Savannah, Georgia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Savannah
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Downtown Savannah viewed from Bay Street
River Street
Forsyth Park
The Gingerbread House in Victorian Historic District
|
|||||
|
|||||
| Nickname(s):
"The Hostess City of the South"
|
|||||
| Country | United States | ||||
| State | Georgia | ||||
| County | Chatham | ||||
| Established | February 12, 1733 | ||||
| Founded by | James Oglethorpe | ||||
| Named for | Savannah River | ||||
| Area | |||||
| • City | 113.27 sq mi (293.36 km2) | ||||
| • Land | 108.50 sq mi (281.01 km2) | ||||
| • Water | 4.77 sq mi (12.35 km2) | ||||
| Elevation | 20 ft (6 m) | ||||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||||
| • City | 147,780 |
||||
| • Rank | 185th in the United States 5th in Georgia |
||||
| • Density | 1,300/sq mi (500/km2) | ||||
| • Urban | 309,466 (US: 132nd) | ||||
| • Urban density | 1,503.4/sq mi (580.5/km2) | ||||
| • Metro | 404,798 (US: 135th) | ||||
| Demonym(s) | Savannahian | ||||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) | ||||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | ||||
| ZIP Codes |
31401–31412, 31414-31416, 31418-31421
|
||||
| Area code(s) | 912 | ||||
| FIPS code | 13-69000 | ||||
| GNIS feature ID | 0322590 | ||||
Savannah is the oldest city in the U.S. state of Georgia. It is also the main city of Chatham County. The city was started in 1733 along the Savannah River.
Savannah became the capital of the Province of Georgia when it was a British colony. Later, it was the first state capital of Georgia. Savannah was an important port city during the American Revolution and the American Civil War. Today, it is a busy industrial center and a major seaport on the Atlantic Ocean.
Savannah is Georgia's fifth-largest city. In 2020, about 147,780 people lived there. The larger Savannah metropolitan area had a population of 404,798 in 2020. This makes it Georgia's third-largest metropolitan area.
Millions of people visit Savannah every year. They come to see its unique cobblestone streets, beautiful parks, and famous historic buildings. Some of these places include:
- The birthplace of Juliette Gordon Low, who started the Girl Scouts of the USA.
- The Georgia Historical Society, the oldest historical society in the South.
- The Telfair Academy of Arts and Sciences, one of the first public museums in the South.
- The First African Baptist Church, one of the oldest African-American Baptist churches in the U.S.
- Temple Mickve Israel, the third-oldest synagogue in the U.S.
- The Central of Georgia Railway roundhouse complex, the oldest standing rail facility from before the Civil War. It is now a museum.
Savannah's downtown area is a National Historic Landmark District. This means it is a very important historical place. It includes the Savannah Historic District and its 22 park-like squares. The Savannah Victorian Historic District is also part of it. This area still looks much like the original town plan designed by its founder, James Oglethorpe. This design is called the Oglethorpe Plan.
During the 1996 Summer Olympics in Atlanta, Savannah hosted the sailing competitions. These took place in the nearby Wassaw Sound.
Contents
History of Savannah
Founding the Colony and City

On February 12, 1733, General James Oglethorpe and settlers arrived on the ship Anne. They landed at Yamacraw Bluff. Tomochichi, the leader of the Yamacraw people, and Indian traders John and Mary Musgrove welcomed them. Mary Musgrove often helped by translating between the groups.
On this day, the city of Savannah and the colony of Georgia were officially started. In 1751, Savannah became the capital of Georgia, which was then a Royal Colony. This meant it was directly controlled by the British king.
Savannah During Wars
By the time the American Revolutionary War began, Savannah was the most southern trading port in the Thirteen Colonies. British soldiers took control of the city in 1778. The next year, American and French soldiers, including some from Haiti, tried to take the city back. But they failed during the Siege of Savannah. The British finally left Savannah in July 1782. In December 1804, the state government decided to move the capital to Milledgeville.
Savannah was a busy seaport throughout the 1800s. During the American Civil War, it was one of the largest cities in the Confederate States of America. It was a main target for General William T. Sherman during his famous Sherman's March to the Sea. On December 21, 1864, local leaders agreed to surrender peacefully. This saved Savannah from being destroyed, and Union troops entered the city.
How Savannah Got Its Name
Savannah was named after the Savannah River. The river's name likely comes from different names for the Shawnee people. They were a Native American group who moved to the river area in the 1680s. The Shawnee were known by names like Shawano, Savano, Savana, and Savannah.
Another idea is that the name Savannah refers to the large marshlands around the river. It might come from the English word "savanna," which means a type of grassland. This word came from the Spanish word sabana, which came from the Taino word zabana. Other ideas suggest the name comes from Algonquian words meaning "southerners" or even "salt."
Geography and Climate
Where Savannah is Located
Savannah is located on the Savannah River. It is about 20 miles (32 km) upriver from the Atlantic Ocean. The city covers about 108.7 square miles (281.5 km2). Most of this is land, with some water.
Savannah is the main port on the Savannah River. It is also the largest port in Georgia. The city is close to the Intracoastal Waterway, a route for boats along the coast. The Ogeechee River flows south of downtown Savannah. It forms the city's southern border.
Savannah can sometimes experience flooding. This is because it gets a lot of rain and is only a little bit above sea level. The shape of the coastline also makes it more likely to flood during hurricanes. To help with flooding, the city uses five canals and several pumping stations.
Savannah's Weather Patterns
Savannah has a humid subtropical climate. This means it has long, warm, and often tropical summers. Winters are short and mild. The city usually has only a few days of freezing temperatures each year. Snowfall is very rare.
Because it is close to the Atlantic coast, Savannah does not usually get extremely hot or cold temperatures like areas further inland in Georgia. However, the highest temperature ever recorded was 105°F (41°C) in July. The lowest was 3°F (−16°C) in January.
Summers in Savannah are hot and humid. They often have quick thunderstorms because of the warm, tropical air. Even though summers are often sunny, half of Savannah's yearly rain falls from June to September.
Winters are mild and sunny. The average high temperature in January is about 61.4°F (16.3°C). November and December are usually the driest months. Savannah typically has about 21 days a year when temperatures drop below freezing.
Hurricanes and Weather Records
Savannah is at risk for hurricanes, especially during the peak of hurricane season. However, its location in the Georgia Bight (the curved coastline) means it has a lower risk than some other coastal cities.
In the 20th century, Savannah was not often hit by hurricanes. Hurricane David in 1979 was one exception. But historical records show that many storms affected the city in the late 1800s. The 1893 Sea Islands hurricane was one of the worst, causing many deaths.
More recently, Hurricane Matthew in 2016 and Hurricane Irma in 2017 affected Savannah. In 2024, Hurricane Debby and Hurricane Helene also impacted the area.
| Climate data for Savannah, Georgia (Savannah/Hilton Head Int'l), 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1871–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 84 (29) |
87 (31) |
94 (34) |
95 (35) |
102 (39) |
104 (40) |
105 (41) |
104 (40) |
102 (39) |
97 (36) |
89 (32) |
83 (28) |
105 (41) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 77.5 (25.3) |
80.9 (27.2) |
84.9 (29.4) |
89.1 (31.7) |
94.0 (34.4) |
97.5 (36.4) |
98.8 (37.1) |
97.6 (36.4) |
94.0 (34.4) |
88.6 (31.4) |
83.3 (28.5) |
78.2 (25.7) |
99.7 (37.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 61.4 (16.3) |
65.1 (18.4) |
71.4 (21.9) |
78.2 (25.7) |
84.7 (29.3) |
89.6 (32.0) |
92.3 (33.5) |
90.8 (32.7) |
86.4 (30.2) |
79.0 (26.1) |
70.2 (21.2) |
63.7 (17.6) |
77.7 (25.4) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 50.7 (10.4) |
54.0 (12.2) |
60.0 (15.6) |
66.7 (19.3) |
74.1 (23.4) |
80.1 (26.7) |
83.0 (28.3) |
82.1 (27.8) |
77.7 (25.4) |
68.8 (20.4) |
59.1 (15.1) |
53.2 (11.8) |
67.5 (19.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 40.0 (4.4) |
42.9 (6.1) |
48.6 (9.2) |
55.2 (12.9) |
63.4 (17.4) |
70.7 (21.5) |
73.7 (23.2) |
73.3 (22.9) |
69.0 (20.6) |
58.6 (14.8) |
48.0 (8.9) |
42.6 (5.9) |
57.2 (14.0) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 23.3 (−4.8) |
26.5 (−3.1) |
31.2 (−0.4) |
39.4 (4.1) |
49.8 (9.9) |
62.7 (17.1) |
68.6 (20.3) |
67.2 (19.6) |
57.1 (13.9) |
42.1 (5.6) |
31.4 (−0.3) |
26.9 (−2.8) |
21.6 (−5.8) |
| Record low °F (°C) | 3 (−16) |
8 (−13) |
20 (−7) |
28 (−2) |
39 (4) |
49 (9) |
61 (16) |
57 (14) |
43 (6) |
28 (−2) |
15 (−9) |
9 (−13) |
3 (−16) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.28 (83) |
2.80 (71) |
3.50 (89) |
3.39 (86) |
3.62 (92) |
6.65 (169) |
5.75 (146) |
5.46 (139) |
4.35 (110) |
3.72 (94) |
2.39 (61) |
3.21 (82) |
48.12 (1,222) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 8.5 | 7.8 | 7.9 | 6.7 | 7.3 | 12.3 | 12.4 | 12.8 | 9.9 | 6.8 | 6.8 | 8.4 | 107.6 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 69.6 | 67.0 | 66.8 | 65.4 | 70.1 | 73.6 | 76.0 | 78.6 | 77.7 | 72.9 | 72.3 | 70.8 | 71.7 |
| Average dew point °F (°C) | 37.0 (2.8) |
38.8 (3.8) |
45.7 (7.6) |
51.6 (10.9) |
60.8 (16.0) |
67.8 (19.9) |
71.2 (21.8) |
71.6 (22.0) |
67.5 (19.7) |
56.5 (13.6) |
48.0 (8.9) |
40.5 (4.7) |
54.8 (12.6) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 175.5 | 181.0 | 232.0 | 275.6 | 288.9 | 276.0 | 271.3 | 245.8 | 214.3 | 228.6 | 193.5 | 174.2 | 2,756.7 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 55 | 59 | 62 | 71 | 67 | 65 | 62 | 60 | 58 | 65 | 61 | 56 | 62 |
| Source: NOAA (relative humidity, dew point and sun 1961–1990) | |||||||||||||
The first weather observations in Savannah likely started around 1827. Since 1948, the Savannah-Hilton Head International Airport has been the official weather station.
Cityscape and Neighborhoods
Exploring Savannah's Neighborhoods
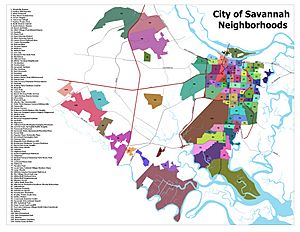
Savannah has many different neighborhoods. There are over 100 distinct areas. These are grouped into six main parts of the city. They include Downtown, Midtown, Southside, Eastside, Westside, and Southwest/West Chatham.
Historic Districts to Visit
Besides the large Savannah Historic District, there are five other official historic districts. These areas are special because they have many old and important buildings.
- Savannah Victorian Historic District
- Cuyler–Brownsville District
- Thomas Square Historic District
- Pin Point Historic District
- Ardsley Park–Chatham Crescent Historic District
People and Culture
Population and Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1800 | 5,146 | — | |
| 1810 | 5,215 | 1.3% | |
| 1820 | 7,523 | 44.3% | |
| 1830 | 7,303 | −2.9% | |
| 1840 | 11,214 | 53.6% | |
| 1850 | 15,312 | 36.5% | |
| 1860 | 22,292 | 45.6% | |
| 1870 | 28,235 | 26.7% | |
| 1880 | 30,709 | 8.8% | |
| 1890 | 43,189 | 40.6% | |
| 1900 | 54,244 | 25.6% | |
| 1910 | 65,064 | 19.9% | |
| 1920 | 83,252 | 28.0% | |
| 1930 | 85,024 | 2.1% | |
| 1940 | 95,996 | 12.9% | |
| 1950 | 119,638 | 24.6% | |
| 1960 | 149,245 | 24.7% | |
| 1970 | 118,349 | −20.7% | |
| 1980 | 141,654 | 19.7% | |
| 1990 | 137,560 | −2.9% | |
| 2000 | 131,510 | −4.4% | |
| 2010 | 136,286 | 3.6% | |
| 2020 | 147,780 | 8.4% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 147,748 | 8.4% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1850-1870 1870-1880 1890-1910 1920-1930 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020 2023 |
|||
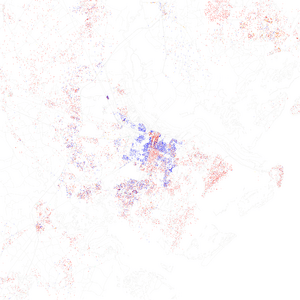
In 2020, Savannah's population was 147,780 people. This was an increase from 136,286 residents in 2010. The wider Savannah Metropolitan Statistical Area had 404,798 people in 2020. This area includes Bryan, Chatham, and Effingham counties.
The racial and ethnic makeup of Savannah has changed over time. In 2020, about 48.62% of the population was Black or African American. About 36.60% were non-Hispanic white. Other groups included Asian (3.80%), Native American (0.21%), and Pacific Islander (0.16%). About 6.62% of the population was Hispanic or Latino.
| Race / Ethnicity (NH = Non-Hispanic) | Pop 2000 | Pop 2010 | Pop 2020 | % 2000 | % 2010 | % 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White alone (NH) | 49,903 | 49,381 | 54,082 | 37.95% | 36.23% | 36.60% |
| Black or African American alone (NH) | 74,691 | 74,782 | 71,845 | 56.79% | 54.87% | 48.62% |
| Native American or Alaska Native alone (NH) | 277 | 315 | 311 | 0.21% | 0.23% | 0.21% |
| Asian alone (NH) | 1,984 | 2,697 | 5,610 | 1.51% | 1.98% | 3.80% |
| Pacific Islander alone (NH) | 78 | 130 | 238 | 0.06% | 0.10% | 0.16% |
| Some Other Race alone (NH) | 188 | 242 | 692 | 0.14% | 0.18% | 0.47% |
| Mixed Race or Multi-Racial (NH) | 1,451 | 2,347 | 5,213 | 1.10% | 1.72% | 3.53% |
| Hispanic or Latino (any race) | 2,938 | 6,392 | 9,789 | 2.23% | 4.69% | 6.62% |
| Total | 131,510 | 136,286 | 147,780 | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
Religious Diversity in Savannah
Before British settlers arrived, Native Americans in the coastal region had their own spiritual beliefs. Since then, Savannah has mostly been a Christian city. However, a Jewish community has been in Savannah since the colony's first year. Over time, Gullah-Geechee culture and Hoodoo practices also became part of the local culture, often alongside Christianity.
Christ Church was founded in 1733, the same year Georgia was established. It is the oldest continuous Christian church in Georgia. Famous early leaders included Methodist preachers John Wesley and George Whitefield. The church is still active today on its original site.
Other important historic churches include:
- The Independent Presbyterian Church, founded in 1755.
- The First Bryan Baptist Church, an African American church started in 1788.
- First African Baptist Church.
- St. Benedict the Moor Church, the first African American Catholic church in Georgia.
The oldest church building still standing is First Baptist Church (built in 1833). It is located on Chippewa Square. Other historic places of worship include the Roman Catholic Cathedral of St. John the Baptist, the Episcopal St. John's Church, and Temple Mickve Israel. Temple Mickve Israel is the third-oldest synagogue in the U.S.
Most Christians in Savannah are Protestants, especially Baptists. These include groups like the Southern Baptist Convention. Non-denominational Protestants are the second-largest Christian group. Methodists are also a significant group. The Roman Catholic Church is the second-largest single Christian group.
Among non-Christian religions, Hinduism is the second-largest in Savannah. Judaism is the third-largest, with a history going back to 1733. Islam is the fourth-largest, followed by the Baha'i Faith.
Economy and Industry
Early Economic Activities
For its first two centuries, farming was very important to Savannah's economy. Early products sent to England included silk and indigo. By 1767, almost a ton of silk was exported each year. Georgia's mild climate was perfect for growing cotton. Cotton became the main product after the American Revolution. Growing cotton on large farms using forced labor and shipping it through the Port of Savannah helped many European immigrants become wealthy.
Savannah's Important Port
By the 1800s, the Port of Savannah was one of the busiest in the United States. Goods made in the New World had to pass through Atlantic ports like Savannah's to be sent to England. Today, the Port of Savannah is North America's fourth-largest port for shipping containers. In 2023, the port handled 4.9 million twenty-foot equivalent container units (TEU).
Major Businesses and Employers
Savannah's first hotel, City Hotel, was built in 1821. It also had the city's first United States Post Office. From 1912 to 1968, the Savannah Machine & Foundry Company built ships in Savannah.
For many years, Savannah was home to Union Camp, which had the world's largest paper mill. This plant is now owned by International Paper and is still one of Savannah's biggest employers. Savannah is also home to Gulfstream Aerospace, a company that makes private jets. Other important industries are also here. TitleMax has its main office in Savannah. Morris Multimedia, a newspaper and television company, is also based in Savannah.
In 2000, JCB, a large construction equipment maker, built its North American headquarters near Savannah. In 2023, Naturals2Go moved to Savannah. Amazon has also been operating in Savannah and its surrounding area since 2021.
Arts and Culture Scene
Savannah is known for its beautiful architecture and rich history. It also has a lively arts scene and hosts many cultural events all year.
Books and Literature in Savannah
- The Savannah Book Festival is an annual event. It takes place in February near Telfair and Wright squares. It features free talks by over 35 authors.
- The Flannery O'Connor Childhood Home is a museum. It honors the famous writer Flannery O'Connor, who lived in Savannah as a child. The museum also hosts literary events.
- Midnight in the Garden of Good and Evil is a famous non-fiction book by John Berendt. It was published in 1994 and is set in Savannah's historic downtown. The book was later made into a movie.
- Other notable writers connected to Savannah include Conrad Aiken and Mary Kay Andrews. The songwriter Johnny Mercer was also from Savannah.
Dance and Music Performances
- The Savannah Ballet Theatre started in 1998. It is now the city's largest dance company.
- The Coastal Jazz Association hosts jazz performances and the annual Savannah Jazz Festival.
- The Savannah Children's Choir is for children in grades 2-8. They perform throughout the community.
- The Savannah Concert Association brings guest artists for chamber music. These shows are often at the Lucas Theatre for the Arts.
- The Savannah Music Festival is an annual event. It is Georgia's largest music festival and is known worldwide.
- The Savannah Orchestra is the city's professional orchestra. It performs classical and popular concerts.
- The Savannah Philharmonic is another professional music group. It performs orchestral and choral concerts all year.
Theater and Live Shows
- The American Traditions Vocal Competition is an annual singing contest. It celebrates American musical styles.
- The Savannah Children's Theatre offers drama and musical productions for students and adults.
- The Savannah Community Theatre presents a full season of plays.
- The Little Theatre of Savannah started in 1950. It is a volunteer group that celebrates theater arts.
- The Savannah Theatre is the city's only professional resident theater. It puts on music shows with live singers, dancers, and a band.
- The Savannah Repertory Theatre is a non-profit professional theater. It has been part of Savannah's culture since 2016.
- The Lucas Theatre for the Arts opened in 1921. It hosts the annual Savannah Film Festival.
- The Trustees Theater also hosts various performances and concerts.
- Odd Lot Improv is a family-friendly comedy group. They perform weekly shows.
Visual and Community Arts
- Art Rise Savannah, Inc. is a local non-profit group. It works to make art more accessible and create opportunities for artists in the city.
Savannah's Unique Charm and Attractions


Savannah is famous around the world for its architecture, history, and Southern charm. Its old nickname was "the Hostess City of the South." Another old nickname was "the Forest City" because of its many live oak trees. These trees were important for shipbuilding in the 1800s. In 2019, Savannah welcomed 14.8 million tourists.
The city's location offers access to coastal islands and the Savannah Riverfront. Both are popular with tourists. Tybee Island is east of Savannah. It has the Tybee Island Light Station, the first lighthouse on the southern Atlantic coast. Nearby towns include Thunderbolt, Beaulieu, Vernonburg, and the Isle of Hope. These started as summer resorts for Savannah residents.
The Savannah International Trade & Convention Center is on Hutchinson Island. It is across from downtown Savannah, surrounded by the Savannah River. The Savannah Belles Ferry connects the island to the mainland. The Talmadge Memorial Bridge also connects them.
The Georgia Historical Society has a research center in Savannah. Its library holds the oldest materials about Georgia's history. The Savannah Civic Center hosts over 900 events each year.
Travel + Leisure magazine has often named Savannah one of "America's Favorite Cities." In 2012, it ranked Savannah highest for "Quality of Life and Visitor Experience." Savannah was also ranked first for "Public Parks and Outdoor Access" and as a romantic getaway. It was named America's second-best city for "Cool Buildings and Architecture."
Jones Street is a mile long. It has been called one of the most charming streets in America.
Savannah's Famous Squares
Savannah is known for its 22 squares and small parks. These are found along five historic streets. Each street has between three and five squares. The squares are different sizes and styles. Some, like Johnson Square, have fountains and monuments. Others, like Crawford, have playgrounds.
Three squares were lost due to city development in the 1950s: Elbert, Ellis, and Liberty Squares. Ellis Square was rebuilt in 2010. Efforts are now underway to bring back Elbert and Liberty Squares.
Franklin Square has Savannah's Haitian Monument. It honors the brave efforts of the Chasseurs-Volontaires de Saint-Domingue. These soldiers from Haiti fought for America in the 1779 Siege of Savannah. Chippewa Square honors the Battle of Chippawa from the War of 1812. It has a large statue of James Oglethorpe, the city's founder. In the movie Forrest Gump, the main character sits on a bench in this square.
Some squares have been renamed. Calhoun Square was renamed Taylor Square in 2024.
Historic Homes to Explore
Many historic homes have been saved in Savannah. These include:
- The Olde Pink House
- The Sorrel–Weed House
- Juliette Gordon Low's birthplace
- The Davenport House Museum
- The Green–Meldrim House
- The Owens–Thomas House
- The William Scarbrough House
- The Wormsloe plantation
The Mercer Williams House is in Monterey Square. It was the main setting for the book Midnight in the Garden of Good and Evil.
Historic Cemeteries and Forts
Colonial Park Cemetery was the city's main burial ground when Georgia was a British colony. Laurel Grove Cemetery was Savannah's main cemetery in the 1800s. It has graves of Confederate soldiers and enslaved African Americans. Bonaventure Cemetery was once a plantation. It is the final resting place for some famous Savannah residents. The Mordecai Sheftall Cemetery and the Levi Sheftall Family Cemetery are also in Savannah. They date back to the late 1700s.
Fort Jackson is on the Savannah River. It was built between 1808 and 1812 to protect the city from sea attacks. It was one of several forts that defended Savannah during the American Civil War. Fort Pulaski National Monument is 17 miles (27 km) east of Savannah. It was the largest fort protecting the city during the war. Union soldiers attacked Fort Pulaski in 1862 with new rifled cannons. The Confederate troops surrendered, and these cannons showed that brick forts were no longer effective.
Other Historic Sites and Attractions
- Savannah Historic District and the Savannah Victorian Historic District.
- Forsyth Park
- Juliette Gordon Low Historic District
- Central of Georgia Railroad: Savannah Shops and Terminal Facilities and Central of Georgia Depot and Trainshed – a historic area listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
- John P. Rousakis Riverfront Plaza.
- Factors Walk and River Street's pedestrian area. These have restored 19th-century cotton warehouses, shops, bars, and restaurants.
- City Market – Savannah's restored central market. It has antiques, souvenirs, eateries, and outdoor plazas.
- Savannah State University campus and Walter Bernard Hill Hall. These are recognized by the Georgia Historical Marker Program. Hill Hall was built in 1901 and added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1981.
- Telfair Museum of Art and Telfair Academy of Arts of Sciences – the South's first public art museum.
- Wormsloe Plantation – a partially restored 18th-century Georgia plantation.
Shopping and Other Fun Places
Savannah has many shopping centers. These include Abercorn Common, the Savannah Historic District, Oglethorpe Mall, Savannah Mall, and Abercorn Walk.
Other attractions include:
- American Prohibition Museum – This museum in City Market shows the history of prohibition in America.
- Clary's Cafe – Featured in the book and movie Midnight in the Garden of Good and Evil.
- Club One – Also featured in Midnight in the Garden of Good and Evil.
- Coastal Georgia Botanical Gardens – A growing botanical garden south of Savannah.
- Crystal Beer Parlor – The city's oldest restaurant.
- Oatland Island Wildlife Center – East of Savannah, this center has wildlife from coastal Georgia and South Carolina.
- Leopold's Ice Cream – A popular ice cream shop.
- Ossabaw Island – An environmentally protected island south of Savannah.
- Pinkie Masters Bar – A popular bar visited by President Jimmy Carter.
- Pirates' House – A historic restaurant and tavern downtown.
- Ralph Mark Gilbert Civil Rights Museum – A museum about African-American history in Savannah.
- Skidaway Island – A community south of Savannah with Skidaway Island State Park and the University of Georgia Aquarium.
- Tybee Island – A popular beach town east of Savannah.
- Waving Girl statue – Honors Florence Martus.
Sports and Recreation
Parts of the East Coast Greenway run through Savannah. This is a 3,000-mile (5,000-kilometer) trail system from Maine to Florida.
Professional Sports Teams
| Team | Sport | League | Venue | Championships | Years |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Savannah Braves | Baseball | Southern League | Grayson Stadium | 1971–1983 | |
| Savannah Cardinals / Savannah Sand Gnats | Baseball | South Atlantic League | Grayson Stadium | 4 (1993, 1994, 1996, 2013) | 1984–2015 |
| Savannah Spirits | Basketball | Continental Basketball Association | Savannah Civic Center | 1986–1988 | |
| Savannah Wildcats | Basketball | Continental Basketball League | Georgia Southern University–Armstrong Campus | 1 (2010) | 2010 |
| Savannah Storm / C-Port Trojans | Basketball | East Coast Basketball League | Savannah High School | 2010–2018 | |
| Savannah Steam | American football | American Indoor Football | Tiger Arena | 2015–2016 | |
| Savannah Bananas | Baseball | Coastal Plain League / Banana Ball Championship League | Grayson Stadium | 3 (2016, 2021, 2022) | 2016–present |
| Savannah Clovers FC | Soccer | United Premier Soccer League / National Independent Soccer Association | Memorial Stadium | 1 (2019) | 2016–present |
| Savannah Ghost Pirates | Ice hockey | ECHL | Enmarket Arena | 2022–present | |
| Savannah Buccaneers | Basketball | The Basketball League | Tiger Arena | 2023–present |
College Sports Teams
| Club | Affiliation | Conference | Venues | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Savannah College of Art and Design Bees | NAIA | Sun Conference | SCAD Athletic Complex, Ronald C. Waranch Equestrian Center | |
| Savannah State Tigers and Lady Tigers | NCAA Division II | Southern Intercollegiate Athletic Conference | Tiger Arena, Ted Wright Stadium |
Education and Learning
Savannah has several colleges and universities. They offer different degree programs. These include:
- Georgia Southern University-Armstrong Campus
- Savannah College of Art and Design (SCAD)
- Savannah State University
- South University
Georgia Tech Savannah offers special certificate programs. Georgia Southern University also has a campus downtown. Savannah Technical College is a two-year school. The Skidaway Institute of Oceanography is a marine science research center. It is part of the University of Georgia. Savannah is also home to Ralston College, a liberal arts college.
Mercer University started a four-year medical program in Savannah in 2008. This was the first medical school in southern Georgia.
Savannah is home to most of the schools in the Savannah-Chatham County Public Schools district. Some notable high schools include:
- Beach High School*
- Benedictine Military School
- Calvary Day School
- Groves High School*
- Islands High School*
- Jenkins High School*
- Johnson High School*
- New Hampstead High School*
- Saint Andrew's School
- St. Vincent's Academy
- Savannah Arts Academy*
- Savannah Christian Preparatory School
- Savannah Country Day School
- Savannah High School*
- Windsor Forest High School*
The Oatland Island Wildlife Center of Savannah is also part of the public school system. It is an environmental education center. It has a 2-mile (3.2 km) nature trail where visitors can see native animals. These include Florida panthers, Eastern timber wolves, and alligators.
Media and News
Savannah has several major television stations. These include WSAV-TV (NBC), WTOC-TV (CBS), WJCL (ABC), and WTGS (Fox). There are also two PBS stations, WVAN and WJWJ-TV.
The Georgia Gazette was the first newspaper in the Georgia colony. It started in Savannah in 1763. Today, the Savannah Morning News is Savannah's only daily newspaper. The Savannah Tribune and the Savannah Herald are weekly newspapers that focus on the African-American community. Connect Savannah was a free weekly newspaper that stopped publishing in 2024. The Coastal Buzz focuses on positive news in the area.
Transportation and Infrastructure
Getting Around Savannah
Savannah/Hilton Head International Airport is located west of Savannah, near Interstate 95.
Amtrak has a passenger terminal in Savannah. Their Palmetto and Silver Service trains stop here daily. These trains travel between New York City and Miami.
Public transportation is provided by Chatham Area Transit (CAT). They have 17 bus routes. CAT also has a free downtown transportation system called dot. This system offers free bus service on the Forsyth Loop and Downtown Loop. It also provides free ferry rides between River Street and Hutchinson Island. The Georgia Queen and Savannah River Queen paddle steamers are also docked on River Street.
The Georgia Hi–Lo Trail is a 211-mile (340 km) trail. When finished, it will connect Savannah to Athens, Georgia.
Major Roads and Highways
 Interstate 95 runs north-south west of the city. It connects to the airport and Interstate 16.
Interstate 95 runs north-south west of the city. It connects to the airport and Interstate 16. Interstate 16 ends in downtown Savannah. It connects with Interstate 95 and Interstate 516.
Interstate 16 ends in downtown Savannah. It connects with Interstate 95 and Interstate 516. Interstate 516 is a highway that connects southside Savannah to the port area. It is also known as Lynes Parkway.
Interstate 516 is a highway that connects southside Savannah to the port area. It is also known as Lynes Parkway.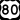 U.S. Route 80 (Victory Drive) runs east-west through midtown Savannah. It connects the city to Thunderbolt and the islands, including Tybee.
U.S. Route 80 (Victory Drive) runs east-west through midtown Savannah. It connects the city to Thunderbolt and the islands, including Tybee.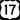 U.S. Route 17 (Ocean Highway) runs north-south through Savannah. It crosses the Talmadge Memorial Bridge into South Carolina.
U.S. Route 17 (Ocean Highway) runs north-south through Savannah. It crosses the Talmadge Memorial Bridge into South Carolina.- Harry S. Truman Parkway runs through eastside Savannah. It connects downtown with southern neighborhoods.
- Veterans Parkway connects Interstate 516 with southside Savannah. It helps traffic move faster north-south.
- Islands Expressway is an extension of President Street. It helps traffic flow between downtown Savannah, the barrier islands, and Tybee Island beaches.
Police and Fire Services
In 2003, Savannah and Chatham County decided to combine their police departments. The Savannah-Chatham Metropolitan Police Department was formed in 2005.
However, in 2018, the city and county ended this merger. Now, the Savannah Police Department and the Chatham County Police Department operate separately again. Both departments have special units like K-9, SWAT, and Marine Patrol. The 9-1-1 Communications Dispatch Center handles all emergency calls for the county and city. The Savannah Fire Department serves the City of Savannah. Other parts of Chatham County have their own fire departments.
Sister Cities
Savannah has several sister cities around the world:
Notable People from Savannah
See also
 In Spanish: Savannah para niños
In Spanish: Savannah para niños