Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Royal coat of armsof the United Kingdom |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Versions | |

|
|
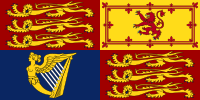
The banner of arms, which serves as a royal standard
|
|
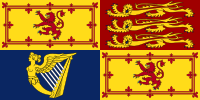
The banner of arms, which serves as a royal standard in Scotland
|
|

Herald’s tabard
|
|
| Armiger | Elizabeth II in Right of the United Kingdom |
| Adopted | 1837 |
| Crest | Upon the helm, a royal crown proper thereon a lion statant guardant Or langued Gules armed Argent, royally crowned Proper; mantled Or doubled Ermine |
| Blazon | Quarterly, I and IV Gules, three lions passant guardant in pale Or langued and armed Azure. II Or a lion rampant Gules armed and langued Azure within a double tressure flory-counter-flory Gules. III Azure a harp Or stringed Argent.; quarters for England and Scotland are exchanged in Scotland. |
| Supporters | On the dexter a lion rampant guardant Or langued and armed Gules, royally crowned Proper. On the sinister a Unicorn rampant Argent armed crined and unguled Or, and gorged with a Coronet composed of crosses patee and fleurs-de-lis, a chain affixed thereto passing through the forelegs and reflexed over the back Or |
| Compartment | Tudor rose, Shamrock, and Thistle |
| Motto | French: Dieu et mon droit, lit. 'God and my right' |
| Order(s) | Order of the Garter |
| Earlier version(s) | see below |
| Use | On all Acts of Parliament; the cover of all UK passports; various government departments; adapted for the reverse of coins of the pound sterling (2008) |
The royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom is the official symbol of the British monarch, currently Queen Elizabeth II. It's like a special emblem that shows who is in charge. The Queen uses these arms for her official duties in the United Kingdom.
Other members of the royal family and the British Government also use versions of these arms. They are seen on government papers, passports, and in courts. There's a special Scottish version of the royal arms used in Scotland. The arms also form the design for the Queen's official flag, called the Royal Standard.
The main part of the arms is a shield divided into four sections, called "quarters."
- The first and fourth quarters show three golden lions walking and looking forward. These represent England.
- The second quarter shows a red lion standing on its back legs, surrounded by a fancy border. This represents Scotland.
- The third quarter shows a golden harp, which stands for Ireland.
Above the shield is a crest. This is a golden lion wearing a crown, standing on another crown. On either side of the shield are the "supporters."
- On the right (called the "dexter" side) is a crowned English lion.
- On the left (called the "sinister" side) is a Scottish unicorn.
In the Scottish version of the arms, the English and Scottish parts on the shield and the supporters switch places.
Below the shield, you can see a thistle, a Tudor rose, and a shamrock. These plants represent Scotland, England, and Ireland. The whole design includes a motto in French, "Dieu et mon droit" (which means "God and my right"). This motto has been used by English monarchs for a long time.
Around the shield, there is a special belt called the Garter circlet. It has the motto of the Order of the Garter, "Honi soit qui mal y pense" (meaning "Shame on him who thinks evil of it"). In Scotland, the arms use the motto of the Order of the Thistle, "Nemo me impune lacessit" (meaning "No one provokes me with impunity").
Contents
What the Royal Arms Are Used For
The Queen is the only one who can use the exact Royal Arms shown above. However, you'll see them in many important places.
In Courts and Government
The Royal Arms are displayed in courtrooms. This is because the monarch is seen as the source of all justice in the UK. Judges are like representatives of the Crown. So, the Royal Arms are usually behind the judge's seat in courts. In Northern Ireland, there are special rules about where the arms can be shown.
Since the UK government acts in the monarch's name, it also uses the Royal Arms as a national symbol. You can find them on:
- Government documents and forms.
- The cover of all UK passports.
- The entrances to embassies and consulates in other countries.
When the government uses the arms, they often leave out the helmet and crest. The Scotland Office uses a simplified Scottish version.
On Coins and Flags
The Royal Arms have been on British coins for a long time. In 2008, new coin designs were made. The full Royal Arms appear on the one pound coin. Parts of the arms are on the other six coins, so you can put them together like a puzzle to form the complete arms.
Businesses that supply goods or services to the Royal Household can get a Royal Warrant. This allows them to display the Royal Arms on their products and papers to show they serve the Royal Family.
Many churches in the UK also display the Royal Arms. This shows their loyalty to the monarch.
The Royal Standard, which is a flag with the Royal Arms, is flown from royal palaces like Buckingham Palace and Windsor Castle when the Queen is there. It's also flown from public buildings only when the monarch is visiting. In Scotland, the Scottish version of the Royal Standard is used at places like the Palace of Holyroodhouse when the Queen is in residence. When the Queen is not there, the Union Flag (or the ancient Royal Standard of Scotland in Scotland) is flown instead.
Other Uses
Some newspapers, like The Times, use historical versions of the Royal Arms as their logo. The current Royal Arms are also displayed in courts in some Commonwealth realms, like British Columbia in Canada.
The Scottish Royal Arms
Since 1603, when England and Scotland came under one monarch (the Union of the Crowns), a special version of the Royal Arms has been used in Scotland. This version gives the Scottish symbols a more important place.
On the shield:
- The first and fourth quarters show the Scottish lion.
- The second quarter shows the three English lions.
- The third quarter shows the Irish harp.
The crest above the Crown of Scotland is a red lion, sitting and facing forward. It wears the Scottish Crown and holds the Scottish Sword of State and Sceptre. The Scottish motto, "In my defens God me defend" (meaning "In my defense God defend me"), appears above the crest.
The supporters (the animals holding the shield) also switch sides:
- On the right (dexter) is a crowned and chained unicorn, representing Scotland.
- On the left (sinister) is a crowned lion, representing England.
Each supporter holds a flag of its kingdom.
The Scottish arms also feature the motto "Nemo me impune lacessit" (No one provokes me with impunity). Around the shield is the collar of the Order of the Thistle. The base of the arms shows several thistles, Scotland's national flower.
England, Wales, and Northern Ireland
When Ireland joined with Great Britain in 1801, there wasn't a separate Irish version of the royal arms created. The harp on the shield represents Ireland in both the English and Scottish versions of the arms.
There is no specific symbol for Wales in the Royal Arms. This is because Wales became a part of England a long time ago, before the current arms were designed. So, Wales is considered to be represented within the English part of the arms.
Historically, a Welsh Dragon was used as a supporter on the Royal Arms by the Tudor monarchs, who had Welsh roots. But later kings and queens replaced it with the Scottish unicorn.
Today, the Prince of Wales (the monarch's heir) has his own special arms. These include a small shield with the ancient arms of Wales on them.
History of the Royal Arms
The Royal Arms we see today are a mix of symbols from the old kingdoms that now form the United Kingdom. They have changed many times over the centuries.
Early English and Scottish Arms
The first royal arms of England can be traced back to King Richard I in the late 1100s. His second Great Seal showed three golden lions on a red background. This design was used by English kings for many years.
In 1340, King Edward III added the French fleurs-de-lis (a lily symbol) to the arms. He did this to show his claim to the throne of France.
The Scottish royal arms, with a red lion on a yellow background, were first used by King William I in the 12th century. This became the main symbol for Scotland.
Union of the Crowns and Beyond
In 1603, James VI of Scotland also became King of England and Ireland. This was called the Union of the Crowns. He combined the arms of England, Scotland, and Ireland into one royal coat of arms. The Scottish version of these arms gave more importance to the Scottish symbols.
During the time of the Commonwealth of England (when England was a republic without a king), different arms were used. These included symbols for England, Scotland, and Ireland.
After the monarchy was restored, the traditional Royal Arms returned. Over the years, there were minor changes, especially when different royal families came to the throne. For example, when William III and Mary II ruled together, their arms were combined.
In 1707, the Acts of Union created Great Britain. The arms were updated to reflect this new kingdom. The current design has been in use since 1837.
Other Royal Arms Designs
Royal Family Members' Arms
Members of the Royal Family have their own special coats of arms. These are based on the main Royal Arms but have small differences, called "differences" or "labels." These differences show their place in the family. For example, children of the monarch have a three-point label, and grandchildren have a five-point label.





Wives of royal princes also have their own arms. These usually combine their husband's arms with their own family's arms. However, husbands of a Queen (like Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh) do not use the Royal Arms. They are given their own unique arms.



Government Use of the Arms

The UK government uses simpler versions of the Royal Arms. These often have a crown instead of the helmet and crest. The Scotland Office uses a simplified Scottish version.
You can see these simplified Royal Arms on:
- All Acts of Parliament (laws passed by Parliament).
- The cover of all UK passports.
- Diplomatic flags used by British Ambassadors.
Courts in some Commonwealth countries also use the Royal Arms. For example, courts in British Columbia and South Australia display them.
Other government bodies use parts of the Royal Arms as their symbols, such as the Home Office and the Royal Mint. The Royal Arms are also part of the rank badges for senior Warrant Officers in the British Armed Forces.
Images for kids
-
The arms of Princess Beatrice.
-
The arms of Princess Eugenie.
-
The arms of Prince Edward, Earl of Wessex.
-
The arms of Prince Richard, Duke of Gloucester.
-
The arms of Prince Edward, Duke of Kent.
-
The arms of Prince Michael of Kent.
-
The arms of Princess Alexandra, The Honourable Lady Ogilvy.
-
The early arms of Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh.
-
The arms of Sophie, Countess of Wessex.
-
The arms of Birgitte, Duchess of Gloucester.
-
The arms of Katharine, Duchess of Kent.
-
The arms of Princess Michael of Kent.
See also
 In Spanish: Escudo del Reino Unido para niños
In Spanish: Escudo del Reino Unido para niños
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |





































