction can make an area more likely to suffer from natural disasters like floods and droughts. It can also lead to crop failure, the spread of disease, and water contamination. On the other hand, a healthy ecosystem can help prevent these problems or make them less severe.
Farms can also suffer when the surrounding natural landscape is destroyed. Over the last 50 years, about 40% of farmland worldwide has been damaged by erosion, salt buildup, and pollution due to habitat destruction. People also lose out on enjoying nature, like birdwatching, hunting, fishing, and ecotourism, which depend on healthy habitats. Many people care deeply about the natural world and are concerned about losing habitats and species.
Perhaps the biggest impact of habitat destruction on people is the loss of valuable ecosystem services. These are the benefits we get from nature, like clean air and water. Habitat destruction has changed important natural cycles, leading to problems like acid rain and algal blooms. It has also greatly contributed to global climate change.
Trees, especially in tropical rainforests, help regulate our climate. They absorb carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, through photosynthesis. When forests are destroyed, Earth's ability to do this is reduced. Other services that are lost include managing water, producing oxygen, and pollination for crops.
Losing biodiversity means we lose species that play unique and important roles in ecosystems. This makes the environment less able to recover from big events like earthquakes or floods. We also lose potential new medicines from plants and new ways to protect our crops from pests and diseases.
The negative effects of habitat destruction often hit people in rural areas harder than those in cities. Poorer communities suffer the most because they rely more directly on natural resources. Wealthier people and countries can often pay to get resources from elsewhere.
What We Can Do
The world's population is growing quickly, which means we need more food. Agricultural output needs to increase significantly in the coming years. In the past, people could just move to new land for farming. However, most land suitable for farming is already in use or damaged.
This future food crisis could lead to even more habitat destruction. Farmers might feel pressured to produce more food from the same land, using more fertilizers and caring less about the environment. This could push species out of their homes. Protecting natural habitats will directly compete with the growing demand for resources, especially new farmland.
Solutions to habitat destruction are part of international goals like Sustainable Development Goal 15 ("Life on Land") and Sustainable Development Goal 14 ("Life Below Water"). However, a 2021 report found that many of these efforts have not met their goals.
To stop tropical deforestation, leaders need to understand the specific reasons why forests are being cut down in each country. There isn't one simple solution for every place.
For shoreline erosion, which is a natural process, we can use barriers like seawalls. However, "living shorelines" that use natural plants are becoming popular. These can reduce damage and erosion while also providing benefits like food and cleaner water.
Preventing specialist species from being replaced by generalist invasive species depends on how much habitat has already been destroyed. In areas that are still mostly natural, simply stopping further destruction might be enough. In areas with more extreme damage, like fragmented habitats, we might need to actively restore the environment.
Educating everyone about habitat destruction is very important. We need to change how people view environmental impacts and encourage more sustainable practices. Teaching about family planning can also help slow population growth, which reduces human-caused habitat destruction. Habitat restoration can involve making habitats larger or repairing damaged ones.
Creating and protecting habitat corridors can connect isolated groups of animals and plants, helping them to move and reproduce. These corridors also reduce the negative effects of habitat destruction.
The biggest way to solve habitat destruction is to address the larger problems that cause it. These include how much we consume, how we use resources, creating conservation areas, restoring damaged land, and dealing with climate change.
Government leaders need to focus on the main reasons behind habitat destruction, not just the immediate causes. They should:
- Remember the priceless ecosystem services that natural habitats provide.
- Protect the natural habitats that are still untouched.
- Find ways to grow more food without using more land.
- Work to reduce human population growth and expansion.
It is believed that we can fight habitat loss and fragmentation by including how species move and interact in our restoration plans. However, many current plans do not fully consider these important spatial effects.
See also
 In Spanish: Destrucción de hábitat para niños
In Spanish: Destrucción de hábitat para niños