Weaving facts for kids
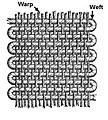
Weaving is a way of making cloth by crossing two sets of threads. Imagine threads going up and down, and other threads going side to side, crossing over and under each other. This is usually done on a special machine called a loom.
One set of threads is called the warp. These threads are held tight and straight on the loom. They run from top to bottom. The other set of threads is called the weft. These threads are wound onto small spools called bobbins. A tool called a shuttle carries the weft thread across the warp threads. The warp threads move up and down, letting the weft thread pass over some and under others. This creates the fabric.
Contents
What is Weaving?
Weaving is an ancient craft that has been around for thousands of years. It's how people have made clothes, blankets, and many other useful items from fibers. The basic idea is simple: you take two groups of threads and interlace them. This means they go over and under each other in a pattern. This process creates a strong and flexible piece of fabric.
The Main Parts of Weaving
To understand weaving, it helps to know the main parts:
- Warp threads: These are the threads that run lengthwise on the loom. They are held under tension, meaning they are pulled tight.
- Weft threads: These are the threads that run across the warp threads. They are woven in and out to create the fabric.
- Loom: This is the machine or frame used to hold the warp threads. Looms can be very simple, like a small frame, or very large and complex, like those in factories.
- Shuttle: This tool carries the weft thread through the warp threads. It helps guide the weft quickly and smoothly.
- Shed: This is the space created when some warp threads are lifted and others are lowered. The shuttle passes through this space with the weft thread.
How Threads Interlace
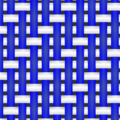
The way the warp and weft threads cross each other creates different patterns and textures in the cloth. The simplest pattern is called plain weave. In plain weave, the weft thread goes over one warp thread and then under the next, and so on. The next row does the opposite. Other common patterns include twill weave, which makes diagonal lines, and satin weave, which creates a smooth, shiny surface.
History of Weaving
Weaving has been a part of human life for a very long time. Early humans used natural fibers like grass, leaves, and animal hair to make simple mats and baskets. As tools improved, people started using plant fibers like flax and cotton, and animal fibers like wool and silk.
Ancient Weaving Techniques
Evidence of weaving goes back thousands of years.
- In ancient Egypt, people wove linen cloth from flax fibers. They used upright looms, as seen in old tomb paintings.
- Many indigenous cultures around the world developed unique weaving styles. For example, the Dogon of Mali are known for weaving long cotton strands.
- In the Andes mountains, ancient civilizations created beautiful textiles with complex patterns. These often told stories or showed important symbols.
- The Navajo people in North America are famous for their beautiful, hand-woven rugs. They traditionally use wool from their own sheep.
Weaving in the Industrial Age
For centuries, weaving was done by hand or on simple looms powered by people.
- Around the 1400s, weavers in places like Nuremberg, Germany, were skilled craftspeople.
- The Industrial Revolution in the 1700s and 1800s changed weaving forever. New machines, like the power loom, were invented.
- By the late 1800s, most cotton weaving was done in large factories called "weaving sheds." These machines were powered by steam engines. This made it possible to produce cloth much faster and cheaper than ever before.
Modern Weaving
Today, weaving is still a very important industry. Most of the clothes we wear and the fabrics we use are made on large, fast looms in factories. However, many people still enjoy weaving by hand as a hobby or to create unique art.
Types of Looms Today
- Handlooms: These are still used by many artists and craftspeople. They can be simple frame looms, back-strap looms (where one end is tied to the weaver's body), or more complex floor looms with pedals.
- Power Looms: These are used in factories for mass production. They are highly automated and can weave huge amounts of fabric very quickly.
Fibers Used in Weaving
Weavers use many different types of fibers:
- Natural fibers: These come from plants or animals. Examples include cotton, wool, silk, linen, and abacá.
- Synthetic fibers: These are man-made fibers, such as polyester, nylon, and rayon. They are often used for their strength, durability, or special properties.
Weaving is a blend of art, science, and history. It's a fundamental skill that has shaped human culture and continues to be important today.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Tejeduría para niños
In Spanish: Tejeduría para niños