Gulf of Bothnia facts for kids
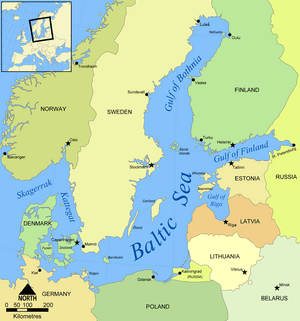
The Gulf of Bothnia is the northernmost part of the Baltic Sea. It is located between the west coast of Finland and the east coast of Sweden. In the southern part of the gulf are the Åland Islands, which sit between the Sea of Åland and the Archipelago Sea. The Gulf of Bothnia is often divided into three main sections. These sections have Finnish names:
- Perämeri: This is the northernmost part of the gulf.
- Merenkurkku: This is the narrowest part, also known as the Kvarken.
- Selkämeri: This is the southernmost part of the gulf.
Contents
A Unique Sea Area
The Gulf of Bothnia is a very special body of water. It is quite shallow and has a low salt content, especially in the northern parts. This is because many rivers flow into it, bringing fresh water from the land. The low saltiness means that some animals and plants that usually live in fresh water can survive here, alongside some sea creatures.
Ice and Seasons
During winter, the northern parts of the Gulf of Bothnia often freeze completely. This creates a thick layer of ice that can last for several months. Icebreakers, which are special ships, are needed to keep shipping lanes open. When spring arrives, the ice melts, and the gulf becomes a busy place for boats and ships again. The changing seasons make the gulf a dynamic environment.
Land Rising from the Sea
A fascinating thing about the Gulf of Bothnia is that the land around it is still rising. This process is called post-glacial rebound. It happens because the heavy ice sheets from the last Ice Age melted away, and the land is slowly bouncing back up. This means that the coastline is constantly changing, and new land areas appear over time. Some old harbors are now far from the water because the land has risen so much!
Life in the Gulf
Despite the low saltiness and cold winters, the Gulf of Bothnia is home to many different kinds of animals and plants.
Animals of the Gulf
You can find various fish species here, including herring, salmon, and pike. Seals, like the ringed seal and the grey seal, also live in the gulf. They are well-adapted to the cold waters and often rest on the ice during winter. Many birds use the gulf as a resting or breeding place, especially during their migrations.
Plants and Ecosystems
The plant life in the gulf is a mix of freshwater and saltwater species. Reeds and other marsh plants grow along the shallow coastlines. Underwater, different types of algae and aquatic plants provide food and shelter for marine life. The unique conditions create a special ecosystem that supports all these creatures.
Human Activities and Importance
The Gulf of Bothnia is very important for the countries around it.
Shipping and Trade
Shipping is a major activity in the gulf. Ships carry goods between Finland and Sweden, and to other parts of the Baltic Sea. Harbors along the coast are busy centers for trade and industry. Even when the gulf freezes, icebreakers work hard to keep these important routes open.
Fishing and Recreation
Fishing has always been a way of life for people living near the gulf. Today, both commercial fishing and recreational fishing are popular. People also enjoy boating, sailing, and swimming in the warmer months. In winter, ice fishing, ice skating, and even driving on the ice are common activities in some areas. The beautiful natural environment also attracts tourists who enjoy hiking and exploring the coast.
Images for kids
-
Satellite image of Fennoscandia in winter. The northern part of the Gulf of Bothnia, the Bothnian Bay, is covered with sea ice.
-
Pilot station and lighthouse in the Hailuoto Island, a municipality island at the Bothnian Bay near the city of Oulu
-
Sandy beaches of Kalajoki at the shores of the Gulf of Bothnia
See also
 In Spanish: Golfo de Botnia para niños
In Spanish: Golfo de Botnia para niños





