Baltic Sea facts for kids
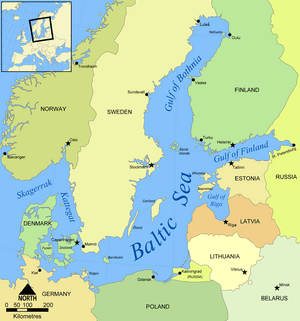
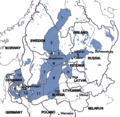
The Baltic Sea is a special sea located in northern Europe. It's surrounded by many countries like Scandinavia (which includes Sweden, Denmark, and Norway), Finland, Russia, the Baltic countries (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania), Poland, and Germany.
Many large rivers from these nearby countries flow into the Baltic Sea. It connects to the big ocean through some narrow and shallow passages called the Danish straits. Because these connections are small, the water in the Baltic Sea doesn't mix much with the ocean. This means it has less salt than the open ocean.
In the northern parts of the Baltic Sea, the water often freezes solid in winter. The ice can become so thick that people can drive cars on it! Special ice roads are sometimes made between islands in the archipelagos, especially between Sweden and Finland. For thousands of years, the Baltic Sea has been a natural highway, connecting the countries along its shores. This has led to many shared traditions and cultures among the people living there.
Contents
What Makes the Baltic Sea Unique?
The Baltic Sea is quite different from other seas and oceans. Its low saltiness makes it a unique environment for plants and animals.
A Mix of Fresh and Salt Water
The Baltic Sea is often called a "brackish" sea. This means its water is a mix of fresh water from rivers and salty water from the ocean. The amount of salt changes depending on where you are. The parts closest to the Danish straits are saltier. The northern parts, like the Gulf of Bothnia and the Gulf of Finland, are much fresher. This mix creates a special home for many types of fish and other sea creatures.
Winter Wonderland: Ice Roads and More
Every winter, especially in the northern areas, the Baltic Sea can turn into a giant ice rink.
- The ice can be strong enough to support cars and even trucks.
- Official ice roads are sometimes opened, making travel easier between islands.
- People also enjoy activities like ice skating, skiing, and ice fishing on the frozen sea.
This freezing is a big part of life for the people living along its northern coasts.
Countries Around the Baltic Sea
Nine countries share the coastline of the Baltic Sea. Each has its own unique connection to this important body of water.
- Sweden: Has a long coastline with many islands and archipelagos.
- Finland: Known for its beautiful Archipelago Sea and many coastal cities.
- Russia: Has important ports like Saint Petersburg on the Gulf of Finland.
- Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania: These are the Baltic countries, with rich maritime histories.
- Poland: Features popular beaches and historic port cities like Gdańsk.
- Germany: Has important harbors and coastal resorts along its Baltic coast.
- Denmark: Connects the Baltic Sea to the North Sea through its straits.
History and Culture of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea has played a huge role in the history and culture of Northern Europe.
Ancient Connections
For thousands of years, people have traveled and traded across the Baltic Sea.
- Ancient tribes and Vikings used the sea for exploration and trade.
- This helped spread ideas, goods, and cultures between different groups of people.
- Many old settlements and trading posts grew up along its shores.
The Hanseatic League
One of the most famous examples of trade on the Baltic Sea was the Hanseatic League.
- This was a powerful group of merchant cities in Northern Europe during the Middle Ages.
- They controlled trade routes across the Baltic and North Seas.
- Cities like Lübeck, Hamburg, Gdańsk, and Riga were important members.
- The League helped spread wealth and culture throughout the region.
Modern Importance
Today, the Baltic Sea remains very important for trade, travel, and the environment.
- It's a busy shipping route for goods traveling between Europe and other parts of the world.
- Many ferries connect cities and countries around the sea.
- It's also a popular place for tourism, with beautiful beaches and historic towns.
Protecting the Baltic Sea
Because the Baltic Sea is partly enclosed and has low saltiness, it's very sensitive to pollution.
- Rivers bring pollution from farms and cities into the sea.
- Shipping traffic also poses risks.
- Many countries and organizations are working together to protect the Baltic Sea.
- They aim to reduce pollution and keep its unique ecosystem healthy for future generations.
Images for kids
-
Åland between Baltic Sea and the Gulf of Bothnia
-
Cape Arkona on the island of Rügen in Germany, was a sacred site of the Rani tribe before Christianization.
-
Main trading routes of the Hanseatic League (Hanse).
-
In 1649 the settlement of the Latvian-speaking Kursenieki spanned from Klaipėda to Gdańsk along the coast of the Baltic Sea.
-
Curonian Spit in Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia
-
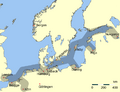
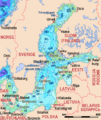
Regions and basins of the Baltic Sea: 1 = Bothnian Bay 2 = Bothnian Sea 1 + 2 = Gulf of Bothnia, partly also 3 & 4 3 = Archipelago Sea 4 = Åland Sea 5 = Gulf of Finland 6 = Northern Baltic Proper 7 = Western Gotland Basin 8 = Eastern Gotland Basin 9 = Gulf of Riga 10 = Bay of Gdańsk/Gdansk Basin 11 = Bornholm Basin and Hanö Bight 12 = Arkona Basin 6–12 = Baltic Proper 13 = Kattegat, not an integral part of the Baltic Sea 14 = Belt Sea (Little Belt and Great Belt) 15 = Öresund (The Sound) 14 + 15 = Danish Straits, not an integral part of the Baltic Sea
-
Baltic Sea near Klaipėda (Karklė).
-
Skerries form an integral and typical part of many of the archipelagos of the Baltic Sea, such as these in the archipelago of Åland, Finland.
-
Aerial view of Bornholm, Denmark
-
Vasilyevsky Island in Saint Petersburg, Russia
-
Stockholm in Sweden
-
Riga in Latvia
-
Helsinki in Finland
-
Gdańsk in Poland
-
Tallinn in Estonia
-
Svetlogorsk resort town in Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia
See also
 In Spanish: Mar Báltico para niños
In Spanish: Mar Báltico para niños
 | Madam C. J. Walker |
 | Janet Emerson Bashen |
 | Annie Turnbo Malone |
 | Maggie L. Walker |