Culture of England facts for kids
The culture of England is made up of the special ways of life and traditions of England and the English people. Because England is a big part of the United Kingdom, it can sometimes be hard to tell English culture apart from the culture of the whole UK.
However, England has had its own unique culture for a very long time, different from Welsh, Scottish, or Irish cultures. This has been true since the time of the Anglo-Saxons.
Contents
- Amazing Buildings and Gardens
- English Art and Paintings
- Tasty English Food
- English Stories and Legends
- The English Language
- Famous English Books and Writers
- English Music and Musicians
- English Cinema and Films
- Fun Performing Arts
- English Thinkers and Ideas
- Religion in England
- Blue Plaques: Marking History
- Science and Inventions
- Sports and Fun Activities
- English Symbols
- Images for kids
- See also
Amazing Buildings and Gardens
English buildings have a long history, starting with the Anglo-Saxons. Many old churches from that time still stand today, even if they have been changed a lot. These early buildings were made of stone or brick.
After the Normans took over England, they brought their own style, called Norman architecture. Later, this changed into English Gothic architecture, which has three main periods. In more recent times, people started building in classical styles, like those from ancient Greece and Rome. During the Victorian era, the Gothic style became popular again for many buildings.
Big churches called cathedrals and local parish churches often feel very traditionally English. So do grand 'stately homes'. Many people love visiting these old houses and gardens, which are looked after by groups like English Heritage and the National Trust.
The idea of landscape gardening, made famous by Capability Brown, became popular all over the world. Gardening and visiting gardens are still very English hobbies.
Seaside Piers: Walkways to the Sea
The first seaside pier was built in England in 1814, on the Isle of Wight. Soon, piers became very popular at English seaside towns, especially during the Victorian era. They were like long walkways stretching out into the sea.
These piers are seen as some of the best Victorian buildings. They are a well-known symbol of British seaside holidays. By 1914, there were over 100 piers around the UK coast. Today, about 55 seaside piers still stand.
English Art and Paintings
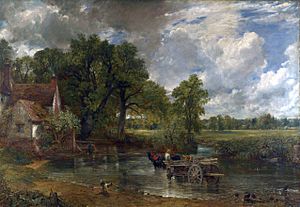
For a long time, many artists in England came from other countries. But in the 1700s, English artists became very famous. They were known for landscape paintings, like the works of J. M. W. Turner and John Constable. Artists who painted portraits, like Thomas Gainsborough and Joshua Reynolds, were also very important.
William Hogarth was a famous artist who created funny pictures that made fun of society. These pictures often told a story. After Hogarth, political cartoons became popular in England in the late 1700s, thanks to artists like James Gillray. Gillray's funny drawings often made fun of kings, prime ministers, and generals.
Tasty English Food


For hundreds of years, English food has been known for being simple and using fresh, good quality ingredients. Traditional meals include bread and cheese, roasted meats, meat pies, and fish. An old English cookbook from the 1300s, called The Forme of Cury, has recipes for these dishes.
Today, it can be hard to tell English food apart from all British cuisine. But some dishes are definitely English. The full English breakfast is a famous one. It usually has bacon, eggs, fried or grilled tomatoes, fried mushrooms, fried bread or toast, and sausage. You might also have black pudding or hash browns.
A traditional English Christmas dinner often has turkey, which first appeared in 1573. It's usually served with roast beef or ham, parsley stuffing, gravy, roast potatoes, mashed potatoes, and vegetables.
Tea and beer are very popular drinks in England. Cider is made in the West Country, and some parts of England now make white wine.
Roast beef is a food strongly linked to the English. This link became famous with a song called "The Roast Beef of Old England" and a painting by William Hogarth. In fact, the French have called the English "les rosbifs" (the roast beefs) since the 1700s!
England makes many different kinds of cheese, including:
- Cheddar cheese
- Stilton cheese (from Leicestershire)
- Wensleydale cheese
- Lancashire cheese
- Dorset Blue Vinney cheese
- Cheshire cheese
- Double Gloucester cheese
- Red Leicester
- Blue cheese
Other special English dishes include:
- The English crumpet, which is thicker than the Scottish one.
- Muffins, known as 'English muffins' in North America.
- Lancashire hotpot
- Mushy peas
- Beef Wellington
- Worcester sauce
- Clotted cream from Devon and Cornwall
- Yorkshire pudding
- Sausage and mash
- Eccles cake (from Eccles, Greater Manchester)
- Cumberland sausage
- Lincolnshire sausage
- Balti, a type of curry created in Birmingham in the 1900s.
- Apple pie
- Banoffee pie
English Stories and Legends

English folklore has grown over many centuries. Some stories and characters are known all over England, but most belong to certain regions. Common magical creatures include pixies, giants, elves, bogeymen, trolls, goblins, and dwarves.
Many old legends, like tales of Wayland the Smith, are very ancient. Others came after the Normans arrived. Robin Hood and his Merry Men from Sherwood Forest, who fought the Sheriff of Nottingham, are probably the most famous.
During the Middle Ages, stories like the Arthurian legend became popular. These tales, from Welsh sources, feature King Arthur, his sword Excalibur, and the wizard Merlin. The poet Wace added the idea of the Knights of the Round Table. These stories were collected in a book called Historia Regum Britanniae.

Some folk figures are based on real or semi-real people whose stories have been told for hundreds of years. For example, Lady Godiva supposedly rode naked through Coventry. Hereward the Wake was an English hero who fought against the Norman invasion. Herne the Hunter is a ghost linked to Windsor Forest. Mother Shipton is a famous witch.
On November 5th, people light bonfires, set off fireworks, and eat toffee apples to remember the Gunpowder Plot, which was stopped by Guy Fawkes. This is called Guy Fawkes Night.

A book from 1724, A General History of the Pyrates by Captain Charles Johnson, told the stories of many famous pirates. Many English pirates from the "Golden Age" came from the West Country. The idea of "walking the plank" became popular from the book Peter Pan, where Captain Hook's pirates do it.
The Gremlin is a creature from RAF folklore, first mentioned in the 1920s. Gremlins were said to be mischievous creatures that messed with aircraft. In London, stories about figures like Sweeney Todd, the murderous barber of Fleet Street, became romanticized.
The English Language
English people traditionally speak the English language, which belongs to the West Germanic family. Modern English grew from Middle English, which was spoken from the 1100s to the 1400s. Middle English was influenced by French and Latin. Before that, people spoke Old English. In some parts of England, Danish settlers also influenced the language. Over time, Modern English has borrowed many words from other languages like French, Latin, and Dutch.
There used to be many different English dialects (ways of speaking) in England. But today, Standard English is much more common because of education, media, and other reasons.
Cornish, a Celtic language, is spoken again in Cornwall after almost disappearing. Another Celtic language, Cumbric, was spoken in Cumbria but died out in the 1000s.
Modern English began in the late 1400s with the invention of the printing press and changes in how words were pronounced. Because of the British Empire, English spread around the world from the 1600s to the mid-1900s. Today, English is a global language for business, science, communication, sports, and diplomacy.
Common English Surnames
Here are some of the most common family names (surnames) in England:
| Rank | Surname | Origin | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Smith | England | 1.44 |
| 2 | Jones | England and Wales | 0.75 |
| 3 | Taylor | England and Scotland | 0.59 |
| 4 | Brown | Scotland | 0.56 |
| 5 | Williams | England and Wales | 0.39 |
| 6 | Wilson | Scotland and England | 0.39 |
| 7 | Johnson | England | 0.37 |
| 8 | Davis | Wales | 0.34 |
| 9 | Robinson | England | 0.32 |
| 10 | Wright | England | 0.32 |
| 11 | Thompson | England | 0.31 |
| 12 | Evans | Wales | 0.30 |
| 13 | Walker | England | 0.30 |
| 14 | White | England | 0.30 |
| 15 | Roberts | England | 0.28 |
| 16 | Green | England | 0.28 |
| 17 | Hall | England | 0.28 |
| 18 | Wood | England and Scotland | 0.27 |
| 19 | Jackson | England and Scotland | 0.27 |
| 20 | Clarke | England | 0.26 |
Famous English Books and Writers
English literature started with Anglo-Saxon literature, written in Old English. For many years, Latin and French were the main languages for writing in England. But in the medieval period, literature written in Middle English became very popular. Geoffrey Chaucer is the most famous writer from this time.
The Elizabethan era (when Queen Elizabeth I ruled) is often called a golden age for English literature. Many great poets wrote in English, and the Elizabethan theatre gave us William Shakespeare. He is often called England's national poet.
Because English became a world language during the time of the British Empire, literature is now written in English all over the world. Writers often linked to England include Shakespeare, Jane Austen, and Charles Dickens. Dickens is famous for his stories about London.
In 2003, the BBC asked people in the UK to vote for their "nation's best-loved novel." Books by English writers J. R. R. Tolkien, Jane Austen, Philip Pullman, Douglas Adams, and J. K. Rowling were the top five.
English Music and Musicians


England has a long and rich history of music. In the last half of the 1900s, there was a big interest in traditional folk music.
Important composers from the 1500s include Thomas Tallis and William Byrd. Later, George Frideric Handel became very popular in England. One of his songs, Zadok the Priest, has been played at every British coronation since 1727. In the 1800s, composers like Edward Elgar and Arthur Sullivan brought new energy to English music. In the 1900s, Benjamin Britten became a famous opera composer.
A huge change in music happened in Liverpool in 1962. The Beatles became the most popular band of their time. They, especially John Lennon and Paul McCartney, showed that musicians could write their own songs. Before them, most singers performed songs written by others. The Beatles opened the door for many other English bands to become famous around the world, like The Rolling Stones, Led Zeppelin, Pink Floyd, and Queen.
Later, bands like the Sex Pistols and The Clash started punk rock. Today, many English artists are famous, including Adele, Ed Sheeran, Coldplay, and One Direction.
English Cinema and Films

England has had a big impact on movies, producing many great actors, directors, and films. Famous names include Alfred Hitchcock, Charlie Chaplin, David Lean, Laurence Olivier, and Helen Mirren. Hitchcock's film The Lodger: A Story of the London Fog (1926) helped create the thriller movie style. His 1929 film, Blackmail, is often called the first British sound movie.
Major film studios in England include Pinewood, Elstree, and Shepperton. Some of the most successful film series ever, like Harry Potter and James Bond, were made in England. Ealing Studios in London is thought to be the oldest continuously working film studio in the world.
The BFI Top 100 British films list includes Monty Python's Life of Brian (1979), which many people vote as the funniest film ever. English directors like Christopher Nolan and Sam Mendes are very successful today. Many Hollywood films are also based on English people, stories, or events. Disney animated films like Alice in Wonderland and Winnie the Pooh are examples of this.
Fun Performing Arts
Big outdoor music festivals like Glastonbury are very popular in England during the summer. The main opera house in England is the Royal Opera House in London. The Proms, a series of classical music concerts at the Royal Albert Hall, is a big event every year. The Royal Ballet is one of the best classical ballet companies in the world.

The funny puppet show Punch and Judy first appeared in London in 1662. These shows are full of wild comedy and are still a popular part of British seaside culture. Mr. Punch is seen as a British cultural icon, known for being a bit rebellious.

The circus is a traditional form of entertainment in the UK. Chipperfield's Circus has been around for over 300 years. Philip Astley is known as the father of the modern circus. In 1768, he created the circus ring, which is still the standard size today. He added acrobats, tightrope-walkers, jugglers, and a clown to his horse-riding shows, and the modern circus was born. Joseph Grimaldi is considered the father of modern clowning.
The Notting Hill Carnival is a huge annual street festival in Notting Hill, London, that started in 1966. It's led by the British African-Caribbean community and attracts about a million people, making it one of the largest festivals in the world.

Pantomime (or "panto") is a British musical comedy show for families. It's performed in theatres across the UK during Christmas and New Year. It started in the 1700s and now includes songs, funny slapstick comedy, dancing, and actors who play characters of the opposite gender. The audience often sings along and shouts out phrases to the performers.
Music hall was a popular type of British entertainment from the Victorian era to the mid-1900s. It had a mix of popular songs, comedy, and different acts. Famous performers like Charlie Chaplin and Stan Laurel started their careers in music hall.
English Thinkers and Ideas
Important English thinkers, called philosophers, include Francis Bacon, Sir Thomas More, John Locke, Thomas Hobbes, and Isaac Newton.
Religion in England
Christianity became the most common religion in England many centuries ago. Before that, people practiced different polytheistic religions, often called paganism. These included Celtic, Norse, and Roman religions.
Christianity first came to England with the Romans. Later, missionaries from Scotland and Europe helped bring it back. In 597 AD, St Augustine became the first Archbishop of Canterbury. Early English Christian books, like the Lindisfarne Gospels from the 600s, are from this time.
In 1536, the Church in England separated from the Roman Catholic Church. This happened because King Henry VIII wanted to end his marriage. This led to the creation of the Church of England, which is still the official church in England today. The British Monarch is the head of the Church of England. Its spiritual leader is the Archbishop of Canterbury.
Saint George is the patron saint of England. Before him, St Edmund was the patron saint. The flag of England is the red cross of St George.
How Christmas is Celebrated

In the 1600s, a group called the Puritans did not like the celebration of Christmas. They even banned it in 1647 after winning the English Civil War.
But people protested, and there were riots in some cities. People decorated their doors with holly and shouted royalist slogans. A book called The Vindication of Christmas (1652) argued against the Puritans and described old English Christmas traditions like dinner, roasted apples, card games, and carol singing. When King Charles II returned to power in 1660, the ban on Christmas ended.
In the early 1800s, writers started to imagine Christmas as a time of joyful celebration. In 1843, Charles Dickens wrote his famous story A Christmas Carol. This book helped bring back the "spirit" of Christmas and encouraged people to be generous and joyful. Dickens wanted Christmas to be a family-focused holiday. Many things we do today at Christmas, like family gatherings and festive food, were influenced by Dickens. The phrase "Merry Christmas" became very popular after his story.
The revival of Christmas carols also began around this time. In 1843, the first commercial Christmas card was made, leading to people exchanging cards.
Blue Plaques: Marking History
A blue plaque is a special sign placed in public places in the UK. It marks a spot where a famous person lived or an important event happened. It's the oldest scheme of its kind in the world, started in 1866. Since 1986, English Heritage has managed it.
The first plaque was put up in 1867 for Lord Byron at his birthplace. Other plaques mark events like John Logie Baird's first television demonstration or Roger Bannister running the first four-minute mile.
Science and Inventions
England and Scotland were very important places during the Scientific Revolution in the 1600s. English scientists and engineers have made huge contributions. Famous people include Isaac Newton, Charles Darwin, and Alan Turing. England is home to important scientific places like the Royal Institution and the Royal Society. It also has the Greenwich Observatory, which is where Greenwich Mean Time comes from.
The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution began in England. This was a time of huge changes in how things were made and how people lived. It happened because of social, economic, and political changes in Britain. Unlike many other European countries, Britain had laws that protected people's property and rights after the Glorious Revolution of 1688. This encouraged people to start new businesses.
England also had good natural resources, like a long coastline, many rivers for transport, and lots of high-quality coal. Historian Jeremy Black said it was "an unprecedented explosion of new ideas, and new technological inventions." This changed how we used energy and created an industrial and urban country with new roads, railways, canals, factories, and cities.
In the 1700s, Josiah Wedgwood made pottery manufacturing much more efficient. He created things like tableware for the growing middle class. Wedgwood is also known for inventing modern marketing techniques, like direct mail and money back guarantees.
Many Quaker families (a religious group) were successful in business and helped the Industrial Revolution. This included families involved in ironmaking, banking, and making chocolate. Matthew Boulton was another important business leader, known for helping to market James Watt's steam engine.
Other important English engineers and inventors from this time include George Stephenson, who developed railways, and Isambard Kingdom Brunel, who built famous railways and steamships. England has the oldest railway networks in the world. The Stockton and Darlington Railway, opened in 1825, was the first public railway to use steam trains. The London Underground, opened in 1863, was the world's first underground railway.
Sports and Fun Activities
Many sports were created in England and then spread around the world. These include badminton, cricket, croquet, football, field hockey, lawn tennis, rugby league, rugby union, table tennis, and horse racing. In the late 1700s, the English game of rounders went to America and became baseball. Association football, cricket, and rugby union are considered England's national sports.
The rules of football were first written in 1863 by Ebenezer Cobb Morley. England has the oldest football clubs in the world. Sheffield F.C., founded in 1857, is the world's oldest football club. The first international football match was between England and Scotland in 1872. England hosted and won the 1966 FIFA World Cup. The Barclays Premier League is the most-watched football league in the world. Famous clubs include Manchester United and Liverpool.

The modern game of tennis started in Birmingham, England, in the 1860s. Major Walter Clopton Wingfield helped create the game. The world's oldest tennis tournament, the Wimbledon championships, first happened in 1877. It takes place every year in late June and early July. Strawberries and cream, a dessert created in the time of Henry VIII, is famously eaten at Wimbledon.

England competes as a separate nation in some international sports events, like football, cricket, and rugby. However, in the Olympic Games, England is part of the Great Britain team. English fans often carry the Cross of Saint George flag instead of the British Union Flag.
Football is very popular across England and often shows trends in wider English culture, like in clothing and music. Different sports are sometimes linked to different social groups in England. For example, rugby league was traditionally linked to old factory towns in the north-west, while cricket and rugby union started in private schools.
English Symbols

The English national flag is the red cross of St George. St George's Day is celebrated as the patron saint's day and also as the birthday and death day of William Shakespeare.
In 1198, King Richard the Lionheart introduced the coat of arms of England, which showed "three lions." These three lions are now used on the emblems of English national sports teams, like the England national football team and the England cricket team. The English oak tree and the Tudor rose are also English symbols. The Tudor rose is used by the England national rugby union team.
England does not have an official national song. However, the United Kingdom's "God Save the Queen" is commonly used. Other songs sometimes used include "Land of Hope and Glory" and "Jerusalem".
Images for kids
-
Durham Cathedral, built in 1093.
-
The Staffordshire Hoard is the largest collection of Anglo-Saxon gold and silver ever found.
-
A detailed painting of George Clifford, 3rd Earl of Cumberland from around 1590.
-
Flatford Mill by John Constable, painted around 1816.
-
King's College in Cambridge is a great example of late English Gothic architecture.
-
The Roman Baths in Bath, a lasting monument from Roman Britain.
-
The Royal College of Music in London, a music school founded in 1882.
-
Christopher Lee as Dracula in 1958, from a British horror film.
-
The Royal Albert Hall in London, where many national performing arts events and The Proms are held.
-
The wizard Merlin is a famous character in many stories and shows.
-
Canterbury Cathedral is the main church of the Church of England.
-
The Lady Chapel of Wells Cathedral.
-
The Lindisfarne Gospels, an ancient illuminated manuscript.
-
Charles Dickens' 1843 story A Christmas Carol helped bring back the "spirit" of Christmas.
-
Sir Isaac Newton, a very influential scientist from the Scientific revolution.
-
King Charles II, who supported the Royal Society, a scientific group.
-
Francis Bacon in a portrait from 1617. His ideas helped develop the scientific method.
-
The England playing Australia at Lord's Cricket Ground in 2009.
-
The Wimbledon tennis tournament is the oldest in the world.
-
A statue of King Alfred the Great in Winchester. He encouraged education in Old English.
See also
 In Spanish: Cultura de Inglaterra para niños
In Spanish: Cultura de Inglaterra para niños
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |





































