England facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
England
|
|
|---|---|
Location of England (dark green)
– on the European continent (green & dark grey) |
|
| Status | Country |
| Capital and largest city
|
London 51°30′N 0°7′W / 51.500°N 0.117°W |
| National language | English |
| Regional languages | Cornish |
| Ethnic groups
(2021)
|
List
|
| Religion
(2021)
|
List
46.3% Christianity
36.7% no religion 6.7% Islam 1.8% Hinduism 0.9% Sikhism 0.5% Judaism 0.5% Buddhism 0.6% other 6.0% not stated |
| Demonym(s) | English |
|
|
| Government | Part of a constitutional monarchy, direct government exercised by the UK Government |
|
• Monarch
|
Charles III |
| Parliament of the United Kingdom | |
| • House of Commons | 533 MPs (of 650) |
| Establishment | |
| by 12 July 927 | |
| 1 May 1707 | |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
132,932 km2 (51,325 sq mi) |
|
• Land
|
130,310 km2 (50,310 sq mi) |
| Population | |
|
• Mid-2022 estimate
|
|
|
• 2021 census
|
|
|
• Density
|
438/km2 (1,134.4/sq mi) |
| GVA | 2022 estimate |
| • Total | £1.940 trillion |
| • Per capita | £33,976 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
|
• Total
|
£2.162 trillion |
|
• Per capita
|
£37,852 |
| Currency | Pound sterling (GBP; £) |
| Time zone | UTC+0 (Greenwich Mean Time) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC+1 (British Summer Time) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy (AD) |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +44 |
| ISO 3166 code | GB-ENG |
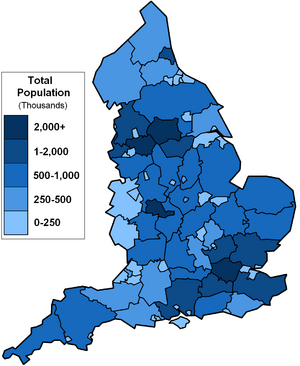
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It covers about 62% of the island of Great Britain. England also includes over 100 smaller islands nearby. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west. To the east, you'll find the North Sea, to the south the English Channel, and to the west the Irish Sea and Celtic Sea. Continental Europe is to the south-east, and Ireland is to the west. In 2021, England's population was over 56 million people. London is both the largest city and the capital.
Contents
What Does the Name England Mean?
The name "England" comes from the Old English word Englaland. This means "land of the Angles". The Angles were one of the Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain long ago. They came from a place called Angeln, near the Baltic Sea. The name "Engla londe" was first written down in the late 800s.
Sometimes, England is also called Albion. This name used to refer to the whole island of Great Britain. Now, "Albion" is a poetic way to talk about England. Another old name for England is Loegria. This name is linked to the Welsh word for England, Lloegr. It became popular from stories about King Arthur.
A Brief History of England
Early Times: Prehistory and Ancient History

The first signs of humans in England are from about 780,000 years ago. The oldest human bones found are 500,000 years old. Modern humans lived here during the Stone Age. But people only started living in permanent homes about 6,000 years ago.
After the last ice age, large animals like mammoths lived here. Around 11,000 years ago, as the ice melted, people came back to the area. They likely came from the northern part of Spain. Back then, Britain was connected to Ireland and Europe by land bridges.
As sea levels rose, Britain separated from Ireland 10,000 years ago. It separated from Europe about 2,000 years later.
The Beaker culture arrived around 2,500 BC. They brought clay pots for food and drinks. They also used pots to melt copper. These people learned to make bronze by mixing tin and copper. Later, they made iron from iron ores. Making iron helped them create better tools for farming. It also led to more effective weapons.
During the Iron Age, Celtic culture came from Central Europe. People spoke a language called Brythonic. The Romans tried to invade Britain twice in 55 BC. They didn't fully succeed but set up a friendly king.
The Romans successfully invaded Britain in 43 AD. This was during the time of Emperor Claudius. They conquered much of Britain and made it a Roman province called Britannia. Boudica, a queen of the Iceni tribe, led a famous uprising. But her rebellion ended after the Battle of Watling Street. The Romans brought their laws, buildings, water systems, and farming methods.
Christianity likely arrived in England by the 4th century, possibly earlier.
The Middle Ages in England

When the Roman soldiers left Britain, new invaders arrived. These were pagan warriors from northern Europe. They were mainly the Angles, Saxons, and Jutes. They had been raiding the coasts and began to settle, especially in the east. This time is often called a "Dark Age" because there are few written records.
About a dozen kingdoms formed, including Northumbria, Mercia, and Wessex. In the 7th century, Northumbria and Mercia fought for power. Mercia became the strongest in the 8th century. Then, in the early 9th century, Wessex became the most powerful kingdom. Later, the Danes conquered much of northern and eastern England. Wessex, led by Alfred the Great, was the only English kingdom left. Alfred's successors slowly expanded their control. This led to England becoming a single country. Æthelstan first achieved this in 927. Eadred made it permanent in 953.
New attacks from Scandinavia happened in the late 900s. Sweyn Forkbeard conquered England in 1013. His son, Cnut, conquered it again in 1016. England became the center of a short-lived North Sea Empire. But the original English royal family returned in 1042 with Edward the Confessor.
After Edward's death, there was a fight for the throne. This led to the Norman conquest of England in 1066. An army led by Duke William of Normandy won. The Normans came from Scandinavia and had settled in Normandy. This conquest replaced the English leaders with a new French-speaking upper class.
The House of Plantagenet family took over the English throne with Henry II. They ruled for 300 years. Important kings included Richard I, Edward I, Edward III, and Henry V. During this time, trade and laws changed. The Magna Carta was signed. This important document limited the king's power and protected people's rights.
In the 1300s, the Plantagenets and the French Valois family both claimed the French throne. This led to the Hundred Years' War. In 1348, the Black Death hit England. It killed up to half of the people. From 1453 to 1487, a civil war called the Wars of the Roses took place. This was between two parts of the royal family: the Yorkists and the Lancastrians. Eventually, the Welsh Tudors took the throne.
Early Modern England
During the Tudor period, the Renaissance arrived in England. England started to become a strong naval power. Explorers began to travel west across the ocean.
King Henry VIII separated England from the Catholic Church in 1534. He became the head of the new Church of England. He also officially joined Wales with England. There were religious conflicts during the reigns of his daughters, Mary I and Elizabeth I.
England started to compete with Spain for colonies. The first English colony in America was founded in 1585 in Virginia. It was called Roanoke but later became known as the "lost colony" because everyone disappeared. England also competed with the Dutch and French in the East through the East India Company.
In 1588, during the Elizabethan period, an English fleet led by Francis Drake defeated the Spanish Armada. In 1603, James VI, the King of Scots, also became King of England. He called himself King of Great Britain.
The English Civil War was fought between supporters of Parliament and King Charles I. Parliament won, and Charles I was executed. England became a republic called the Commonwealth. Oliver Cromwell, the leader of Parliament's forces, became Lord Protector in 1653. After Cromwell's death, Charles II was invited back as king in 1660. This event is known as the Restoration.
After the Glorious Revolution in 1688, it was decided that the King and Parliament would rule together. But Parliament would have the real power. This was set out in the Bill of Rights in 1689. It stated that only Parliament could make laws and raise an army. Also, no British monarch has entered the House of Commons when it is meeting since then. This shows Parliament's independence from the monarch.
In 1666, the Great Fire of London almost destroyed the city. But it was rebuilt quickly. Many important buildings were designed by Sir Christopher Wren. In Parliament, two groups formed: the Tories and Whigs. In 1707, the parliaments of England and Scotland agreed to join. This created the Kingdom of Great Britain.
Modern and Contemporary England
England's trade overseas grew hugely, protected by the Royal Navy. This led to the creation of the British Empire. At home, it started the Industrial Revolution. This was a time of big changes in English culture and society. In 1825, the world's first public passenger railway opened. It was the Stockton and Darlington Railway.
During the Industrial Revolution, many people moved from the countryside. They went to new and growing cities to work in factories.
During the Napoleonic Wars, Napoleon planned to invade England. But his attempt failed. The British defeated his forces at sea and on land.

London became the largest city in the world during the Victorian era. In World War I, many English soldiers died fighting for the United Kingdom. Twenty years later, in World War II, the United Kingdom was one of the Allies. After the war, the British Empire quickly lost its colonies.
Geography of England
Land and Rivers
England covers the central and southern parts of Great Britain. It also includes islands like the Isle of Wight and the Isles of Scilly. Scotland is to the north, and Wales is to the west. England is separated from France by a 21-mile sea gap. They are connected by the Channel Tunnel. England also has coasts on the Irish Sea, North Sea, and Atlantic Ocean.
The River Severn is the longest river flowing through England, at 220 miles. It flows into the Bristol Channel. It is known for its "Severn Bore," a wave that can be 2 meters high. The longest river entirely in England is the River Thames, which is 215 miles long. England has many lakes. The largest is Windermere.

The Pennines are the oldest mountains in England. They are called the "backbone of England." They formed about 300 million years ago. The highest point in England is Scafell Pike in Cumbria, at 978 meters. The Cheviot Hills are on the border between England and Scotland.
The English Lowlands are south of the Pennines. They have green, rolling hills. These include the Cotswold Hills, Chiltern Hills, and the North Downs and South Downs. Where these hills meet the sea, they form white cliffs, like the White Cliffs of Dover.
Climate and Weather
England has a mild maritime climate. Winters are around 0°C, and summers are usually not hotter than 32°C. The weather is often damp and can change quickly. January and February are the coldest months. July is usually the warmest. The west of England gets more rain. Parts of the Lake District get the most rain in the country.
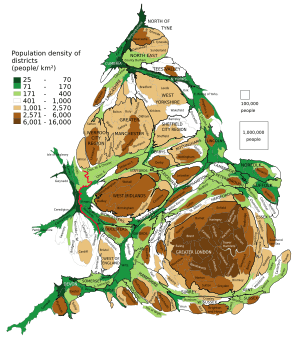
Major Cities and Urban Areas
The Greater London Built-up Area is the biggest urban area in England. It is one of the busiest cities in the world.
Many cities in England are quite large. These include Birmingham, Sheffield, Manchester, Liverpool, Leeds, and Newcastle. But a city's size is not the only reason it gets "city status."
| Largest urban areas of England 2011 census |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Conurbation | Pop. | Principal settlement
|
||||||
| 1 | Greater London | 9,787,426 | London | ||||||
| 2 | Greater Manchester | 2,553,379 | Manchester | ||||||
| 3 | West Midlands | 2,440,986 | Birmingham | ||||||
| 4 | West Yorkshire | 1,777,934 | Leeds | ||||||
| 5 | Liverpool | 864,122 | Liverpool | ||||||
| 6 | South Hampshire | 855,569 | Southampton | ||||||
| 7 | Tyneside | 774,891 | Newcastle upon Tyne | ||||||
| 8 | Nottingham | 729,977 | Nottingham | ||||||
| 9 | Sheffield | 685,368 | Sheffield | ||||||
| 10 | Bristol | 617,280 | Bristol | ||||||
England's Economy


England has one of the world's largest and most active economies. The average income per person is about £28,100. The official money in England is the pound sterling.
England is a leader in making chemicals and medicines. It's also strong in high-tech industries like aerospace (planes and space travel) and software. London is the biggest financial center in Europe. In 2014, it was the second largest in the world. Manchester has the biggest financial and professional services outside London.
The Bank of England is the central bank for the whole United Kingdom.
England used to have many heavy industries like factories. But since the 1970s, it has focused more on service industries. Tourism is now a big part of the economy. Millions of people visit England every year. England exports things like medicines, cars (even if some brands are foreign-owned), oil, airplane engines, and alcoholic drinks.
Farming in England is very modern and efficient. It produces 60% of the food needed with only 2% of the workers. Two-thirds of farming is for animals, and one-third is for crops. Main crops include wheat, barley, oats, potatoes, and sugar beets. England also has a fishing industry. It catches many kinds of fish. The country is rich in natural resources like coal, petroleum, natural gas, tin, and limestone.
Science and Technology in England

Many famous English people have made big contributions to science and math. These include Sir Isaac Newton, Michael Faraday, Charles Darwin, Alan Turing, and Stephen Hawking. Some experts believe the first idea for a metric system came from John Wilkins in 1668.
England was a key place for the Scientific Revolution in the 1600s. As the birthplace of the Industrial Revolution, England had many important inventors in the late 1700s and early 1800s. Famous English engineers include Isambard Kingdom Brunel. He built the Great Western Railway, famous steamships, and many bridges. His work changed public transport and modern engineering. Thomas Newcomen's steam engine helped start the Industrial Revolution.
George Stephenson, known as the "Father of Railways," built the world's first public inter-city railway. It was the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, opened in 1830. Matthew Boulton helped market and make the steam engine. He is seen as one of history's most important business people. The doctor Edward Jenner created the smallpox vaccine. It is said to have saved more lives than all wars combined.
English inventions and discoveries include the jet engine, the first industrial spinning machine, the first computer, and the World Wide Web. Other inventions are the first successful human blood transfusion, the motorized vacuum cleaner, the lawn mower, and the seat belt. Newton developed ideas like gravity and calculus. Robert Hooke discovered his law of elasticity.
The Royal Society is the UK's national science academy. It was founded in 1660 by King Charles II. It is the oldest national scientific group in the world. It helps science by promoting its benefits, supporting research, and advising on policy.
Science research is still important in England's universities. Many have science parks to work with industries. Between 2004 and 2008, the UK produced 7% of the world's science papers. It had 8% of science citations, ranking third and second globally. Famous science journals from the UK include Nature and the British Medical Journal.
Transport in England

The Department for Transport is the government group that manages transport in England. The Secretary of State for Transport leads it.
England has a very good and modern transport system. There are many motorways (large highways) and other main roads. The longest motorway in England is the M6. It runs for 232 miles from Rugby to the Scottish border.
Buses are common across the country. The red double-decker buses in London are a famous symbol of England.
The National Cycle Route offers bike paths across the country. Two English cities have rapid transit systems: the London Underground and the Tyne and Wear Metro in Newcastle. There are also several tram networks.
Train travel in England is the oldest in the world. Passenger railways started in England in 1825. Much of Britain's 10,000-mile rail network is in England. You can travel by train to France and Belgium through the Channel Tunnel, which opened in 1994.
England has many flights within the country and to other countries. The largest airport is Heathrow. Other big airports include Gatwick and Manchester.
By sea, there are ferries for local and international travel. These go from places like Liverpool to Ireland and Hull to the Netherlands. England has about 4,400 miles of waterways that boats can use. The River Thames is the main waterway.
Tourism in England

English Heritage is a government group that looks after England's historic sites and artifacts. The National Trust is a charity that also maintains many sites. Out of 25 UNESCO World Heritage Sites in the UK, 17 are in England.
Some famous World Heritage Sites include Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites, the Tower of London, and the Jurassic Coast. Others are the Palace of Westminster, Roman Baths, and Saltaire. The northernmost part of the Roman Empire, Hadrian's Wall, is 73 miles long in northern England.
The government minister for tourism is the Secretary of State for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport.
A blue plaque is a special sign put up in public places in England. It marks a link between that spot and a famous person or event. This idea started in 1863. In 2011, England had about 1,600 museums. Most state-supported museums and galleries are free to enter.
London is one of the most visited cities in the world. It is known as a global center for money, arts, and culture.
People and Languages of England
Population of England
England has over 53 million people. This makes it the most populated country in the United Kingdom. It accounts for 84% of the UK's total population.
England has one native national minority group: the Cornish people. The UK government recognized them in 2014.
Languages Spoken in England
| Language | Native speakers
(thousands) |
|---|---|
| English | 46,937 |
| Polish | 529 |
| Punjabi | 272 |
| Urdu | 266 |
| Bengali | 216 |
| Gujarati | 212 |
| Arabic | 152 |
| French | 145 |
| Portuguese | 131 |
| Welsh | 8 |
| Cornish | 0.6 |
| Other | 2,267 |
| Population | 51,006 |
As its name suggests, the English language started in England. Today, hundreds of millions of people around the world speak it. In England, 98% of people speak English as their main language.
England also has two other native languages: Cornish and Welsh. Cornish stopped being a common language in the 1700s. But it is now being brought back. It is protected by a European agreement. About 0.1% of people in Cornwall speak Cornish. It is taught in some schools.
State schools teach students a second language from age seven. Most often, these are French, Spanish, or German.
Religion in England

In the 2011 census, 59.4% of people in England said they were Christian. 24.7% said they had no religion. 5% were Muslim, and 3.7% belonged to other religions. 7.2% did not answer.

The patron saint of England is Saint George. His cross is on the flag of England and also on the Union Flag. There are many other English saints. Some famous ones are Cuthbert, Edmund, and Thomas Becket.
Non-Christian religions are also practiced. Jewish people have lived in England as a small group since 1070. They were forced to leave in 1290 but were allowed back in 1656.
Culture of England
Architecture and Buildings

Very old stone monuments were built in prehistoric times. Famous ones include Stonehenge and Castlerigg. When the Romans arrived, they brought their style of building. They built basilicas, baths, amphitheaters, and aqueducts. The Romans founded the first cities like London, Bath, and York. Hadrian's Wall is a well-known Roman structure across northern England. The Roman Baths in Bath are another good example.
In the early Middle Ages, buildings were simple, mostly made of wood with thatched roofs. Churches had unique designs. After the Norman conquest in 1066, many castles were built. These helped rulers keep control and protect against invasions. Some famous medieval castles are the Tower of London, Warwick Castle, and Windsor Castle.
During the Plantagenet era, English Gothic architecture became popular. Cathedrals like Canterbury Cathedral, Westminster Abbey, and York Minster are great examples. This style also influenced castles, palaces, and large houses. The 16th-century Tudor style finished the medieval period. It featured the "Tudor arch" and wattle and daub houses. After the Renaissance, the English Baroque style appeared, mixing classical and Christian ideas. Architect Christopher Wren was very important in this style.
Georgian architecture followed, with a simpler, more refined look. The Royal Crescent in Bath is a good example. During the Victorian period, the Gothic Revival style returned. The Industrial Revolution also led to new buildings like The Crystal Palace. Since the 1930s, modernist styles have appeared. These are sometimes controversial, but traditional styles are still supported.
English Folklore and Legends

English folklore has grown over many centuries. Some stories are known across England, but most belong to specific regions. Common folk creatures include pixies, giants, elves, bogeymen, and trolls. Many legends are very old, like tales of Offa of Angel. Others are newer, from after the Norman invasion. Robin Hood and his Merry Men from Sherwood Forest are perhaps the most famous. They fought against the Sheriff of Nottingham.
During the Middle Ages, stories from Celtic traditions became part of English folklore. These were the Arthurian myths. They came from French and Welsh sources. They feature King Arthur, Camelot, Excalibur, Merlin, and the Knights of the Round Table like Lancelot. These stories are mostly found in Geoffrey of Monmouth's History of the Kings of Britain.
Some folk figures are based on real or semi-real people. Hereward the Wake was an English hero who fought the Norman invasion. Herne the Hunter is a ghost linked to Windsor Forest. Mother Shipton is a famous witch. On November 5th, people light bonfires and set off fireworks. They eat toffee apples to remember the Gunpowder Plot and Guy Fawkes.
There are many folk activities still done today. These include Morris dancing, Maypole dancing, and cheese-rolling. England does not have an official national costume. But some are well-known, like the Pearly Kings and Queens and the Morris costume.
English Food and Drink



Historically, English food was known for being simple. It relied on good quality natural ingredients. In the Middle Ages and Renaissance, English cooking had a great reputation. But it declined during the Industrial Revolution as people moved to cities. Recently, English cuisine has seen a comeback. Food critics have given it good reviews. An early English recipe book is the The Forme of Cury from King Richard II's court.

Traditional English meals include the Sunday roast. This is roasted meat (like beef or chicken) with vegetables, Yorkshire pudding, and gravy. Other popular dishes are fish and chips and the full English breakfast. This breakfast usually has bacon, sausages, eggs, and baked beans.
Various meat pies are eaten, such as steak and kidney pie. Sausages are common, often in bangers and mash. Lancashire hotpot is a famous stew. Popular cheeses include Cheddar and Blue Stilton. Many Anglo-Indian dishes, like chicken tikka masala, have been created. Traditional English desserts include apple pie and spotted dick, often served with custard. Sweet pastries like scones and Eccles cakes are also popular.
Common drinks include tea, which became popular thanks to Catherine of Braganza. Alcoholic drinks often include wines, ciders, and English beers like bitter and stout.
Visual Arts in England

The oldest art found in England is prehistoric rock and cave art. These are mostly in North Yorkshire and Northumberland. When the Romans arrived, they brought art like statues, mosaics, and glasswork. Many Roman artifacts still exist. During the early Middle Ages, art included sculpted crosses, ivory carvings, and gold jewelry. These often had detailed, interwoven designs. The Lindisfarne Gospels are a famous example. Later, Gothic art was popular.
The Tudor era saw important artists in the royal court. Portrait painting became a lasting part of English art. German artist Hans Holbein the Younger helped this. Native artists like Nicholas Hilliard continued this style. Under the Stuarts, Flemish artists like Anthony van Dyck were influential. The 1700s were important for art, with the founding of the Royal Academy of Arts. Thomas Gainsborough and Joshua Reynolds became two of England's most loved artists.
The Norwich School continued the tradition of landscape painting. The Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood brought back an earlier Renaissance style. Their work was vivid and detailed. Holman Hunt and Dante Gabriel Rossetti were leaders. In the 20th century, Henry Moore became a key figure in British sculpture. Modern painters include Lucian Freud. His painting Benefits Supervisor Sleeping set a world record in 2008.
Literature, Poetry, and Philosophy
Early writers like Bede wrote in Latin. The period of Old English literature gave us the epic poem Beowulf. It also produced the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle and Christian writings. After the Norman conquest, Latin was still used by educated people.
Middle English literature began with Geoffrey Chaucer, who wrote The Canterbury Tales. William of Ockham and Roger Bacon were important philosophers in the Middle Ages. Julian of Norwich was a famous Christian mystic. With the English Renaissance, literature in Early Modern English appeared. William Shakespeare is one of the most celebrated English writers. His works include Hamlet, Romeo and Juliet, and Macbeth.
Other important writers of the Elizabethan age include Christopher Marlowe and Ben Jonson. Francis Bacon and Thomas Hobbes wrote about empiricism (learning from experience) and the scientific method. John Milton wrote Paradise Lost during the Restoration.
This royal throne of kings, this sceptred isle, this earth of majesty, this seat of Mars, this other Eden, demi-paradise; this fortress, built by nature for herself. This blessed plot, this earth, this realm, this England.
Important philosophers of the Enlightenment were John Locke and Thomas Paine. The poet Alexander Pope was known for his satirical poems. The English played a big role in romanticism. Key figures included Samuel Taylor Coleridge, Lord Byron, and William Wordsworth.
Writers from the Victorian era include Charles Dickens, the Brontë sisters, Jane Austen, and H. G. Wells. Since then, England has produced many famous novelists. These include George Orwell, C. S. Lewis, Agatha Christie, J. R. R. Tolkien, and J. K. Rowling.
Performing Arts in England
The traditional folk music of England is very old. It has influenced many music styles. It includes sea shanties, jigs, and dance music. Some well-known songs are Greensleeves and Maggie May. Many nursery rhymes are English, such as Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star and London Bridge Is Falling Down. Traditional English Christmas carols include "We Wish You a Merry Christmas".

Early English composers of classical music include Thomas Tallis and William Byrd. Later came Henry Purcell. German-born George Frideric Handel lived most of his life in London. He wrote famous works like The Messiah. His song Zadok the Priest has been played at every British coronation since 1727. In the 20th century, composers like Edward Elgar and Benjamin Britten became famous. Today, Andrew Lloyd Webber is known for his successful musicals.
In popular music, many English bands and artists are among the most influential. Bands like The Beatles, Led Zeppelin, Pink Floyd, and Queen are some of the world's best-selling musicians. Many music styles started in England. These include British invasion, progressive rock, heavy metal, and Britpop.
Large outdoor music festivals are popular in summer. Examples are Glastonbury and V Festival. The main opera house in England is the Royal Opera House in London. The Proms are a series of classical concerts held yearly at the Royal Albert Hall. The Royal Ballet is one of the world's top ballet companies.
English Cinema

England has greatly influenced cinema. It has produced many great actors, directors, and films. These include Alfred Hitchcock, Charlie Chaplin, David Lean, and Laurence Olivier. Hitchcock's The Lodger: A Story of the London Fog (1926) helped create the thriller genre. His 1929 film Blackmail is often seen as the first British sound movie.
Major film studios in England include Pinewood and Elstree. Some of the most successful films ever were made in England. These include the Harry Potter and James Bond series. Ealing Studios in London might be the oldest working film studio in the world. The London Symphony Orchestra first played film music in 1935.
Monty Python's Life of Brian (1979) is a film often voted the funniest by the UK public. English producers also work on international films. English actors and directors are often in American movies. Recent successful English directors include Christopher Nolan and Ridley Scott. Current actors include Tom Hardy and Emma Watson. Many Hollywood films are based on English people, stories, or events. Disney animated films like Alice in Wonderland are part of the 'English Cycle'.
Museums, Libraries, and Galleries

English Heritage is a government body that manages England's historic sites. The National Trust is a charity that also looks after many places. England has 17 of the UK's 25 World Heritage Sites.
Some of the most famous sites are Hadrian's Wall, Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites, and the Tower of London.
England has many museums. The most notable is London's British Museum. It has over seven million objects from all over the world. These show the history of human culture. The British Library in London is one of the world's largest research libraries. It holds over 150 million items. The National Gallery in London has over 2,300 paintings from the 1200s to 1900. The Tate galleries hold national collections of British and international modern art.
National Symbols of England
The St George's Cross has been the national flag of England since the 1200s. It was first used by the Republic of Genoa. English ships paid Genoa to fly the flag for protection in the Mediterranean Sea. A red cross was a symbol for many Crusaders. It became linked with Saint George and countries that claimed him as their patron saint. Since 1606, the St George's Cross has been part of the Union Flag.
England has many other symbols. These include the Tudor rose, which is the national floral emblem. The Three Lions are on the Royal Arms of England. The Tudor rose was adopted as a symbol of peace after the Wars of the Roses. It combines the white rose of the Yorkists and the red rose of the Lancastrians. It is also called the Rose of England.
The oak tree is a symbol of England. It stands for strength and endurance. The Royal Oak symbol remembers when King Charles II hid in an oak tree to escape capture.
The Royal Arms of England, with its three lions, started with Richard the Lionheart in 1198. It is a very important symbol of England.
England does not have its own official national anthem. The United Kingdom uses God Save the King. However, some songs are often considered unofficial English anthems. These include Jerusalem and Land of Hope and Glory. England's National Day is April 23rd, which is St George's Day.
Sports in England
England has a strong history in sports. In the 1800s, many sports that are now played worldwide were created here. Sports that started in England include association football, cricket, rugby union, rugby league, tennis, and boxing. England also helped develop golf and Formula One.
Football is the most popular sport in England.
FIFA recognizes England as the birthplace of club football. Sheffield F.C., founded in 1857, is the world's oldest club. The Football Association is the oldest governing body in the sport. The rules of football were first written in 1863 by Ebenezer Cobb Morley. The FA Cup and The Football League were the first cup and league competitions. Today, the Premier League is the most watched football league in the world.
Rugby union started at Rugby School in the early 1800s. The England rugby union team won the 2003 Rugby World Cup. Jonny Wilkinson scored the winning point against Australia. England also hosted the 2015 Rugby World Cup. The top club league is the English Premiership.
Rugby league began in Huddersfield in 1895. Some successful rugby clubs include Wigan Warriors and St. Helens.
Golf is also popular in England. There are professional tours for men and women. England has produced Grand Slam winners like Nick Faldo. The world's oldest golf tournament, The Open Championship, is played in England and Scotland.

Tennis was created in Birmingham in the late 1800s. The Wimbledon Championships is the oldest and most famous tennis tournament in the world. Fred Perry was the last Englishman to win Wimbledon in 1936.

Darts and snooker are very popular sports in England.
English people enjoy competitive sailing. England has produced great sailors like Ellen MacArthur and Ben Ainslie.
Education in England

Children aged 3 to 5 go to nursery or a reception class in primary school. Primary school is for children aged 5 to 11. Secondary school is for those aged 11 to 16. State-funded schools must teach the National Curriculum. This includes English, math, science, history, geography, and more.
More than 90% of English schools require students to wear uniforms. Each school decides its own uniform rules.
Most secondary schools are "comprehensive," meaning they accept all students. But some are "grammar schools" that require passing an exam. About 7.2% of English children go to private schools, which are paid for privately.
After finishing school at 16, students take GCSE exams. Students can then continue their education for two more years. This is often at a "sixth form college." They take A-level exams, which are used for university applications.
Students usually go to university from age 18. They study for an academic degree. There are over 90 universities in England. Students can get student loans to help with costs. The first degree is a bachelor's degree, which usually takes three years. Students can then study for a postgraduate degree or a doctorate.
England's universities include some of the highest-ranked in the world. University of Cambridge, University of Oxford, and Imperial College London are all in the global top 30. The London School of Economics is known for social science. The London Business School is a leading business school. Degrees are usually graded as first class, upper second class, lower second class, or third.
The King's School, Canterbury and King's School, Rochester are the oldest schools in the English-speaking world. Many famous English schools, like Winchester College and Eton, are fee-paying.
Images for kids
-
View of the ramparts of the developed hillfort of Maiden Castle, Dorset, as they look today
-
King Henry V at the Battle of Agincourt, fought on Saint Crispin's Day and concluded with an English victory against a larger French army in the Hundred Years' War
-
The English Restoration restored the monarchy under King Charles II and peace after the English Civil War.
-
The River Thames during the Georgian period from the Terrace of Somerset House looking towards St. Paul's, c.1750
-
The Battle of Trafalgar was a naval engagement between the British Royal Navy and the combined fleets of the French and Spanish Navies during the Napoleonic Wars.
-
The Victorian era is often cited as a Golden Age.
-
The Malvern Hills located in the English counties of Worcestershire and Herefordshire. The hills have been designated by the Countryside Agency as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty.
-
Deer in Richmond Park. The park was created by Charles I in the 17th century as a deer park.
-
William Beveridge's 1942 report Social Insurance and Allied Services (known as the Beveridge Report) served as the basis for the post-World War II welfare state
-
The landscape garden at Stourhead. Inspired by the great landscape artists of the seventeenth century, the landscape garden was described as a "living work of art" when first opened in 1750s.
-
Robin Hood and Maid Marian.
-
The Hay Wain by John Constable, 1821, is an archetypal English painting.
See also
 In Spanish: Inglaterra para niños
In Spanish: Inglaterra para niños