Gulf Coast of the United States facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Gulf Coast
|
|
|---|---|
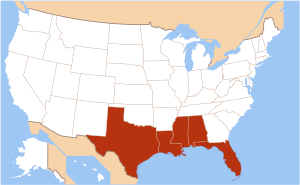
States that border the Gulf of Mexico are shown in red.
|
|
| Country | |
| States | |
| Principal cities | Houston Tampa Mobile New Orleans Pensacola Gulfport Tallahassee |
| Largest city | Houston |
| Largest metropolitan area | Greater Houston |
| Population | |
| • Total | 64,008,345 |
The Gulf Coast of the United States is the coastline where the southern states meet the Gulf of Mexico. It's also called the Gulf South or South Coast. The states that have a shoreline on the Gulf of Mexico are Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida. These are known as the Gulf States.
The economy of the Gulf Coast relies on many industries. These include energy, chemicals, fishing, aerospace, farming, and tourism. Some of the big cities in this region are Houston, Tampa, New Orleans, Mobile, and Pensacola. Many of these cities have large ports, which are important for trade.
Contents
Exploring the Gulf Coast's Geography

The Gulf Coast has many inlets, bays, and lagoons. Rivers flow into the coast, with the Mississippi River being the largest. Much of the land here is, or used to be, marshland. The Gulf Coastal Plain stretches from southern Texas to the western Florida Panhandle.
The western parts of the Gulf Coast have many barrier islands and peninsulas. One example is the 130-mile (209 km) long Padre Island in Texas. These landforms protect the bays and inlets from strong waves. The central Gulf Coast, from eastern Texas through Louisiana, is mostly marshland. The eastern part, mainly Florida, has many bays and inlets.
Understanding the Gulf Coast Climate
The Gulf Coast has a humid subtropical climate. However, Southwest Florida has a tropical climate. Most of the year is warm to hot. The winter months bring some cool or cold weather mixed with mild days.
This area often experiences hurricanes, floods, and strong thunderstorms. Many places along the Gulf Coast get the most rain in summer. July or August are often the wettest months. This is because of frequent summer thunderstorms and tropical weather systems like hurricanes. Winter and early spring can also have heavy rainfall.
Cities like Houston, New Orleans, Mobile, Alabama, and Pensacola, Florida show this rain pattern. But central and southern Florida, and South Texas, have dry winters. This is true for Tampa and Fort Myers. On the central and southern Texas coast, winter, early spring, and mid-summer are drier. September is usually the wettest month in Corpus Christi and Brownsville, Texas.
Tornadoes are rare right on the coast but happen more often inland. Extreme rainfall is a big threat from Houston eastward. Tropical storms can bring 4 to 10 inches (100 to 250 mm) or more of rain in one day. In August 2017, Hurricane Harvey hit the Texas coast. It then stayed over the Houston area for days. This caused huge, record-breaking rainfall of over 40 inches (1,000 mm) in many places, leading to widespread flooding. Scientists expect more hurricanes for Florida and the Texas coastline. Earthquakes are very rare here. But a 6.0 earthquake in the Gulf of Mexico in 2006 was felt from New Orleans to Tampa.
Rising Sea Levels and Their Impact
Due to greenhouse gas emissions, glaciers and ice sheets are melting. This causes the oceans to expand. U.S. coastlines are expected to rise about 1 foot (30 cm) in the next three decades. By 2050, the average rise will be between 10 and 12 inches (25 to 30 cm). The Gulf Coast will likely see the biggest change. Sea levels there are expected to rise between 14 and 18 inches (35 to 45 cm).
A report on sea level rise predicts more frequent and destructive high tide flooding. It also expects taller storm surges by 2050. Scientists found that high tide flooding has been "increasingly common" due to rising sea levels. The effects are expected to be serious. Low-lying coastal areas will face more flooding and faster erosion. They will also lose wetlands and land ecosystems. Saltwater will get into freshwater sources.
Rising sea levels and erosion will also harm important habitats. Many valuable fish depend on these inshore waters for living or for nurseries. In 2021, rising sea levels cost the United States about $2.6 billion in relief efforts. They also caused at least seven deaths. By 2051, the cost of flood damage is expected to go up by 61%, or $32 billion.
Economic Activities in the Gulf Coast Region
The Gulf Coast is a very important area for the economy. The marshlands along the Louisiana and Texas coasts are breeding grounds for ocean life. This supports the fishing and shrimping industries. The Port of South Louisiana and the Port of Houston are among the busiest ports in the world. In 2004, seven of the top ten busiest ports in the U.S. were on the Gulf Coast.
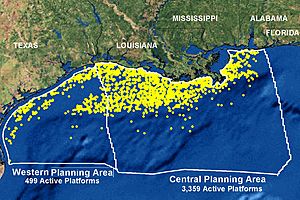
The discovery of oil and gas deposits here, both on land and offshore, has made the Gulf Coast a center for the U.S. petrochemical industry. There are nearly 4,000 oil platforms off the coast.
Besides these, the region has other key industries. These include aerospace and biomedical research. Older industries like agriculture are also important. Since the 1920s, tourism has grown a lot, especially as more people in the U.S. became wealthier.
A Look at Gulf Coast History
Before Europeans arrived, the Gulf Coast was home to several ancient kingdoms. These groups traded widely with empires like the Aztecs and the Mississippi Mound Builders. Shark teeth, alligator teeth, and shells from the Gulf have been found far north in Ohio.
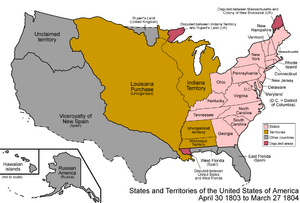
The first Europeans to settle the Gulf Coast were mainly the French and the Spanish. The Louisiana Purchase in 1803, the Adams–Onís Treaty in 1819, and the Texas Revolution (1835-1836) made the Gulf Coast part of the United States. This happened during the first half of the 19th century. As the U.S. population moved westward, the Gulf Coast became a key area in the South. It offered access to shipping routes and trade.
The growth of sugar and cotton production helped the South become wealthy. By the mid-19th century, New Orleans was a major city. It was important for trade on the Mississippi River and in the Gulf. It became the largest U.S. city not on the Atlantic seaboard. It was the fourth largest city in the U.S. overall.
Two big events changed the early history of the Gulf Coast. The first was the American Civil War. This war badly damaged some parts of the economy in the South, including the Gulf Coast. The second event was the Galveston Hurricane of 1900. At the end of the 19th century, Galveston was one of the most developed cities in the region, along with New Orleans. Galveston had the third busiest port in the U.S. Its financial area was known as the "Wall Street of the South."
Since then, many other hurricanes have hit the Gulf Coast. On August 29, 2005, Hurricane Katrina struck the Gulf Coast as a Category 3 hurricane. It was the most damaging storm in U.S. history. It caused over $80 billion in damages and led to over 1,800 deaths. In 2008, Hurricane Ike hit the Gulf Coast. Because it was so large, Ike caused damage from the Louisiana coast to the Texas region near Corpus Christi. Ike also caused flooding and damage along the Mississippi coast and the Florida Panhandle. Ike killed 112 people and left over 300 missing. Hurricane Ike was the third most damaging storm in U.S. history. It caused over $25 billion in damage. Hundreds of thousands of people lost their homes. It also led to the largest search-and-rescue operation in U.S. history.
Despite the hurricanes, the Gulf Coast has developed a lot during the 20th century. It is now highly populated. The petrochemical industry grew with the discovery of oil in Texas and the Gulf waters. This led to much development in the central and western Gulf regions. Texas has greatly benefited from this industry. Its economy has become diverse. This has made Texas a popular place to live. It is home to more Fortune 500 companies than any other U.S. state. Florida has also grown. This is largely due to its long-standing tourism industry. It is also a gateway to the Caribbean and Latin America. As of 2024, Texas and Florida are the second and third most populated states in the nation. Other Gulf Coast areas have grown less. However, tourism has increased property values along the coast. This now poses a serious threat to the valuable but fragile ecosystems of the Gulf Coast.
Major Cities and Metro Areas of the Gulf Coast
The table below lists the 11 largest metropolitan areas along the Gulf Coast. These are important centers for living and working.
| Rank | Metropolitan statistical area | 2020 pop. (est.) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Houston-The Woodlands, TX Combined Statistical Area | 7,340,823 |
| 2 | Tampa-St. Petersburg-Clearwater, FL Metropolitan Statistical Area | 3,243,963 |
| 3 | New Orleans-Metairie-Hammond, LA-MS Combined Statistical Area | 1,510,672 |
| 4 | Cape Coral-Fort Myers-Naples, FL Combined Statistical Area | 1,226,553 |
| 5 | North Port-Sarasota, FL Combined Statistical Area | 1,087,915 |
| 6 | McAllen-Edinburg, TX Combined Statistical Area | 939,466 |
| 7 | Baton Rouge, LA Metropolitan Statistical Area | 858,571 |
| 8 | Mobile-Daphne-Fairhope, AL Combined Statistical Area | 661,964 |
| 9 | Lafayette-Opelousas-Morgan City, LA Combined Statistical Area | 619,529 |
| 10 | Pensacola-Ferry Pass, FL-AL Combined Statistical Area | 547,784 |
| 11 | Corpus Christi-Kingsville-Alice, TX Combined Statistical Area | 536,258 |
Transportation in the Gulf Coast
The Gulf Coast has a strong transportation network. This includes major roads, airports, and train services.
Key Roadways: Interstates and U.S. Routes
Major Interstate Highways
| Highway | Significant cities served |
|---|---|
| Harlingen, McAllen | |
| Tampa | |
| Houston, Beaumont, Lake Charles, New Orleans, Gulfport, Mobile, Pensacola | |
| Baton Rouge, Slidell | |
| Corpus Christi | |
| Galveston, Houston | |
| Lafayette, New Orleans (future) | |
| Hammond | |
| Slidell | |
| Mobile | |
| Houston | |
| Brownsville, Harlingen, Corpus Christi | |
| Naples, Fort Myers, Sarasota, Tampa |
Major U.S. Routes
| Highway | Significant cities served |
|---|---|
| New Orleans | |
| Punta Gorda | |
| St. Petersburg, Tampa | |
| Pensacola | |
| Spanish Fort | |
| Naples, Fort Myers, Sarasota, Tampa | |
| Mobile | |
| Mobile | |
| Biloxi, Gulfport | |
| Hammond | |
| Houston | |
| New Orleans | |
| Beaumont, Port Arthur | |
| Brownsville, Corpus Christi, Harlingen | |
| Brownsville, Harlingen | |
| Port Lavaca, Victoria | |
| Beaumont, Biloxi, Houston, Lafayette, Lake Charles, Mobile, New Orleans, Pensacola | |
| St. Petersburg, Tampa | |
| Beaumont, Port Arthur | |
| Fort Walton Beach, Mobile, Pensacola, Panama City |
Other Important Routes
| Highway | Significant cities served |
|---|---|
| Grand Isle, Port Fourchon | |
| Crestview, Fort Walton Beach | |
| Houston, Bay City, Corpus Christi | |
| Houston, Lake Jackson |
Air Travel: International Airports
Many airports along the Gulf Coast offer flights to other countries. This connects the region to the rest of the world.
International Destinations from Gulf Coast Airports
| George Bush Intercontinental Airport - Houston | |
| Louis Armstrong New Orleans International Airport | |
| Southwest Florida International Airport | |
| Tampa International Airport | |
| William P. Hobby Airport - Houston |
Rail Travel: Amtrak Services
Amtrak provides passenger train service to many cities along the Gulf Coast.
Amtrak Train Routes and Stops
| Train | Route | Gulf Coast cities served |
|---|---|---|
| City of New Orleans | Chicago to New Orleans | New Orleans |
| Crescent | New York City to New Orleans | New Orleans, Picayune, MS, Slidell, LA |
| Silver Star | New York City to Miami | Tampa, with connection available to Amtrak Thruway to Clearwater, FL, Bradenton, FL, Sarasota, FL, Port Charlotte, FL and Fort Myers, FL |
| Sunset Limited | Los Angeles to Orlando (temporarily New Orleans) | Bay St. Louis, MS, Beaumont, TX, Biloxi, Crestview, FL, Gulfport, MS, Houston, Lafayette, LA, Lake Charles, LA, Baton Rouge, LA, Mobile, New Orleans, Panama City, FL, Scriever, LA, Pascagoula, MS, Pensacola, FL |
See also
 In Spanish: Costa del golfo de Estados Unidos para niños
In Spanish: Costa del golfo de Estados Unidos para niños