Flag of the United Kingdom facts for kids
 |
|
| Name | Union Jack, Union Flag, British flag, UK flag |
|---|---|
| Use | National flag |
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Adopted | 1 January 1801 |
| Design | A white-fimbriated symmetric red cross on a blue field with a white-fimbriated counterchanged saltire of red and white. |

Variant flag of the United Kingdom of
Great Britain and Northern Ireland |
|
| Use | Civil ensign |
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Design | A red field with the Union Flag in the canton. See Red Ensign. |

Variant flag of the United Kingdom of
Great Britain and Northern Ireland |
|
| Use | State ensign |
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Design | A blue field with the Union Flag in the canton. See Blue Ensign. |
Variant flag of the United Kingdom of
Great Britain and Northern Ireland |
|
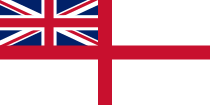
| Use | Naval ensign |
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Design | A symmetric red cross on a white field with the Union Flag in the canton. See White Ensign. |

Variant flag of the United Kingdom of
Great Britain and Northern Ireland |
|
| Use | Air force ensign |
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Design | A field of air force blue with the Union Flag in the canton and the RAF roundel in the middle of the fly. |
The national flag of the United Kingdom is called the Union Jack or Union Flag. It is the official flag for the whole of the UK.
The design of the Union Jack comes from the Act of Union 1801. This act joined the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland. Together, they formed the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland.
The flag shows a red cross for England (Saint George is its patron saint). This red cross has a white border. It sits on top of the saltire (a diagonal cross) of Ireland (Saint Patrick is its patron saint). This diagonal red cross also has a white border. Both of these are on top of the saltire of Scotland (Saint Andrew is its patron saint). This is a diagonal white cross on a blue background.
Wales is not shown on the Union Flag. This is because Wales was already part of the Kingdom of England when the flag was designed. The flag's usual size is twice as long as it is tall (1:2 proportion). The flag used by the British Army is slightly different, with a 3:5 proportion.
Contents
Understanding the Union Flag's Design
The Union Flag has a special design that combines different crosses. It uses the crosses of the patron saints of England, Scotland, and Ireland.
How the Crosses Combine
The flag looks like it's the same upside down, but it's not. The white lines around the diagonal red cross are different widths. On the side closest to the flagpole, the white line above the red diagonal is wider. On the other side, the white line below the red diagonal is wider. This means the flag is not perfectly symmetrical.
The red diagonal cross of Saint Patrick is placed slightly off-centre. This makes sure it doesn't just look like a border for the white diagonal cross of Saint Andrew. Saint Andrew's cross is higher up on the side near the flagpole. Saint Patrick's cross is higher on the opposite side.
What if the Flag is Upside Down?
Flying the flag upside down is usually seen as disrespectful. It's like showing a lack of respect for the country. However, flying it upside down can also be a signal for help or distress. This is rare, but it has been used in emergencies, like during the Boer War.
Flying the Flag on Public Buildings
Anyone in Great Britain can fly the Union Flag on any day they choose. However, there are some rules for government buildings, especially in Northern Ireland.
When the Flag Flies at Half-Mast
Sometimes, the Union Flag is flown at half-mast. This means it's lowered part-way down the flagpole. This is done to show sadness or respect, usually after someone important has died.
The flag flies at half-mast when:
- The King or Queen dies. (But on the day a new King or Queen is announced, it flies all the way up from 11 am to sunset.)
- A member of the Royal Family has a funeral.
- A foreign Head of State has a funeral.
- A former British Prime Minister has a funeral.
The King or Queen can also ask for the flag to be flown at half-mast on other special days. When it's at half-mast, the flag is about two-thirds of the way up the pole. There should be at least the height of the flag itself between the top of the flag and the very top of the flagpole.
Special Flag Days
Before 2007, government buildings only flew the Union Flag on a few special days each year. Now, the flag flies every day from the front of 10 Downing Street, where the Prime Minister lives. Other government buildings in London also do this. This change was made to help people feel more connected to their British identity.
The special days when the flag is flown include:
- Birthdays of members of the Royal Family.
- The Monarch's wedding anniversary.
- Commonwealth Day.
- Accession Day (when the Monarch started their reign).
- Coronation Day (when the Monarch was crowned).
- The King's official birthday.
- Remembrance Sunday.
- The days when Parliament opens or closes its session.
Since 2020, these days include:
- 9 January: The birthday of The Princess of Wales.
- 20 January: The birthday of The Duchess of Edinburgh.
- 6 February: The anniversary of Queen Elizabeth II's accession in 1952.
- 19 February: The birthday of The Duke of York.
- Second Sunday in March: Commonwealth Day.
- 10 March: The birthday of The Duke of Edinburgh.
- 21 April: The Queen's birthday.
- 2 June: The anniversary of The Queen's 1953 coronation.
- 10 June: The birthday of Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh.
- A Saturday in June: The King's Official Birthday.
- 21 June: The birthday of The Prince of Wales.
- 17 July: The birthday of The Queen Consort.
- 15 August: The birthday of The Princess Royal.
- Second Sunday in November: Remembrance Sunday.
- 14 November: The birthday of The King.
- 20 November: The anniversary of The Queen and The Duke of Edinburgh's wedding.
The flag is also flown on specific days in certain parts of the UK:
- Wales, 1 March: Saint David's Day.
- Northern Ireland, 17 March: Saint Patrick's Day.
- England, 23 April: Saint George's Day.
- Scotland, 30 November: Saint Andrew's Day.
- Greater London: When Parliament opens or closes.
In Scotland, the Flag of Scotland (called "the Saltire") flies every day on government buildings. On "national days," the Saltire is lowered, and the Union Flag is flown instead. An exception is on Saint Andrew's Day. If a building only has one flagpole, the Saltire stays up, and the Union Flag is not flown.
Wales and the Union Flag
Many people in Wales feel that their country is not properly shown on the Union Flag. This is because the flag was designed before Wales was fully seen as a separate nation within the UK.
Ideas for a New Design
In 2007, some politicians suggested changing the Union Flag. They wanted to add the Welsh dragon or the cross of St David to it. This would make sure Wales is represented. However, others thought this idea was not necessary.
The Union Flag in Northern Ireland
In Northern Ireland, there are specific rules about flying the Union Flag on government buildings. These rules are similar to the rest of the UK. However, the Police Service of Northern Ireland is not allowed to fly the Union Flag. They can only fly their own service flag or the Royal Standard if the King or Queen visits.
What if Scotland Becomes Independent?
If Scotland were to become an independent country, some people wonder what would happen to the Union Flag. The flag includes the Scottish diagonal cross. If Scotland left the UK, some suggest the flag might need to change. However, official groups like the College of Arms have said that the flag would not necessarily need to change. The existing flag could still be used if people wanted.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Bandera del Reino Unido para niños
In Spanish: Bandera del Reino Unido para niños

