Canada facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Canada
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Anthem: "O Canada"
|
|
 |
|
| Capital | Ottawa 45°24′N 75°40′W / 45.400°N 75.667°W |
| Largest city | Toronto |
| Official languages | |
| Demonym(s) | Canadian |
| Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
• Monarch
|
Charles III |
| Mary Simon | |
| Mark Carney | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| House of Commons | |
| Independence
from the United Kingdom
|
|
| July 1, 1867 | |
| December 11, 1931 | |
|
• Patriation
|
April 17, 1982 |
| Area | |
|
• Total area
|
9,984,670 km2 (3,855,100 sq mi) (2nd) |
|
• Water (%)
|
11.76 (2015) |
|
• Total land area
|
9,093,507 km2 (3,511,023 sq mi) |
| Population | |
|
• 2024 Q4 estimate
|
|
|
• 2021 census
|
|
|
• Density
|
4.2/km2 (10.9/sq mi) (236th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2024) | ▼ 29.2 low |
| HDI (2022) | very high · 18th |
| Currency | Canadian dollar ($) (CAD) |
| Time zone | UTC−3.5 to −8 |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC−2.5 to −7 |
| Calling code | +1 |
| ISO 3166 code | CA |
| Internet TLD | .ca |
Canada is a large country in North America. It has ten provinces and three territories. These stretch from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean. They also go north into the Arctic Ocean. This makes Canada the world's second-largest country by total area. It also has the longest coastline in the world.
Canada shares the world's longest land border with the United States. The country has many different weather and land regions. It is a sparsely populated country with about 40 million people. Most Canadians live in cities south of the 55th parallel. Ottawa is Canada's capital city. Its three biggest cities are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver.
Indigenous peoples have lived in Canada for thousands of years. In the 16th century, British and French explorers came and settled along the Atlantic coast. After several wars, France gave up most of its North American colonies in 1763. In 1867, three British colonies joined together. This event, called Confederation, formed Canada as a federal dominion with four provinces. Over time, more provinces and territories joined. Canada also gained more independence from the United Kingdom. This process ended in 1982 with the Canada Act 1982. This act made Canada fully independent from the British Parliament.
Canada is a parliamentary democracy. It is also a constitutional monarchy like the United Kingdom. The prime minister is the head of government. They lead the country with the support of the elected House of Commons. The governor general represents the monarch of Canada, who is the head of state. Canada is part of the Commonwealth realm. It is also officially bilingual, meaning both English and French are used by the federal government.
Canada is known for its high quality of life and strong economy. It is one of the world's most diverse and multicultural nations. This is because many people have immigrated to Canada. Canada's long history and close relationship with the United States have shaped its history, economy, and culture. Canada is a developed country with a strong economy. It relies on its many natural resources and international trade. Canada is seen as a "middle power" in global affairs. It often works with other countries to solve problems. Its role in peacekeeping in the 20th century helped shape its image worldwide. Canada is a member of many important international groups.
Contents
What Does "Canada" Mean?
The name Canada comes from the St. Lawrence Iroquoian word kanata. This word means "village" or "settlement." In 1535, Indigenous people near Quebec City used this word. They used it to guide French explorer Jacques Cartier to their village, Stadacona.
Cartier then used Canada to describe not just that village. He used it for the whole area ruled by Donnacona, the chief of Stadacona. By 1545, European maps and books called this small area along the Saint Lawrence River Canada.
From the 16th to the early 18th century, "Canada" referred to the part of New France along the Saint Lawrence River. In 1791, this area became two British colonies. They were called Upper Canada and Lower Canada. These were known as the Canadas until 1841. Then, they united to form the British Province of Canada.
When Confederation happened in 1867, Canada became the new country's legal name. The word dominion was also used as its title. By the 1950s, the United Kingdom no longer used "Dominion of Canada." They saw Canada as a "realm of the Commonwealth."
The Canada Act 1982 gave Canada full control over its own Constitution of Canada. This act only referred to Canada. Later that year, the national holiday's name changed from Dominion Day to Canada Day. The term Dominion was used to tell the federal government apart from the provinces. However, after World War II, "federal" replaced "dominion."
A Brief History of Canada
Who Were the First Peoples of Canada?
Indigenous peoples in Canada today include the First Nations, Inuit, and Métis. The Métis are people of mixed descent. They came about in the mid-1600s when First Nations people married European settlers. They then developed their own culture.
Scientists believe the first people in North America came from Siberia. They crossed the Bering land bridge at least 14,000 years ago. The Paleo-Indian sites at Old Crow Flats and Bluefish Caves are among the oldest places where humans lived in Canada. Early Indigenous societies had permanent homes, farmed, and traded. Some of these cultures had disappeared by the time Europeans arrived. We only know about them through archeology.
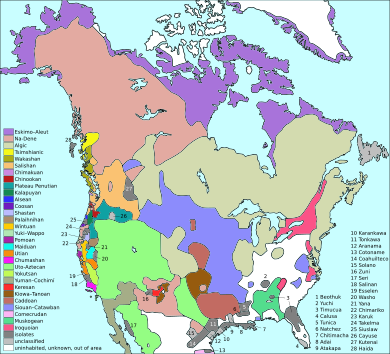
It is thought that between 200,000 and two million Indigenous people lived in Canada when Europeans first settled. The Royal Commission on Aboriginal Peoples suggests a number of 500,000. After European colonization, the Indigenous population dropped by 40 to 80 percent. Some First Nations, like the Beothuk, disappeared. This decline was due to several reasons. These include European diseases like influenza, measles, and smallpox. Indigenous peoples had no natural protection against these. Conflicts over the fur trade and with settlers also played a part. The loss of Indigenous lands also caused problems.
Early interactions between Europeans and Indigenous peoples were mostly peaceful. First Nations and Métis peoples helped European explorers. They guided them across the continent during the North American fur trade. These early friendships changed over time. Treaties were signed, but Indigenous lands were often taken. From the late 1700s, Europeans tried to make Indigenous peoples adopt Western ways. This reached its peak in the late 1800s and early 1900s. Children were forced into state-funded boarding schools. This was an attempt to make them forget their own cultures. There was also health-care segregation and forced movement.
A period of making things right began in 2008. The Truth and Reconciliation Commission of Canada was formed. This group recognized past wrongs, like colonial injustices. They also worked on settlement agreements and racial discrimination.
When Did Europeans Arrive in Canada?
The first European to explore Canada's east coast was likely Norse explorer Leif Erikson. Around 1000 AD, the Norse built a small camp at L'Anse aux Meadows in Newfoundland. They stayed there for about 20 years. No other Europeans explored the area until 1497. That year, John Cabot explored and claimed Canada's Atlantic coast for England. In 1534, French explorer Jacques Cartier explored the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. On July 24, he put up a 10-meter (33 ft) cross. It said, "long live the King of France." He claimed the land, New France, for King Francis I.
In the early 1500s, Basque and Portuguese sailors set up seasonal whaling and fishing posts. These were along the Atlantic coast. Early settlements during the Age of Discovery did not last long. This was due to the harsh climate and difficult trade routes.
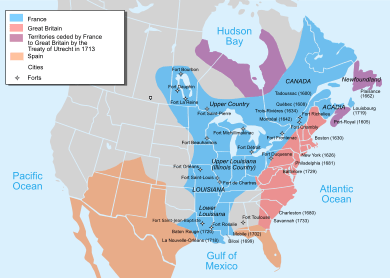
In 1583, Sir Humphrey Gilbert founded St John's, Newfoundland. This was the first English seasonal camp in North America. In 1600, the French set up their first seasonal trading post at Tadoussac. French explorer Samuel de Champlain arrived in 1603. He started the first permanent European settlements. These were at Port Royal (1605) and Quebec City (1608). French colonists, called Canadiens, settled along the Saint Lawrence River. Acadians settled in what is now The Maritimes. Fur traders and missionaries explored the Great Lakes and Hudson Bay. The Beaver Wars started in the mid-1600s. These wars were fought over control of the fur trade.
The English also set up settlements in Newfoundland in 1610. They also had colonies to the south, the Thirteen Colonies. Several wars broke out in North America between 1689 and 1763. Mainland Nova Scotia became British in 1713 after the Treaty of Utrecht. Canada and most of New France became British in 1763 after the Seven Years' War.
How Did British Rule Shape Canada?

The Royal Proclamation of 1763 set up First Nation treaty rights. It also created the Province of Quebec from New France. Cape Breton Island was added to Nova Scotia. St John's Island (now Prince Edward Island) became a separate colony in 1769. To avoid conflict in Quebec, the British Parliament passed the Quebec Act in 1774. This act expanded Quebec's territory. It also gave Quebec special rights and self-rule. This was at a time when the Thirteen Colonies were unhappy with British rule. The Quebec Act brought back the French language, Catholic faith, and French civil law. This helped prevent an independence movement in Quebec. However, the Proclamation and Quebec Act angered many in the Thirteen Colonies. This fueled anti-British feelings before the American Revolution.
After the American War of Independence, the 1783 Treaty of Paris recognized the United States' independence. It gave British territories south of the Great Lakes to the new country. The war also caused many Loyalists to leave the United States. They were settlers who fought against American independence. Many moved to Canada, especially Atlantic Canada. Their arrival changed the population there. New Brunswick was separated from Nova Scotia. This was part of a plan to organize Loyalist settlements. Saint John, New Brunswick, became Canada's first city. To make room for English-speaking Loyalists in Central Canada, the Constitutional Act of 1791 divided the province of Canada. It became French-speaking Lower Canada (later Quebec) and English-speaking Upper Canada (later Ontario). Each had its own elected assembly.

The Canadas were a main battleground in the War of 1812. This war was between the United States and the United Kingdom. Peace came in 1815, and no borders changed. Immigration increased, with over 960,000 people arriving from Britain between 1815 and 1850. Many were refugees from the Great Irish Famine. Others were Gaelic-speaking Scots forced from their homes. Diseases killed many Europeans who came to Canada before 1891.
The desire for responsible government led to the Rebellions of 1837. The Durham Report then suggested responsible government. It also recommended French Canadians become more like English culture. The Act of Union 1840 combined the Canadas into one province. By 1855, all British North American provinces east of Lake Superior had responsible government. Britain and the United States signed the Oregon Treaty in 1846. This ended the Oregon boundary dispute. It extended the border westward along the 49th parallel. This led to British colonies on Vancouver Island (1849) and in British Columbia (1858). The border along the Pacific coast was set by a treaty in 1825. But disputes continued even after the US bought Alaska in 1867.
How Did Canada Grow and Expand?
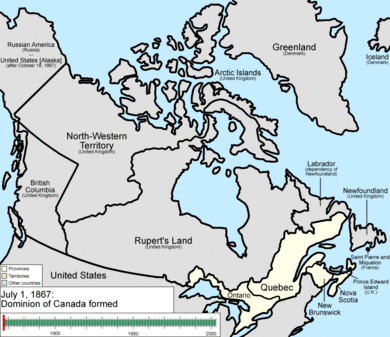
After three meetings, the British North America Act, 1867 officially created Canadian Confederation. This happened on July 1, 1867. It started with four provinces: Ontario, Quebec, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick. Canada took control of Rupert's Land and the North-Western Territory. These formed the Northwest Territories. Here, the Métis' complaints led to the Red River Rebellion. This resulted in the creation of Manitoba province in July 1870.
British Columbia and Vancouver Island joined in 1871. They were promised a railway across the country within 10 years. Prince Edward Island joined in 1873. In 1898, during the Klondike Gold Rush, the Yukon Territory was created. Alberta and Saskatchewan became provinces in 1905. Between 1871 and 1896, almost a quarter of Canadians moved to the US.
To open up the West and encourage European immigration, Canada built three railways. These included the Canadian Pacific Railway. The government also passed the Dominion Lands Act to manage settlement. The North-West Mounted Police were formed to keep order. This westward expansion led to many Indigenous peoples being moved to "Indian reserves." This cleared land for European settlements. It also caused the decline of Plains Bison. European farms then took over the land. Indigenous peoples faced hunger and disease due to the loss of bison and their hunting lands. The government offered help if Indigenous peoples moved to reserves. During this time, Canada introduced the Indian Act. This act gave the government control over First Nations' education, government, and legal rights.
Canada in the 20th Century
Britain controlled Canada's foreign affairs under the British North America Act, 1867. So, when Britain declared war in 1914, Canada automatically joined World War I. Canadian volunteers went to the Western Front. They became part of the Canadian Corps. This group played a big role in the Battle of Vimy Ridge and other major battles. About 625,000 Canadians served in World War I. Around 60,000 were killed and 172,000 were wounded.
The Conscription Crisis of 1917 happened when the government wanted to force people to join the military. French-speaking Quebecers strongly opposed this. The Military Service Act made military service mandatory. This, along with arguments over French language schools, upset French Canadians. It also temporarily split the Liberal Party. In 1919, Canada joined the League of Nations on its own. The Statute of Westminster, 1931, confirmed Canada's independence.
The Great Depression in Canada in the early 1930s caused a big economic downturn. This led to hardship across the country. In response, the Co-operative Commonwealth Federation (CCF) in Saskatchewan introduced many social programs. These were like a welfare state. They were pioneered by Tommy Douglas in the 1940s and 1950s. On September 10, 1939, King George VI declared war on Germany. This was seven days after the United Kingdom. The delay showed Canada's independence.
The first Canadian Army units arrived in Britain in December 1939. Over a million Canadians served in the armed forces during World War II. About 42,000 were killed and 55,000 were wounded. Canadian troops were important in many key battles. These included the 1942 Dieppe Raid, the Allied invasion of Italy, the Normandy landings, and the Battle of the Scheldt in 1944. Canada gave shelter to the Dutch monarchy when their country was occupied. The Netherlands credits Canada for helping with its liberation.
Canada's economy grew a lot during the war. Its factories made military supplies for Canada, Britain, China, and the Soviet Union. Despite another Conscription Crisis in Quebec in 1944, Canada ended the war with a strong army and economy.
Canada in Modern Times
The Great Depression's financial crisis led Dominion of Newfoundland to give up self-government in 1934. It became a Crown colony ruled by a British governor. After two votes, Newfoundlanders chose to join Canada in 1949 as a province.
After World War II, Canada's economy grew. New government policies led to a new Canadian identity. This was shown by the maple leaf flag in 1965. Official bilingualism (English and French) was introduced in 1969. Official multiculturalism began in 1971. Social programs like Medicare, the Canada Pension Plan, and Canada Student Loans were also started. However, some provinces, especially Quebec and Alberta, did not like these. They saw them as interfering with their powers.
More meetings about the constitution led to the Canada Act 1982. This act brought Canada's constitution fully under Canadian control. It also created the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms. Canada became a fully independent country with its own monarchy. In 1999, Nunavut became Canada's third territory. This happened after talks with the federal government.
At the same time, Quebec went through big social and economic changes. This was during the Quiet Revolution of the 1960s. It led to a nationalist movement. The Front de libération du Québec (FLQ) caused the October Crisis in 1970. They carried out bombings and kidnappings. The Parti Québécois was elected in 1976. They held a vote on Quebec becoming more independent in 1980, but it failed. Attempts to include Quebec nationalism in the constitution failed in 1990. This led to the creation of the Bloc Québécois in Quebec. It also strengthened the Reform Party of Canada in the West. A second vote on independence happened in 1995. It was rejected by a very close margin. In 1997, the Supreme Court said a province could not leave Canada on its own. Parliament then passed the Clarity Act. This act set out how a province could leave Canada through negotiation.
Canada sent troops to Afghanistan in 2001. However, it did not join the United States in the invasion of Iraq in 2003. In 2011, Canadian forces helped in the NATO-led action in the Libyan Civil War. They also fought the Islamic State in Iraq in the mid-2010s.
Canada celebrated its 150th birthday in 2017. Three years later, the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada began in January 2020. This caused big social and economic problems. In 2021, possible graves of hundreds of Indigenous people were found. These were near former residential schools. These boarding schools were run by churches and funded by the government from 1828 to 1997. They tried to force Indigenous children to adopt European Canadian culture.
Canada's Geography and Climate
What Does Canada Look Like?
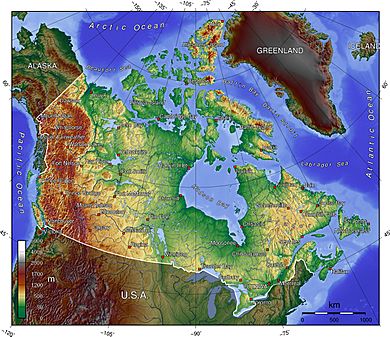
Canada is the second-largest country in the world by total area. This includes its waters. By land area alone, Canada is fourth. This is because it has the most freshwater lakes in the world. Canada stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west. It also goes north to the Arctic Ocean. The country covers 9,984,670 square kilometers (3,854,085 sq mi). Canada also has a huge ocean area. Its coastline is the longest in the world, at 243,042 kilometers (151,019 mi).
Canada shares the world's longest land border with the United States. This border is 8,891 kilometers (5,525 mi) long. Canada also shares a land border with Greenland (part of Denmark) in the northeast. This is on Hans Island. It also has a sea border with France's Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the southeast. Canada is home to the world's northernmost settlement. This is Canadian Forces Station Alert. It is on the northern tip of Ellesmere Island, at 82.5°N latitude. This is 817 kilometers (508 mi) from the North Pole.
Canada has seven main land regions. These are the Canadian Shield, the interior plains, the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Lowlands, the Appalachian region, the Western Cordillera, Hudson Bay Lowlands, and the Arctic Archipelago. Boreal forests cover much of the country. Ice is common in northern Arctic regions and the Rocky Mountains. The flat Canadian Prairies in the southwest are good for farming. The Great Lakes flow into the St. Lawrence River in the southeast. This lowland area is where much of Canada's economy is located.
Canada has over 2,000,000 lakes. 563 of these are larger than 100 square kilometers (39 sq mi). These lakes hold much of the world's fresh water. There are also freshwater glaciers in the Canadian Rockies, the Coast Mountains, and the Arctic Cordillera. Canada has active geology. It has many earthquakes and potentially active volcanoes. These include Mount Meager massif, Mount Garibaldi, and Mount Cayley.
What is Canada's Climate Like?
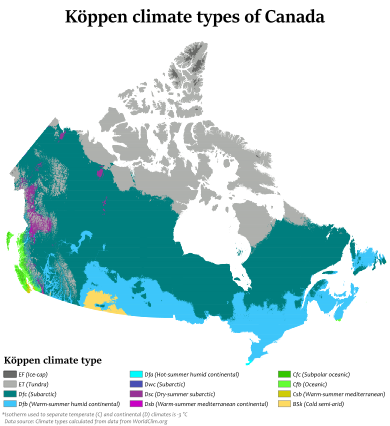
Winter and summer temperatures in Canada vary across regions. Winters can be very cold in many parts of the country. This is especially true in the interior and Prairie provinces. They have a continental climate. Daily average temperatures are around -15°C (5°F). But they can drop below -40°C (-40°F) with strong wind chills. In areas away from the coast, snow can cover the ground for almost six months. In some northern parts, snow can stay all year.
Coastal British Columbia has a mild climate. It has mild and rainy winters. On the east and west coasts, summer high temperatures are usually in the low 20s °C (70s °F). Between the coasts, average summer highs range from 25 to 30°C (77 to 86°F). Some inland places can even reach over 40°C (104°F).
Much of Northern Canada is covered by ice and permafrost. The future of the permafrost is uncertain. This is because the Arctic is warming three times faster than the global average. This is due to climate change in Canada. Canada's average yearly temperature has risen by 1.7°C (3.1°F) since 1948. The warming has been higher in the North and the Prairies. In southern Canada, air pollution from both Canada and the United States causes acid rain. This pollution comes from metal factories, burning coal, and vehicle emissions. Acid rain has badly affected waterways, forests, and farms in Canada.
What Kinds of Plants and Animals Live in Canada?
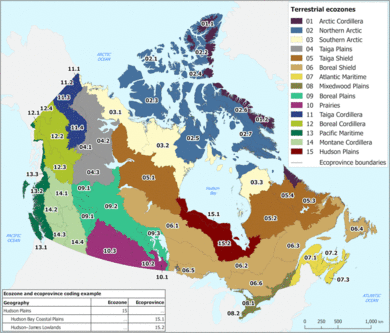
Canada has 15 land and five ocean ecozones. These zones are home to over 80,000 known species of Canadian wildlife. Many more are still unknown or not yet named. Canada has a low number of endemic species (found only there). But due to human actions, invasive species, and environmental problems, over 800 species are at risk of disappearing. About 65 percent of Canada's species are considered "Secure."
Over half of Canada's land is untouched by human development. The boreal forest of Canada is thought to be the largest intact forest on Earth. It has about 3,000,000 square kilometers (1,200,000 sq mi) undisturbed by roads or cities. Since the last ice age, Canada has had eight different forest regions. Forests cover 42 percent of its land area. This is about 8 percent of the world's forested land.
About 12.1 percent of Canada's land and freshwater are conservation areas. This includes 11.4 percent designated as protected areas. About 13.8 percent of its ocean waters are conserved. This includes 8.9 percent designated as protected areas. Canada's first National Park, Banff National Park, was created in 1885. It covers 6,641 square kilometers (2,564 sq mi) of mountains. It has many glaciers, ice fields, and forests. Canada's oldest provincial park, Algonquin Provincial Park, was created in 1893. It covers 7,653.45 square kilometers (2,955.01 sq mi). It has old-growth forests, over 2,400 lakes, and 1,200 kilometers (750 mi) of rivers.
Lake Superior National Marine Conservation Area is the world's largest freshwater protected area. It covers about 10,000 square kilometers (3,900 sq mi) of lakebed. Canada's largest national wildlife region is the Scott Islands Marine National Wildlife Area. It covers 11,570.65 square kilometers (4,467.45 sq mi). It protects important breeding grounds for over 40 percent of British Columbia's seabirds. Canada has 18 UNESCO Biosphere Reserves. They cover a total area of 235,000 square kilometers (91,000 sq mi).
How Canada is Governed
What Kind of Government Does Canada Have?
Canada is known as a "full democracy." It has a history of liberalism and a moderate political outlook. Canada's political culture emphasizes social justice. Important founding ideas of the Canadian government are "Peace, order, and good government" and an Implied Bill of Rights.
At the federal level, two main parties have led Canada. These are the centre-left Liberal Party of Canada and the centre-right Conservative Party of Canada. The Liberals have historically been the most powerful. Five parties had members elected to Parliament in the 2021 election. These were the Liberals (who formed a minority government), the Conservatives (the Official Opposition), the New Democratic Party (on the left), the Bloc Québécois, and the Green Party of Canada. Extreme left or right politics have never been very strong in Canada.
Canada has a parliamentary system and is a constitutional monarchy. The monarchy of Canada is the basis of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. The reigning monarch is also the monarch of 14 other Commonwealth countries. The monarch appoints a governor general to carry out most royal duties in Canada. This is done on the advice of the prime minister.
The monarchy is the source of power in Canada. However, the governor general or monarch usually acts on the advice of the Cabinet. The Cabinet is a group of ministers chosen by the prime minister. The prime minister is the head of government. To keep the government stable, the governor general usually appoints the leader of the party with the most seats as prime minister. The Prime Minister's Office (PMO) is very powerful. It starts most laws and chooses people for important jobs. The leader of the party with the second-most seats becomes the leader of the Official Opposition. This system helps keep the government accountable.

The Parliament of Canada makes all federal laws. It includes the monarch, the House of Commons, and the Senate. Canada adopted the British idea of Parliament being supreme. But after the Constitution Act, 1982, the law became supreme.
Each of the 338 members of Parliament in the House of Commons is elected in an electoral district. The Constitution Act, 1982 says elections must happen at least every five years. The Canada Elections Act sets a "fixed" election date in October every four years. However, general elections are still called by the governor general. They can also be triggered if the prime minister advises it or if the government loses a confidence vote. The 105 members of the Senate are appointed by region. They serve until age 75.
Canadian federalism divides government duties between the federal government and the 10 provinces. Provincial legislatures have one chamber. They work like the House of Commons. Canada's three territories also have legislatures. But these have fewer powers than the provinces.
The Bank of Canada is the country's central bank. The minister of finance and minister of innovation, science, and industry use Statistics Canada for financial planning. The Bank of Canada is the only one allowed to print Canadian bank notes. The Royal Canadian Mint makes Canadian coins.
What Are Canada's Laws Like?
The Constitution of Canada is the highest law in the country. It includes written rules and unwritten traditions. The Constitution Act, 1867 (formerly the British North America Act, 1867) confirmed parliamentary rule. It also divided powers between federal and provincial governments. The Statute of Westminster, 1931 gave Canada full independence. The Constitution Act, 1982 ended all legal ties to Britain. It also added a way to change the constitution and the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms. The Charter protects basic rights and freedoms. Governments usually cannot override these. However, a notwithstanding clause lets Parliament and provinces temporarily override some sections for five years.

Canada's courts are important for interpreting laws. They can strike down laws that go against the constitution. The Supreme Court of Canada is the highest court. It has been led by Richard Wagner since 2017. The governor general appoints the court's nine members. This is done on the advice of the prime minister and minister of justice. The federal Cabinet also appoints judges to higher courts in the provinces and territories.
Common law is used everywhere except Quebec. In Quebec, civil law is used. Criminal law is a federal responsibility. It is the same across Canada. Law enforcement, including criminal courts, is a provincial job. It is done by provincial and city police forces. In many rural and some urban areas, the federal Royal Canadian Mounted Police handles policing.
Canadian Aboriginal law gives certain constitutionally recognized rights to Indigenous groups. These rights cover land and traditional practices. Treaties and court cases have helped define relations between Europeans and Indigenous peoples. The Numbered Treaties are 11 agreements signed between Indigenous peoples and the Canadian monarch from 1871 to 1921. These treaties are agreements with the Canadian government. They include a duty to consult and accommodate. These rights were confirmed by section 35 of the Constitution Act, 1982. They can include services like healthcare and tax exemptions.
How Does Canada Interact with Other Countries?

Canada is known as a "middle power" in international affairs. It often seeks to work with many countries to solve problems. Canada's foreign policy focuses on international peacekeeping and security. This is done through alliances and international groups. Canada's peacekeeping role in the 20th century greatly shaped its global image. The Canadian government's foreign aid policy aims to meet Sustainable Development Goals. It also provides help during humanitarian crises.
Canada and the United States have a long and close relationship. They are strong allies. They work together on military and humanitarian efforts. Canada also has historical ties to the United Kingdom and France. It is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations and the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie. Canada has a good relationship with the Netherlands. This is partly due to its help in the Dutch liberation during World War II. Canada was a founding member of the United Nations. It is also a member of the World Trade Organization, the G20, and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Canada is part of many other international groups for economic and cultural matters. Canada joined the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights in 1976. It joined the Organization of American States (OAS) in 1990. Canada wants to build stronger ties with Pacific Rim economies. It does this through the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation forum (APEC).
Canada's strong ties to the British Empire led it to contribute to British military efforts. These included the Second Boer War (1899–1902), World War I (1914–1918), and World War II (1939–1945). Since then, Canada has supported working with other nations to solve global issues. During the Cold War, Canada sent many troops to UN forces in the Korean War. It also founded the North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD) with the United States. This was to defend against air attacks from the Soviet Union.
During the Suez Crisis in 1956, future prime minister Lester B. Pearson helped ease tensions. He suggested creating the United Nations Peacekeeping Force. For this, he won the 1957 Nobel Peace Prize. This was the first UN peacekeeping mission. Pearson is often seen as the inventor of peacekeeping. Canada has since served in over 50 peacekeeping missions. This includes every UN peacekeeping effort until 1989. It has also kept forces in international missions in Rwanda and the former Yugoslavia. Canada has sometimes faced criticism for its involvement in other countries. One example is the 1993 Somalia affair.
In 2001, Canada sent troops to Afghanistan. They were part of the US stabilization force and the NATO-led International Security Assistance Force. In August 2007, Canada's territorial claims in the Arctic were challenged. This happened after a Russian underwater expedition to the North Pole. Canada has considered that area its own territory since 1925.
The unified Canadian Forces (CF) include the Royal Canadian Navy, Canadian Army, and Royal Canadian Air Force. Canada has a professional, volunteer force. It has about 68,000 active members and 27,000 reserve members. This will increase to 71,500 and 30,000. It also has about 5,000 Canadian Rangers. In 2021, Canada spent about $26.4 billion on its military. This was about 1.3 percent of the country's gross domestic product (GDP). Military spending is expected to reach $32.7 billion by 2027. Canada's military currently has over 3000 people deployed overseas. These operations include Operation Snowgoose in Cyprus and Operation Unifier supporting Ukraine.
What Are Canada's Provinces and Territories?
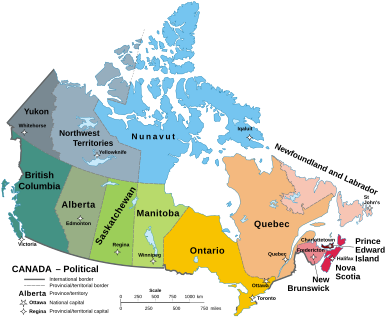
Canada is a federation with 10 provinces and three federal territories. These can be grouped into four main regions: Western Canada, Central Canada, Atlantic Canada, and Northern Canada. (Eastern Canada refers to Central Canada and Atlantic Canada together.) Provinces and territories are responsible for social programs. These include healthcare, education, and welfare. They also manage justice (but not criminal law).
Together, the provinces collect more money than the federal government. This is rare among other federations. The federal government can start national policies in provincial areas. These include health and child care. Provinces can choose not to join these programs, but they rarely do. Equalization payments are made by the federal government. These ensure similar standards of services and taxes between richer and poorer provinces.
The main difference between a Canadian province and a territory is their power source. Provinces get their power from the Crown and the Constitution Act, 1867. Territorial governments get their powers from the Parliament of Canada. Changes to provincial powers need a constitutional amendment. Changes to territorial powers can be made by Parliament alone.
Canada's Economy
How Does Canada Make Money?
Canada has a highly developed mixed-market economy. It is the world's ninth-largest economy as of 2023. Its nominal GDP is about US$2.221 trillion. Canada is one of the world's largest trading nations. Its economy is very globalized. In 2021, Canadian trade in goods and services reached $2.016 trillion. Canada's exports were over $637 billion. Its imported goods were over $631 billion. About $391 billion of imports came from the United States. In 2018, Canada had a trade deficit in goods of $22 billion. It also had a trade deficit in services of $25 billion. The Toronto Stock Exchange is the ninth-largest stock exchange in the world. It lists over 1,500 companies worth over US$2 trillion.
Canada has a strong cooperative banking sector. It has the most credit union members per person in the world. It ranks low in the Corruption Perceptions Index (14th in 2023). It is seen as one of the least corrupt countries. It ranks high in the Global Competitiveness Report (14th in 2019) and Global Innovation Index (15th in 2023). Canada's economy ranks above most Western nations on The Heritage Foundation's Index of Economic Freedom. It has relatively low income differences. The average Canadian household's disposable income is "well above" the OECD average. Canada ranks among the lowest of developed countries for housing affordability and foreign direct investment.
Since the early 1900s, Canada's economy has changed. It went from being mostly rural to urban and industrial. This was due to growth in manufacturing, mining, and services. Like many developed countries, Canada's economy is mostly based on the service industry. This industry employs about three-quarters of the workforce. Canada also has an important primary sector. The forestry and petroleum industries are the biggest parts of this. Many towns in northern Canada, where farming is hard, rely on nearby mines or timber.
Canada's economic ties with the United States have grown a lot since World War II. The Automotive Products Trade Agreement of 1965 opened Canada's borders to car manufacturing trade. The Canada – United States Free Trade Agreement (FTA) of 1988 removed tariffs between the two countries. The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) added Mexico in 1994. It was later replaced by the Canada–United States–Mexico Agreement. As of 2023, Canada has 15 free trade agreements with 51 different countries.
Canada is one of the few developed nations that export more energy than they import. Atlantic Canada has large offshore natural gas deposits. Alberta has the world's fourth-largest oil reserves. The huge Athabasca oil sands and other oil reserves give Canada 13 percent of global oil reserves. This makes it the world's third or fourth-largest. Canada is also one of the world's largest suppliers of farm products. The Canadian Prairies are a major global producer of wheat, canola, and other grains. The country is a top exporter of zinc, uranium, gold, nickel, and other metals. Canada has a big manufacturing sector in southern Ontario and Quebec. Cars and aeronautics are very important industries. The fishing industry also contributes a lot to the economy.
What About Science and Technology in Canada?
In 2020, Canada spent about $41.9 billion on research and development. This is expected to be $43.2 billion in 2022. As of 2023, Canada has produced 15 Nobel Prize winners in physics, chemistry, and medicine. Canada ranks seventh globally for articles published in scientific journals. It is also home to several global technology companies. Canada has one of the highest levels of Internet access in the world. Over 33 million people use the Internet, which is about 94 percent of its population.

Canada has made many scientific and technological advances. These include creating the modern alkaline battery. They also discovered insulin and developed the polio vaccine. Canadians also made discoveries about the inside of the atomic nucleus. Other big Canadian science contributions include the artificial cardiac pacemaker. They also mapped the visual cortex and developed the electron microscope. Canadians contributed to plate tectonics, deep learning, and multi-touch technology. They also identified the first black hole, Cygnus X-1. Canada has a long history of discoveries in genetics. These include stem cells, site-directed mutagenesis, and the T-cell receptor. They also found the genes that cause Fanconi anemia, cystic fibrosis, and early-onset Alzheimer's disease.
The Canadian Space Agency has a very active space program. It does research on deep space, planets, and aviation. It also develops rockets and satellites. Canada was the third country to design and build a satellite. This was after the Soviet Union and the United States. Canada launched its Alouette 1 satellite in 1962. Canada is part of the International Space Station (ISS). It is a leader in space robotics. It built the Canadarm, Canadarm2, Canadarm3 and Dextre robotic arms for the ISS and NASA's Space Shuttle. Since the 1960s, Canada's aerospace industry has built many satellites. These include Radarsat-1 and 2, ISIS, and MOST. Canada also made one of the world's most successful sounding rockets, the Black Brant.
People and Culture in Canada
Who Lives in Canada?
The 2021 Canadian census counted 36,991,981 people in Canada. This was an increase of about 5.2 percent from 2016. It is thought that Canada's population passed 40,000,000 in 2023. The main reasons for population growth are immigration and, to a lesser extent, natural growth. Canada has one of the highest immigration rates per person in the world. This is mainly due to economic policy and family reunification. A record 405,000 immigrants came to Canada in 2021. Canada leads the world in resettling refugees. It resettled over 28,000 in 2018. New immigrants mostly settle in major cities like Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver.
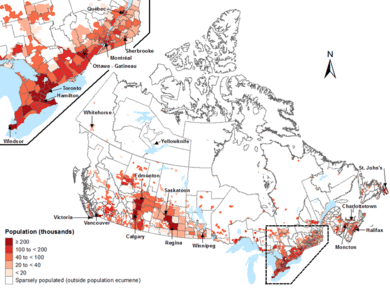
Canada's population density is 4.2 people per square kilometer (10.9/sq mi). This is one of the lowest in the world. Canada stretches from the 83rd parallel north to the 41st parallel north. About 95 percent of the population lives south of the 55th parallel north. About 80 percent of people live within 150 kilometers (93 mi) of the border with the United States. Canada is very urbanized. Over 80 percent of the population lives in cities. The most crowded part of the country is the Quebec City–Windsor Corridor. This area is in Southern Quebec and Southern Ontario. It is along the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence River. Almost 50 percent of Canadians live there.
Most Canadians (81.1 percent) live in family households. 12.1 percent live alone. 6.8 percent live with other relatives or unrelated people. Fifty-one percent of households are couples with or without children. 8.7 percent are single-parent households. 2.9 percent are multi-generational households. 29.3 percent are single-person households.
|
Largest metropolitan areas in Canada
2021 Canadian census |
||
|---|---|---|
| Rank | Pop. | |
| 1 | Toronto | 6,202,225 |
| 2 | Montreal | 4,291,732 |
| 3 | Vancouver | 2,642,825 |
| 4 | Ottawa–Gatineau | 1,488,307 |
| 5 | Calgary | 1,481,806 |
| 6 | Edmonton | 1,418,118 |
| 7 | Quebec City | 839,311 |
| 8 | Winnipeg | 834,678 |
| 9 | Hamilton | 785,184 |
| 10 | Waterloo Region | 575,847 |
What Are the Different Ethnic Groups in Canada?
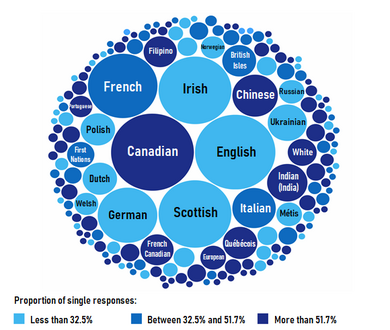
According to the 2021 Canadian census, Canadians reported over 450 different "ethnic or cultural origins." The main groups chosen were: European (52.5 percent), North American (22.9 percent), Asian (19.3 percent), North American Indigenous (6.1 percent), African (3.8 percent), Latin, Central and South American (2.5 percent), Caribbean (2.1 percent), Oceanian (0.3 percent), and other (6.0 percent). Over 60 percent of Canadians reported only one origin. 36 percent reported having multiple ethnic origins. So, the total is more than 100 percent.
The ten largest specific ethnic or cultural origins reported in 2021 were: Canadian (15.6 percent), English (14.7 percent), Irish (12.1 percent), Scottish (12.1 percent), French (11.0 percent), German (8.1 percent), Chinese (4.7 percent), Italian (4.3 percent), Indian (3.7 percent), and Ukrainian (3.5 percent).
Of the 36.3 million people counted in 2021, about 25.4 million reported being "White." This is 69.8 percent of the population. The Indigenous population was 5 percent, or 1.8 million people. This group grew by 9.4 percent from 2016 to 2021. The non-Indigenous population grew by 5.3 percent. One out of every four Canadians, or 26.5 percent, belonged to a non-White and non-Indigenous visible minority. The largest of these in 2021 were South Asian (2.6 million people; 7.1 percent), Chinese (1.7 million; 4.7 percent), and Black (1.5 million; 4.3 percent).
Between 2011 and 2016, the visible minority population grew by 18.4 percent. In 1961, less than two percent of Canada's population (about 300,000 people) were visible minorities. The 2021 census showed that 8.3 million people, or almost one-quarter (23.0 percent) of the population, reported being a landed immigrant or permanent resident. This is higher than the 1921 census record of 22.3 percent. In 2021, India, China, and the Philippines were the top three countries where immigrants to Canada came from.
What Languages Are Spoken in Canada?
Canadians speak many languages. English and French are the official languages. They are the mother tongues of about 54 percent and 19 percent of Canadians, respectively. As of the 2021 census, over 7.8 million Canadians said their first language was not English or French. Some common non-official first languages include Mandarin (679,255 speakers), Punjabi (666,585), Cantonese (553,380), Spanish (538,870), Arabic (508,410), Tagalog (461,150), Italian (319,505), German (272,865), and Tamil (237,890).
Canada's federal government uses official bilingualism. This means English and French have equal status in federal courts, Parliament, and all federal institutions. Citizens have the right to receive federal government services in either English or French, where there is enough demand. Also, official-language minorities are guaranteed their own schools in all provinces and territories.
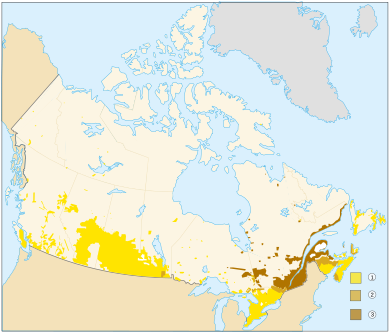
Quebec's 1974 Official Language Act made French the only official language of the province. More than 82 percent of French-speaking Canadians live in Quebec. But there are many Francophone people in New Brunswick, Alberta, and Manitoba. Ontario has the largest French-speaking population outside Quebec. New Brunswick is the only officially bilingual province. Its French-speaking Acadian minority makes up 33 percent of the population. There are also groups of Acadians in southwestern Nova Scotia, on Cape Breton Island, and in central and western Prince Edward Island.
Other provinces do not have official languages. But French is used for teaching, in courts, and for other government services, along with English. Manitoba, Ontario, and Quebec allow both English and French to be spoken in their provincial legislatures. Laws are also made in both languages. In Ontario, French has some legal status, but it is not fully co-official. There are 11 Indigenous language groups. These have more than 65 different languages and dialects. Several Indigenous languages are official in the Northwest Territories. Inuktitut is the main language in Nunavut and is one of three official languages there.
Canada also has many sign languages, including some Indigenous ones. American Sign Language (ASL) is used across the country. This is because ASL is common in schools. Quebec Sign Language (LSQ) is mainly used in Quebec.
What Religions Are Practiced in Canada?
Canada has many different religions, beliefs, and customs. The Constitution of Canada mentions God. The monarch has the title Defender of the Faith. However, Canada has no official church. The government supports religious pluralism, meaning many religions can exist. Freedom of religion in Canada is a right protected by the constitution. It allows people to gather and worship freely.
The number of people practicing religion has been going down since the 1970s. Christianity was once very important in Canadian culture. Now, Canada is becoming a post-Christian, secular state. Most Canadians think religion is not important in their daily lives. But they still believe in God. Practicing religion is generally seen as a private matter in Canada.
According to the 2021 census, Christianity is the largest religion in Canada. Roman Catholics make up 29.9 percent of the population. Christians overall are 53.3 percent of the population. After Christians, 34.6 percent of people reported having no religion. Other faiths include Islam (4.9 percent), Hinduism (2.3 percent), Sikhism (2.1 percent), Buddhism (1.0 percent), Judaism (0.9 percent), and Indigenous spirituality (0.2 percent). Canada has the second-largest Sikh population outside of India.
Health and Education in Canada
How Does Healthcare Work in Canada?
Healthcare in Canada is provided through provincial and territorial systems. These are publicly funded health care systems, often called Medicare. They are guided by the Canada Health Act of 1984 and are universal. Canadians often see universal access to publicly funded health services as a basic value. It ensures everyone has national healthcare insurance. About 30 percent of Canadians' healthcare is paid for by the private sector. This mostly covers services not fully covered by Medicare. These include prescription drugs, dentistry, and optometry. About 65 to 75 percent of Canadians have extra health insurance. Many get it through their jobs or social programs.
Like many developed countries, Canada's healthcare costs are rising. This is because the population is getting older. There are more retirees and fewer working-age people. In 2021, the average age in Canada was 41.9 years. Life expectancy is 81.1 years. A 2016 report found that 88 percent of Canadians said they had "good or very good health." This is one of the highest rates among G7 countries. Canada has one of the highest rates of adult obesity among OECD countries. This contributes to about 2.7 million cases of diabetes. Four chronic diseases—cancer (the leading cause of death), heart diseases, respiratory diseases, and diabetes—cause 65 percent of deaths in Canada.
In 2021, the Canadian Institute for Health Information reported that healthcare spending reached $308 billion. This was 12.7 percent of Canada's GDP that year. In 2022, Canada's spending per person on health ranked 12th among OECD health-care systems. Canada has performed near or above the average on most OECD health measures since the early 2000s. It ranks above average for wait times and access to care. It has average scores for quality of care and resource use. The Commonwealth Fund's 2021 report compared healthcare systems in 11 developed countries. Canada ranked second-to-last. Weaknesses included a higher infant mortality rate, many chronic conditions, long wait times, poor after-hours care, and a lack of prescription drug and dental coverage. A growing problem in Canada's health system is a shortage of healthcare workers.
What is Education Like in Canada?

Education in Canada is mostly publicly provided. It is funded and overseen by federal, provincial, and local governments. Education is a provincial responsibility. The province controls the curriculum. Education in Canada is generally divided into primary education, then secondary education, and then post-secondary. Education in both English and French is available in most places. Canada has many universities, and almost all are publicly funded. Established in 1663, Université Laval is the oldest university in Canada. The largest university is the University of Toronto with over 85,000 students. Four universities are often ranked among the top 100 worldwide. These are the University of Toronto, University of British Columbia, McGill University, and McMaster University. A total of 18 universities are ranked in the top 500 worldwide.
According to a 2019 report, Canada is one of the most educated countries in the world. It ranks first globally in the percentage of adults with tertiary education. Over 56 percent of Canadian adults have at least a college or university degree. Canada spends about 5.3 percent of its GDP on education. The country invests a lot in university education (more than US$20,000 per student). As of 2014, 89 percent of adults aged 25 to 64 have a high-school degree. The OECD average is 75 percent.
The mandatory education age is between 5–7 and 16–18 years. This helps create an adult literacy rate of 99 percent. Just over 60,000 children were homeschooled in 2016. The Programme for International Student Assessment shows Canadian students do very well. They perform above the OECD average, especially in math, science, and reading. Canadian 15-year-olds rank sixth-best in the world for overall knowledge and skills. However, these scores have been going down recently. Canada is a strong OECD country in reading, math, and science. The average student scored 523.7 in 2015, compared to the OECD average of 493.
Canadian Culture and Arts
What Makes Canadian Culture Unique?

Canada's culture is influenced by its many different nationalities. Its policies promote a "just society" and are protected by the constitution. Since the 1960s, Canada has focused on equality and inclusion for everyone. The official policy of multiculturalism is often seen as one of Canada's big achievements. It is a key part of Canadian identity. In Quebec, cultural identity is strong. There is a French Canadian culture that is different from English Canadian culture. Overall, Canada is like a cultural mosaic of regional ethnic groups.
Canada's approach to government emphasizes multiculturalism. This is based on careful immigration, social integration, and stopping extreme politics. This approach has wide public support. Government policies like publicly funded healthcare and higher taxes to share wealth show Canadian values. Other examples are the ending of capital punishment, efforts to reduce poverty, strict gun control, and a social liberal view on women's rights. Canadians also connect with the country's foreign aid, peacekeeping roles, national parks, and the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms.
Historically, Canada has been shaped by British, French, and Indigenous cultures. Indigenous peoples continue to influence Canadian identity through their language, art, and music. In the 20th century, Canadians from African, Caribbean, and Asian backgrounds added to Canadian identity and culture.
What Are Canada's National Symbols?

Nature, pioneers, trappers, and traders were important in early Canadian symbols. Modern symbols highlight Canada's geography, cold climate, and lifestyles. They also show how European and Indigenous symbols became Canadian. The maple leaf has been a Canadian symbol since the early 1700s. It is on Canada's current and previous flags and on the Arms of Canada. Canada's official tartan, the "maple leaf tartan," has four colors. These colors show the maple leaf changing through the seasons: green in spring, gold in early autumn, red at the first frost, and brown after falling. The Arms of Canada are similar to those of the United Kingdom. They have French and unique Canadian elements added or changed.
Other important symbols include the national motto, "A mari usque ad mare" ("From Sea to Sea"). Also, the sports of ice hockey and lacrosse, the beaver, Canada goose, common loon, Canadian horse, the Royal Canadian Mounted Police, the Canadian Rockies, and, more recently, the totem pole and Inuksuk. Canadian beer, maple syrup, tuques, canoes, nanaimo bars, butter tarts, and poutine are seen as uniquely Canadian. Canadian coins feature many of these symbols: the loon on the $1 coin, the Arms of Canada on the 50¢ piece, and the beaver on the nickel. An image of the previous monarch, Queen Elizabeth II, appears on $20 bank notes and on all current Canadian coins.
What Kind of Food Does Canada Have?
Canadian cuisine changes a lot depending on the region. The four earliest types of Canadian food come from Indigenous, English, Scottish, and French roots. Foods often seen as national dishes of Canada include poutine and butter tarts.
-
Inuit bannock fried bread
-
Montreal smoked meat sandwich
-
Fish and brewis: salted cod and hard tack
-
Canadian peameal bacon
-
Poutine is made with french fries, curds and gravy
-
Oreilles de crisse: deep fried pork skin and fat
-
Arctic berries Sxusem
The table below lists some of the most famous Canadian foods.
| Dish | Description | Pacific | Mountain | The Prairies | Ontario | Quebec | Atlantic | Northern |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calgary-style ginger beef | Candied and deep fried beef, with sweet ginger sauce. | X | O | X | ||||
| Roast beef with Yorkshire pudding | Traditionally a common Sunday dinner among Canadians of British ancestry | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Roast turkey | North American roast turkey | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Baked beans | Beans cooked with maple syrup | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| B.C. roll | A variety of sushi containing salmon | O | X | X | ||||
| California roll | A variety of sushi | O | X | X | X | |||
| Dynamite roll | A variety of sushi typically containing prawn tempura | O | X | X | X | |||
| Sushi pizza | Fusion sushi dish with fried rice patty as base, with sushi ingredients on top | X | X | X | O | X | X | |
| Jiggs dinner | A Sunday meal similar to the New England boiled dinner | O | ||||||
| Back or peameal bacon | Bacon that includes the pork loin from the back of the pig | X | X | X | O | X | ||
| Tourtière | A meat pie made of pork and lard | X | X | X | X | O | X | |
| Montreal-style smoked meat | Deli style cured beef | X | X | X | O | X | ||
| Bannock | A fried bread and dough food | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Bouilli | Québécois beef and vegetable potroast | O | ||||||
| Bologna stew | A stew made of cubed chunks of Bologna sausage | O | ||||||
| Yellow pea soup | Split pea soup eaten by settlers such as the Habitant | X | X | O | X | |||
| Poutine | A dish of fries topped with cheese curds and gravy | X | X | X | X | O | X | X |
| Montreal-style bagels | A sweet, firm, wood-fired bagel | X | O | |||||
| Pemmican | Ground dried meat, fat, and berries | X | X | |||||
| Oka cheese | Cheese originally manufactured by Trappist monks | X | X | O | ||||
| Flipper pie | Pie made with harp seal flipper | O | ||||||
| Hot chicken sandwich | Chicken (or turkey) sandwich doused in gravy and peas | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| Toutons | Fried bread from Newfoundland | O | ||||||
| Fish and brewis | Salt cod and hardtack, with pork cracklings | O | ||||||
| Rappie pie | Grated potato and meat casserole | O | ||||||
| Cretons | Pork spread containing onions and spices | X | O | |||||
| Poutine râpée | Grated Acadian stuffed potato dumpling | O | ||||||
| Nova Scotian donair | Ground beef doner kebab served with a sweet milk sauce | X | X | X | O | |||
| Garlic fingers | Dough with cheese, garlic, and sometimes meat on top, similar to pizza | X | X | X | X | O | ||
| Lobster roll | Lobster meat mixed with mayonnaise and served in a toasted hot dog bun | X | X | O | ||||
| Cipaille/sea-pie | Fish and meat layered in a pie | X | O | X | ||||
| Pictou County pizza | Regional pizza variant from Nova Scotia with its unique sauce | O |
What About Canadian Books and Stories?
Canadian literature is often split into French and English writings. These come from the writing traditions of France and Britain. The first Canadian stories were about travel and exploration. Later, three main themes appeared in Canadian literature: nature, frontier life, and Canada's place in the world. All these relate to the idea of a "garrison mentality." In recent years, Canadian literature has been greatly influenced by immigrants from around the world. By the 1990s, Canadian literature was seen as some of the best globally.
Many Canadian authors have won international awards. These include novelist and poet Margaret Atwood, who won two Booker Prizes. Nobel laureate Alice Munro is called the best living writer of short stories in English. Booker Prize winner Michael Ondaatje wrote The English Patient. This novel was made into a movie that won the Academy Award for Best Picture. L. M. Montgomery wrote a series of children's novels. The first was Anne of Green Gables in 1908.
How Does Canadian Media Work?

Canada's media is very independent and uncensored. It is also diverse and very regional. The Broadcasting Act says the media system should "protect, enrich, and strengthen Canada's cultural, political, social, and economic fabric." Canada has a well-developed media sector. But its cultural products, especially English films, TV shows, and magazines, are often overshadowed by imports from the United States. Because of this, the federal government supports Canadian culture. It does this through programs, laws, and institutions. Examples include the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (CBC), the National Film Board of Canada (NFB), and the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC).
Canadian mass media, both print and digital, in both official languages, is mostly controlled by a few large companies. The biggest is the national public broadcaster, the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. It plays a big role in creating Canadian cultural content. It runs its own radio and TV networks in both English and French. Some provincial governments also offer their own public educational TV services. Examples are TVOntario and Télé-Québec.
Non-news media content in Canada, like film and TV, is influenced by local creators. It also gets content from the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia, and France. To reduce foreign-made media, the government helps TV broadcasting. This includes regulating content and providing public money. Canadian tax laws limit foreign competition in magazine advertising.
What About Canadian Art?
Art in Canada has been shaped by thousands of years of Indigenous peoples living there. Later, artists combined British, French, Indigenous, and American art traditions. They sometimes used European styles while promoting Canadian identity. Canadian art shows these different origins. Artists have taken their traditions and adapted them to reflect life in Canada.
The Canadian government has helped develop Canadian culture. The department of Canadian Heritage gives money to art galleries. It also sets up and funds art schools and colleges. The Canada Council for the Arts, a national public arts funder, helps artists, galleries, and magazines. This helps create Canadian cultural works.
Canadian visual art has been led by artists like Tom Thomson and the Group of Seven. The Group of Seven were painters with a nationalistic and idealistic focus. They first showed their unique works in May 1920. Although called "seven," five artists were key to the group's ideas. These were Lawren Harris, A. Y. Jackson, Arthur Lismer, J. E. H. MacDonald, and Frederick Varley. Frank Johnston and Franklin Carmichael briefly joined. A. J. Casson became part of the group in 1926. Another famous Canadian artist, Emily Carr, was linked to the group. She was known for her landscapes and paintings of Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast.
What is Canadian Music Like?

Canadian music shows a variety of regional styles. Canada has a large music system. This includes church halls, chamber halls, conservatories, academies, performing arts centres, record companies, radio stations, and TV music video channels. Government programs, like the Canada Music Fund, help musicians and businesses. They create, produce, and sell original Canadian music. Because of its cultural importance and government support, the Canadian music industry is one of the largest in the world. It produces internationally famous composers, musicians, and groups. Music broadcasting in Canada is regulated by the CRTC. The Canadian Academy of Recording Arts and Sciences gives out Canada's music awards, the Juno Awards. The Canadian Music Hall of Fame honors Canadian musicians for their lifetime achievements.
Patriotic music in Canada is over 200 years old. The earliest patriotic song, "The Bold Canadian", was written in 1812. "The Maple Leaf Forever", written in 1866, was a popular patriotic song in English Canada. For many years, it was an unofficial national anthem. "O Canada" also served as an unofficial national anthem for much of the 20th century. It became the country's official anthem in 1980. Calixa Lavallée wrote the music. It was set to a patriotic poem by Sir Adolphe-Basile Routhier. The words were originally only in French. They were adapted into English in 1906.
What Sports Are Popular in Canada?

The history of organized sports in Canada goes back to the 1770s. This led to the development and popularity of major professional games. These include ice hockey, lacrosse, curling, basketball, baseball, soccer, and Canadian football. Canada's official national sports are ice hockey and lacrosse. Other popular sports are golf, volleyball, skiing, cycling, swimming, badminton, tennis, bowling, and martial arts. These are widely enjoyed by youth and amateurs. Great achievements in Canadian sports are recognized by Canada's Sports Hall of Fame. There are many other sport "halls of fame" in Canada, like the Hockey Hall of Fame.
Canada shares several major professional sports leagues with the United States. Canadian teams in these leagues include seven teams in the National Hockey League. There are also three Major League Soccer teams. One team is in Major League Baseball and one in the National Basketball Association. Other popular professional competitions include the Canadian Football League, National Lacrosse League, the Canadian Premier League, and various curling tournaments.
Canada has done well at both the Winter Olympics and Summer Olympics. It is especially known as a "winter sports nation." Canada has hosted several big international sporting events. These include the 1976 Summer Olympics, the 1988 Winter Olympics, and the 2010 Winter Olympics. It also hosted the 2015 FIFA Women's World Cup. Most recently, Canada hosted the 2015 Pan American Games and 2015 Parapan American Games in Toronto. The country will co-host the 2026 FIFA World Cup with Mexico and the United States.
Related pages
See also
 In Spanish: Canadá para niños
In Spanish: Canadá para niños
 | DeHart Hubbard |
 | Wilma Rudolph |
 | Jesse Owens |
 | Jackie Joyner-Kersee |
 | Major Taylor |