Industrial Revolution facts for kids

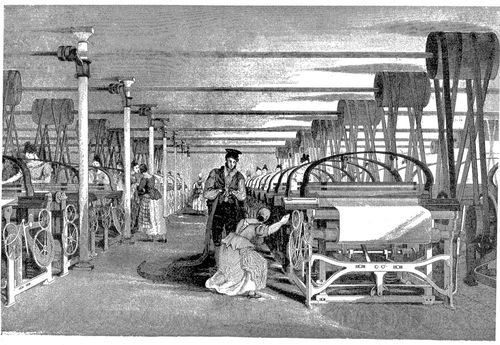
The Industrial Revolution was a time in history when the way things were made changed a lot and very quickly. Before this, most products were made by hand in small workshops. But during the Industrial Revolution, machines in large factories started making things. This meant products could be made much faster and cheaper, and in huge amounts.
Because of these changes, many people moved from farms in the countryside to towns. Factories in towns offered more jobs and often paid better.
Contents
How the Industrial Revolution Started
The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain in the 1700s. Many new inventions and ways of doing things came from Britain. For example, the county of Shropshire was very important. It had lots of iron ore and coal, which are key minerals. It also had the River Severn for transport. This led to many industries growing around the Ironbridge Gorge and the town of Coalbrookdale.
In the mid-1700s, Britain was a top trading country. It had a big trading empire with lands in North America and Africa. It also had influence in India through the East India Company. This growth in trade and business helped kickstart the Industrial Revolution.
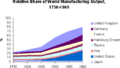
This period was a huge turning point in history. It changed almost every part of daily life. People's average income went up, and the population grew quickly. Some experts say that for the first time ever, the standard of living for most people started to get better. However, others believe this improvement didn't really happen until much later, in the late 1800s and early 1900s.
By the early 1800s, the revolution had spread to Europe and the United States. An English factory worker named Samuel Slater secretly traveled to America. He rebuilt a spinning machine from memory and opened his own factory.
New ideas and inventions were also used in mining, working with metals, and moving goods. Around the same time, new farming methods meant fewer farm workers were needed. These workers then moved to industrial towns to find jobs in factories.
One of the most important inventions was the steam engine. James Watt greatly improved the steam engine around 1776. These engines were used to power factories and pump water out of deep mines. They were also used in railway engines. Burning coal became the main source of power.
Challenges of the Industrial Revolution
While living standards generally improved and people became richer and healthier, the rapid population growth in England also caused new problems. Before, only a few landowners were rich. Now, more people became very wealthy thanks to industry. However, many people were still poor and lived in difficult conditions.
Children and women often had to work long hours for very little pay. It was common for several families to live crowded together in tiny apartments. Family members might take turns sleeping when they weren't working, making it hard for families to spend time together. Workdays of 12, 14, or even 18 hours were common. The Industrial Revolution brought its own set of challenges.
Key Advancements and Inventions
During the Industrial Revolution, many new technologies brought big changes. Here are some examples:
- Canals: These waterways were built to easily move heavy goods where they were needed.
- Steam Engine: The steam engine became the main source of power. It replaced horses and human labor.
- Cheap Iron and Steel: Iron and steel began to be mass-produced (made in large quantities). Steel replaced wood for building many new things.
- Machine Tools: These tools became common, allowing things to be mass-produced in factories instead of by hand.
- Agricultural Machinery: Inventions like seed drills led to a British agricultural revolution. Fewer people were needed on farms, so many moved to towns for factory jobs. Some of these new jobs could be tough and even dangerous.
- Railways: Train tracks were built across England and then around the world. They carried freight and passengers much faster and cheaper than before.
- Steamships: Steamships started to replace sailing ships. They were larger, faster, and didn't rely on wind and weather.
- Textile Machines: The spinning Jenny and power loom made it easy to mass-produce clothes and fabrics.
Images for kids
-
Handloom weaving in 1747, from William Hogarth's Industry and Idleness
-
A model of the spinning jenny in a museum in Wuppertal. Invented by James Hargreaves in 1764, the spinning jenny was one of the innovations that started the revolution.
-
The only surviving example of a spinning mule built by the inventor Samuel Crompton. The mule produced high-quality thread with minimal labour. Bolton Museum, Greater Manchester
-
The interior of Marshall's Temple Works in Leeds, West Yorkshire
-
Lombe's Mill site today, rebuilt as Derby Silk Mill
-
The reverberatory furnace could produce cast iron using mined coal. The burning coal remained separate from the iron and so did not contaminate the iron with impurities like sulfur and silica. This opened the way to increased iron production.
-
The Iron Bridge, Shropshire, England, the world's first bridge constructed of iron opened in 1781.
-
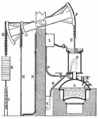
A Watt steam engine. James Watt transformed the steam engine from a reciprocating motion that was used for pumping to a rotating motion suited to industrial applications. Watt and others significantly improved the efficiency of the steam engine.
-
Newcomen's steam-powered atmospheric engine was the first practical piston steam engine. Subsequent steam engines were to power the Industrial Revolution.
-
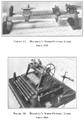
Maudslay's famous early screw-cutting lathes of circa 1797 and 1800
-
The Thames Tunnel (opened 1843). Cement was used in the world's first underwater tunnel.
-
The Crystal Palace housed the Great Exhibition of 1851
-
The Bridgewater Canal, famous because of its commercial success, crossing the Manchester Ship Canal, one of the last canals to be built.
-
Painting depicting the opening of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway in 1830, the first inter-city railway in the world and which spawned Railway Mania due to its success.
-
Winchester High Street, 1853. The number of High Streets (the primary street for retail in Britain) in towns and cities rapidly grew in the 18th century.
-
The Black Country in England, west of Birmingham
-
Manchester, England ("Cottonopolis"), pictured in 1840, showing the mass of factory chimneys
-
Slater's Mill in Pawtucket, Rhode Island.
-
Sächsische Maschinenfabrik in Chemnitz, Germany, 1868
-
Sir Henry Bessemer's Bessemer converter, the most important technique for making steel from the 1850s to the 1950s. Located in Sheffield (Steel City)
-
William and Mary Presenting the Cap of Liberty to Europe, 1716, Sir James Thornhill. Enthroned in heaven with the Virtues behind them are the royals William III and Mary II who had taken the throne after the Glorious Revolution and signed the English Bill of Rights of 1689. William tramples on arbitrary power and hands the red cap of liberty to Europe where, unlike Britain, absolute monarchy stayed the normal form of power execution. Below William is the French king Louis XIV.
-
A Philosopher Lecturing on the Orrery by Joseph Wright of Derby (c. 1766). Informal philosophical societies spread scientific advances
-
A dog forced to eat trash due to pollution, the Industrial Revolution has forced animals into harsh environments most are unable to survive in, leading to starvation and eventual extinction
See also
 In Spanish: Revolución Industrial para niños
In Spanish: Revolución Industrial para niños
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |