American Civil War facts for kids
The American Civil War (1861–1865) was a civil war in the United States. It is also known as "The War Between the States." This war happened because eleven Southern states wanted to leave the United States. They formed their own country called the Confederate States of America, or "the Confederacy." The U.S. government and the states that stayed loyal to it were called "the Union."
One main reason for the war was slavery. Slavery was very common in the Southern states, including all 11 that joined the Confederacy. It was against the law in most Northern states. The Confederate states tried to leave the Union after Abraham Lincoln was elected President. Lincoln did not like slavery. The Union believed that states could not legally leave the country. Five states where slavery was legal stayed with the Union. These were called the "border states." At first, the Union did not plan to end slavery. But by 1862, ending slavery became one of their main goals.
The war began on April 12, 1861. Confederate soldiers attacked Fort Sumter in South Carolina. This fort was held by Union soldiers. The war lasted four years. It caused a lot of damage, especially in the South. The Union won the war. After the Union victory, slavery was made illegal everywhere in the United States.
Contents
Why the Civil War Started
When the United States was founded in 1776, most states allowed slavery. But over the next 84 years, the Northern states decided slavery was wrong. They made it illegal. The Southern states kept slavery legal. Plantation owners in the South grew cotton. They made a lot of money using slaves from Africa to harvest the cotton.
The United States became divided into slave and free states. By 1860, these states were very angry with each other. They argued about whether slavery should be allowed in new lands to the west. In the late 1850s, there was fighting in Kansas. This was between people who wanted slavery and those who wanted it banned.
Abraham Lincoln was from the Republican Party. He won the 1860 presidential election. Lincoln did not want to ban slavery right away. He thought it would hurt the South. But Lincoln and his party disliked slavery. They did not want it to spread to new areas in the west.
Lincoln became president on March 4, 1861. After his election, seven Southern states said they were leaving the Union. The president before Lincoln, James Buchanan, said this was against the law. But he did nothing to stop them. Lincoln and his party saw this secession as a rebellion. No other country ever said the Confederacy was a separate nation. This was because the Union worked hard to stop it. Also, many countries in Europe were against slavery. The Union also used its navy to stop ships from going into or out of Southern ports.
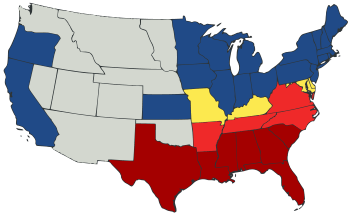
The first seven states to join the Confederacy were South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas. Four more states joined after the fighting began: Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina. The Confederacy also claimed Kentucky and Missouri. But these states never officially joined. Kentucky, Missouri, and Maryland were slave states that tried to stay neutral. Delaware was a slave state that supported the Union. Also, the western parts of Virginia stayed with the Union. They formed a new state called West Virginia.
How the Fighting Started
Fighting began when the Confederates attacked Fort Sumter. This was a Union Army fort. The Confederate States said they owned all federal buildings in the South. Fort Sumter was in South Carolina, a Confederate state. But the Union still controlled it. On April 12, 1861, Confederate forces attacked the fort. They forced the Union soldiers inside to surrender. After this, President Lincoln asked every Union state for volunteers. He wanted them to join the Union Army. Quickly, four more Southern slave states joined the Confederates. They refused to send soldiers to fight against them.
The War Itself
The American Civil War was fought in three main land areas, called "theaters:"
- The Eastern theater was all the land east of the Appalachian Mountains.
- The Western theater was all the land between the Appalachian Mountains and the Mississippi River. It also included the river itself.
- The Trans-Mississippi theater was the land west of the Mississippi river.
Both the Union and the Confederacy had their capital cities in the Eastern theater. Washington, D.C. was the U.S. capital. The South first named Montgomery, Alabama, as its capital. But soon it changed to Richmond, Virginia. Richmond and Washington are only about 90 miles (145 km) apart. One of the first battles was the First Battle of Bull Run in Virginia. It happened on July 21, 1861. The Confederates won this battle. The Union Army of the Potomac then tried to capture Richmond in the Peninsula Campaign in 1862. During this time, Robert E. Lee took command of the Army of Northern Virginia. He defeated the Union army. Lee then won the Second Battle of Bull Run in August 1862. Lee tried to win the war by invading Maryland. But he lost the Battle of Antietam. He then went back to Virginia.
There was a lot of naval warfare in the Civil War. But the Union navy was much stronger. Lincoln created a blockade. This meant the United States Navy would not let any ships into or out of Southern ports. The blockade stopped the Confederacy from selling its cotton. It also made it hard for them to buy weapons and supplies. The Confederates used ships called blockade runners. These ships brought things from Europe, including weapons. Both sides' navies also fought on the rivers. They used special ships like ironclads, which had iron on their sides. They also used cottonclads, which used cotton for protection. At the Battle of Hampton Roads, the Confederate ironclad Virginia fought the Union ironclad Monitor. This was the first time two ironclads fought each other.

In the Western theater, much fighting happened along the Mississippi River. Ulysses S. Grant was an important Union general there. The Confederates tried to send soldiers into Kentucky in 1861. In early 1862, the Union army made the Confederates retreat from Kentucky and western Tennessee. The Confederates tried to take back western Tennessee. They attacked Grant's army at the Battle of Shiloh. Grant won the battle. The Confederates then tried to send soldiers into eastern Kentucky in 1862. They left Kentucky after losing the Battle of Perryville.
The North gained control of almost all of the Mississippi River. They did this by capturing cities along the river in late 1862 and early 1863. But the Confederacy still held Vicksburg. This was an important city and fort. If they held Vicksburg, Confederates could move soldiers and supplies across the river. Grant started the Siege of Vicksburg in May 1863. The siege lasted a long time. On July 4, 1863, the Confederates in Vicksburg surrendered to Grant. This was a major turning point in the war. It split the Confederacy into two parts.
Battles also happened west of the Mississippi River, in the Trans-Mississippi theater. Examples include the Battle of Wilson's Creek and the Battle of Pea Ridge. The Confederates tried to invade New Mexico in early 1862. But they were defeated at the Battle of Glorieta Pass. After the Union captured Vicksburg, this area was cut off from the rest of the Confederate states. Other battles happened there after Vicksburg fell.
While the siege of Vicksburg was happening in the west, another turning point came in the east. After winning some battles, Lee decided to invade the North again. Lee and his Army of Northern Virginia went into Pennsylvania. The Confederate Army met the Union Army near Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. They fought the Battle of Gettysburg. This battle lasted three days: July 1 to 3, 1863. More soldiers died at Gettysburg than in any other Civil War battle. The Union won the battle. This stopped the Confederate Army's invasion of the North. Lee and his troops were pushed back into the South.
After this, President Lincoln decided Grant was his best general. He put Grant in charge of all Union armies. Lincoln also made William T. Sherman the general in charge of Union troops in Georgia. Grant led many attacks on Lee's army. These battles were part of the Overland Campaign. Meanwhile, Sherman burned Atlanta and Savannah. He did this to weaken the South. It made it harder for Southern people to supply the Confederate Army. Sherman then marched north through South Carolina and North Carolina. Confederate general Joseph E. Johnston attacked Sherman at the Battle of Bentonville. Sherman won the battle.
Lee held out as long as he could in Virginia. But he eventually had too few soldiers to keep fighting the Union. The Union had more soldiers and supplies. Lee surrendered to Grant on April 9, 1865. This happened near Appomattox Court House. After Lee surrendered, many other Confederate armies also surrendered. The last Confederate general to surrender was Brigadier General Stand Watie. He surrendered on June 23, 1865, in Oklahoma.
After the war, President Lincoln pardoned all Confederate soldiers. This meant they would not be arrested or punished for fighting. The Southern states were allowed to rejoin the United States. However, some Confederates did not want to return. Some of them moved to Mexico or Brazil.
Money Problems During the War
During the war, prices went up a lot. This is called inflation. It was a problem for the Union. It was an even bigger problem for the Confederacy. Their government paid for the war by printing a huge amount of paper money. Because there was so much money, it lost its value. Everything became more expensive. Many people could not afford food and went hungry. This was one reason the Confederacy eventually surrendered.
After the War: Reconstruction
Many soldiers on both sides died during the war. Most of the fighting happened in the South. Many railroads, farms, houses, and other places were destroyed. Most people in the South became very poor.
The time after the war was called Reconstruction. It lasted from the end of the war until 1877. The Union Army stayed in some Southern states. This meant those areas were under military control. Three important changes were added to the United States Constitution. These changes were suggested by the U.S. government. Not every American supported them, but they got enough support to pass:
- The 13th Amendment said that slavery is not allowed anywhere in the United States. This finished what the Emancipation Proclamation started.
- The 14th Amendment made it clear that all people born in the United States were citizens. They had equal rights.
- The 15th Amendment said that people in the United States could not be stopped from voting because of their race.
After the war, some Union Army leaders went into politics. Generals Grant, Hayes, Garfield, Harrison, and McKinley became presidents. Other veterans were elected to other government jobs.
The Amnesty Act of 1872 gave back the rights to vote and hold political office to most former members of the Confederacy. Some of them also became politicians.
Key Battles of the Civil War

- First Battle of Bull Run
- Second Battle of Bull Run
- Battle of Gettysburg
- Siege of Petersburg
- Battle of Atlanta
- Battle of Antietam
- Battle of Chancellorsville
- Battle of Fort Henry
- Battle of Fort Hindman
- Battle of Fort Sumter
- Battle of Fredericksburg
- Battle of Nashville
- Battle of Pea Ridge
- Battle of Perryville
- Battle of Seven Pines
- Battle of Shiloh
- Battle of Vicksburg
Interesting Facts About the War
- About one-third of the Union army were immigrants.
- People who were drafted could pay someone $300 to fight for them.
- Most of the nearly three million soldiers in the Civil War were volunteers.
- Some people pulled out their front teeth. Soldiers needed front teeth to open gunpowder pouches.
- The oldest soldier was an 80-year-old from Iowa. The youngest was an 11-year-old from Mississippi.
- Black soldiers were paid less than white soldiers. They went on a strike for 18 months. With help from abolitionists, they got equal pay in 1864. This pay was given for all the time they had served.
- Both a Union General and the Confederate President were named Jefferson Davis.
- Abraham Lincoln thought about colonization. He wanted freed black people to be moved to Central America.
- Harriet Tubman helped lead a raid along the Combahee River. She used the chaos to free over 720 slaves.
- A glowing bacterium (P. luminescens) was seen by soldiers. It makes a natural antibiotic. Soldiers with glowing wounds healed faster.
- Generals were more likely to die in battle than regular soldiers. This is because they led their soldiers into the fighting.
- Generals Thomas Leonidas Crittenden and George Crittenden were brothers. They fought on opposite sides of the war.
- Robert E. Lee’s home, called Arlington, was taken because he didn't pay taxes. It later became the famous Arlington National Cemetery.
- Two percent of all Americans died during the Civil War. Two-thirds of those deaths were from disease.
- Every student from the University of Mississippi who joined the Confederate Army died during the war.
- General Ambrose Burnside inspired the term “sideburns.”
- After the war, inflation made Confederate money almost worthless. It took 1200 Confederate dollars to buy one U.S. dollar.
- W.V. Meadows was shot in the eye during the Battle of Vicksburg. He survived and coughed the bullet out of his mouth 58 years later.
Related Pages
- Causes of the American Civil War
- African Americans in the American Civil War
- Confederate States of America
- Abraham Lincoln
- Jefferson Davis
- Robert E. Lee
- United States Constitution
- 13th Amendment
- 14th Amendment
- Reconstruction
Images for kids
-
Uncle Tom's Cabin by Harriet Beecher Stowe, a book that helped people understand how bad slavery was.
-
Frederick Douglass, a former slave, was a leading person who wanted to end slavery.
-
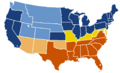
Map of the Union vs. the Confederacy.
-
Rioters attacking a building during the New York anti-draft riots of 1863.
-
River battles involved ironclads, cottonclads, and gunboats.
-
Battle between the USS Monitor and Merrimack.
-
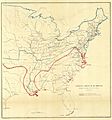
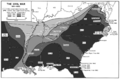
General Scott's "Anaconda Plan" from 1861. It showed how the Union would block ports and control the Mississippi River.
-
A cartoon from 1861 making fun of American actions in the Trent Affair.
-
"Stonewall" Jackson got his nickname at Bull Run.
-
The Battle of Antietam, the Civil War's deadliest one-day fight.
-
Pickett's Charge at Gettysburg.
-
Albert Sidney Johnston died at Shiloh.
-
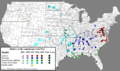
By 1863, the Union controlled much of the Western Theater, especially around the Mississippi River.
-
The Battle of Chickamauga, which had the highest losses over two days.
-
Nathaniel Lyon helped the Union control St. Louis and push Confederate forces out of Missouri.
See also
 In Spanish: Guerra de Secesión para niños
In Spanish: Guerra de Secesión para niños
 | Misty Copeland |
 | Raven Wilkinson |
 | Debra Austin |
 | Aesha Ash |