Protestantism facts for kids
Protestantism is a major branch of Christian faith. It started in northern Europe in the early 1500s. At that time, many people felt that the Roman Catholic Church needed changes. Protestantism became one of the three main parts of Christianity, alongside the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Roman Catholic Church. It greatly shaped the culture, beliefs, and economy of the places where it became popular.
The word Protestantism came from a protest. In 1529, some German princes and free cities spoke out against rules made by the government that were against the Reformation. They "protested" these rules. People who followed Martin Luther in Germany started using the name. In Swiss and French areas, people often used the term Reformed. The Anglican Church sometimes uses Catholic, Reformed, and Protestant. However, the Anglican Church is not always seen as part of Protestantism. This is because it kept many of the old beliefs and practices from the Roman Catholic Church, even after it separated.
Martin Luther was a doctor of theology (the study of religious faith) and a monk. He believed the church should go back to its original teachings. He felt the Bible should be the most important guide (Sola scriptura). Luther thought the Church had moved too far from these early ideas. He wrote 95 points, called the 95 Theses, about the problems he saw in the Catholic Church. Some say he posted them on a church door in Wittenberg in 1517. This event is often seen as the start of the Protestant Reformation.
Main Protestant Churches
Many different churches are part of Protestantism. Some of the largest include:
The Anglican Church is often considered separately. Henry VIII, a king of England, started the Church of England. He wanted to divorce his wife, Catherine of Aragon, but the Pope (the leader of the Roman Catholic Church) said no. So, King Henry created his own church. The Anglican Church is sometimes seen as a middle ground between Roman Catholicism and Protestantism. This is because it kept many traditional roles, like bishops and priests, and many of the old beliefs and worship styles. The main difference was that the Anglican Church completely rejected the authority of the Pope.
Images for kids
-
Door of the Theses in Wittenberg, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany
-
A Lutheran depiction of the Last Supper by Lucas Cranach the Elder, 1547
-
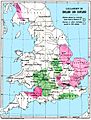
Spread of Lollardy in medieval England and medieval Scotland
-
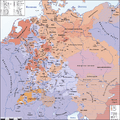
Distribution of Protestantism and Catholicism in Central Europe on the eve of the Thirty Years' War (1618)
-
Dissatisfaction with the outcome of a disputation in 1525 prompted Swiss Brethren to part ways with Huldrych Zwingli
-
Glass window in the town church of Wiesloch (Stadtkirche Wiesloch) with Martin Luther and John Calvin commemorating the 1821 union of Lutheran and Reformed churches in the Grand Duchy of Baden
-
Indonesian Reformed Evangelical Church megachurch
-
Hillsong Church Konstanz, Germany, an evangelical charismatic church
-
Karl Barth, often regarded as the greatest Protestant theologian of the twentieth century
-
Columbia University, established by the Church of England
-
Enlightenment philosopher John Locke argued for individual conscience, free from state control
-
St. Peter's Church (1612), the oldest surviving Protestant church in the "New World" (the Americas and certain Atlantic Ocean islands), the first of nine Parish churches established in Bermuda by the Church of England. Bermuda also has the oldest Presbyterian church outside the British Isles, the Church of Scotland's Christ Church (1719).
-
James Springer White and his wife, Ellen G. White founded the Seventh-day Adventist Church.
-
An Adventist pastor baptizes a young man in Mozambique.
-
Loma Linda University Seventh-day Adventist Church in Loma Linda, California, United States.
-
An Amish family in a horse-drawn square buggy.
-
Alexanderwohl Mennonite Church in rural Goessel, Kansas, United States.
-
Thomas Cranmer, one of the most influential figures in shaping Anglican theology and self-identity.
-
The various editions of the Book of Common Prayer contain the words of structured services of worship in the Anglican Church.
-
British coronations are held in Westminster Abbey, a royal peculiar under the direct jurisdiction of the monarch.
-
Roger Williams was an early proponent of religious freedom and the separation of church and state.
-
Baptists subscribe to a doctrine that baptism should be performed only for professing believers.
-
The First Baptist Church in America. Baptists are roughly one-third of U.S. Protestants.
-
John Calvin's theological thought influenced a variety of Congregational, Continental Reformed, United, Presbyterian, and other Reformed churches.
-
A Congregational church in Cheshire, Connecticut, United States.
-
Altar of the Turku Cathedral, the matrice of the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Finland
-
John Wesley, the primary founder of the Methodism.
-
A United Methodist elder celebrating the Eucharist.
-
Methodist Central Hall in Westminster, London.
-
A hymnal of the Free Methodist Church, a Methodist denomination aligned with the holiness movement.
-
A night shelter of The Salvation Army in Geneva, Switzerland.
-
Charles Fox Parham, who associated glossolalia with the baptism in the Holy Spirit.
-
Contemporary Christian worship in Rock Harbor Church, Costa Mesa, United States.
-
A Pentecostal church in Ravensburg, Germany.
-
George Fox was an English dissenter and a founder of the Religious Society of Friends, commonly known as the Quakers or Friends.
-
William Wilberforce, a British evangelical abolitionist.
-
Billy Graham, a prominent evangelical revivalist, preaching in Duisburg, Germany in 1954.
-
An Evangelical Protestant church in Hämeenlinna, Finland.
-
Philipp Jakob Spener, German pioneer and founder of Pietism.
-
Pilgrim Fathers landing at Plymouth Rock in 1620.
-
Built in 1681, the Old Ship Church in Hingham, Massachusetts is the oldest church in America in continuous ecclesiastical use.
-
A Huguenot, on St. Bartholomew's Day, Refusing to Shield Himself from Danger by Wearing the Roman Catholic Badge by John Everett Millais.
-
The Return of the Prodigal Son, detail, c. 1669 by Rembrandt.
-
The Church at Auvers, 1890. Musée d'Orsay, Paris. By Vincent van Gogh.
See also
 In Spanish: Protestantismo para niños
In Spanish: Protestantismo para niños
 | Jewel Prestage |
 | Ella Baker |
 | Fannie Lou Hamer |