List of English inventions and discoveries facts for kids
England has been a place where many amazing inventions and discoveries have happened! People from England have created or found many things that have changed the world. In fact, one study from Japan suggests that over 40% of the world's inventions and discoveries came from the UK. That's a lot of brilliant ideas!
Here's a look at some of the cool things invented or discovered in England.
Contents
Farming Inventions

Jethro Tull, who made the seed drill better in 1701.
- 1701: The seed drill, a machine that plants seeds neatly, was made much better by Jethro Tull.
- 1780s: Robert Bakewell started using selective breeding to improve farm animals. This means choosing animals with the best traits to have babies.
- 1842: John Bennet Lawes developed superphosphate, which was one of the first chemical fertilizers to help plants grow.
- 1901: The first successful light farm-tractor was invented by Dan Albone.
Time-Telling Tools
- Anglo-Saxon times: Alfred the Great invented a type of candle clock.
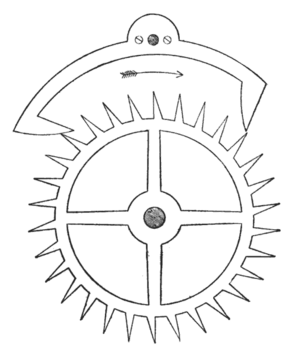
- c. 1657: The anchor escapement, a key part of many clocks, was likely invented by Robert Hooke.
- c. 1657: Robert Hooke also added the balance spring to the balance wheel, making watches much more accurate.
- 1761: The first truly accurate Marine chronometer, a super-precise clock for ships, was perfected by John Harrison. This helped sailors figure out their exact position at sea.
- 1923: The self-winding watch was invented by John Harwood.
- 1955: The first accurate atomic clock, which uses atoms to keep incredibly precise time, was invented by Louis Essen.
Clothes and Fabrics
- 1589: The stocking frame, a machine for knitting clothes, was invented by William Lee.
- 1733: The flying shuttle, which made weaving much faster, was invented by John Kay. This was a big step in the Industrial Revolution.
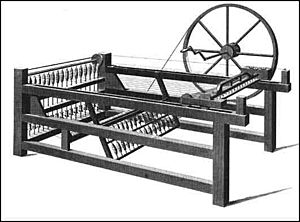
- 1764: The spinning jenny, a machine that could spin many threads at once, was invented by James Hargreaves.
- 1769: The water frame, a spinning machine powered by water, was developed by Richard Arkwright.
- 1775–1779: The spinning mule, which combined features of earlier machines, was invented by Samuel Crompton.
- 1784: The power loom, a machine that could weave fabric automatically, was invented by Edmund Cartwright.
- 1790: The sewing machine was invented by Thomas Saint.
- 1856: Mauveine, the first man-made organic dye, was discovered by William Henry Perkin. This opened up a world of new colors for clothes.
- 1941: Polyester, a strong and durable fabric, was invented by John Rex Whinfield.
Communication Tools
- Pre-1565: The pencil was invented in Seathwaite, Cumbria, using local graphite.
- 1661: The postmark, a stamp on letters showing where and when they were sent, was introduced by Henry Bishop.
- 1714: A patent for what's considered the first typewriter was given to Henry Mill.
- 1831: Michael Faraday discovered electromagnetic induction, which is how electricity can be made using magnets. This was key to developing radio.
- 1837: The first successful electric telegraph was developed by Sir Charles Wheatstone and Sir William Fothergill Cooke. This allowed messages to be sent over long distances using electricity.
- 1840: The postage stamp and the Uniform Penny Post (where all letters cost one penny) were invented by Sir Rowland Hill. This made sending letters much easier and cheaper.
- 1843: The Christmas card was first sold by Sir Henry Cole.
- 1873: Willoughby Smith discovered that the element selenium could change its electrical resistance when light hit it. This led to photoelectric cells, used in early televisions.
- 1879: The first radio transmission was made by David E. Hughes.
- 1888: The world's first moving picture film, Roundhay Garden, was made by Louis Le Prince.
- 1897: The world's first radio station was set up by Marconi on the Isle of Wight.
- 1899: The world's first color motion picture film was produced by Edward Raymond Turner.
- 1931: Stereophonic sound, or stereo, was invented by Alan Blumlein at EMI.
- 1936: The world's first regular public broadcasts of high-definition television began from Alexandra Palace by the BBC Television Service.
- 1945: The idea of geostationary satellites for telecommunications (satellites that stay in the same spot above Earth) was made popular by Arthur C. Clarke.
- 1964 onwards: The use of fibre optics in telecommunications was started by George Hockham and Charles K. Kao. This allows huge amounts of data to be sent using light.
- 1992: The clockwork radio, which doesn't need batteries, was invented by Trevor Baylis.
- 1992: The world's first text/SMS message ("Merry Christmas") was sent by Neil Papworth.
Computers and Digital World
- 1822: Charles Babbage designed the Difference Engine, an automatic mechanical calculator.
- 1837: Charles Babbage then designed the Analytical Engine, which was a plan for a general-purpose computer. He's often called the "Father of the Computer."
- 1842: Ada Lovelace, daughter of the poet Lord Byron, is seen as the first computer programmer. She wrote notes about how Babbage's Analytical Engine could do more than just calculations.
- 1854: George Boole came up with Boolean algebra, which is the basic math used in all digital computers.
- 1936–1937: The Universal Turing machine was invented by Alan Turing. This idea is super important because it showed how a single machine could do any calculation if given the right instructions.
- 1939: Alan Turing also invented the Bombe, a machine used by the British to break German secret codes during World War II.
- 1943–1944: The Colossus computer, the world's first programmable electronic digital computer, was invented by Tommy Flowers.
- 1948: The Manchester Baby, the world's first electronic computer that could store programs, was built by Frederic Calland Williams and Tom Kilburn.
- Late 1940s/early 1950s: The idea for the integrated circuit, or microchip, was thought up and built by Geoffrey Dummer. Microchips are tiny electronic brains found in almost all modern electronics.
- 1951: The Ferranti Mark 1, the world's first successful computer sold to businesses, was invented by Frederic Calland Williams and Tom Kilburn.
- 1952: The first graphical computer game, OXO, was programmed on the EDSAC computer at Cambridge University.
- 1979: The first laptop computer, the GRiD Compass, was designed by Bill Moggridge.
- 1979: The digital audio player (like an MP3 Player) was invented by Kane Kramer.
- 1980–1982: Home computers like the Sinclair ZX80, ZX81, and ZX Spectrum were made by Sir Clive Sinclair. These were popular early computers for many people.
- 1984: The world's first pocket computer, the Psion Organiser, was launched by Psion PLC.
- 1984: Elite, the world's first computer game with 3D graphics, was developed by David Braben and Ian Bell.
- 1985: The ARM architecture was introduced by Acorn Computers. ARM chips are now in 98% of mobile phones and every smartphone!
- 1989: Sir Tim Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web. This changed how we access information forever.
- 1989: He also developed HTTP (the language for web pages) and HTML (the code for building web pages).
- 1990: Sir Tim Berners-Lee invented the world's first web browser and the world's first web server.
- 2012: The Raspberry Pi, a small, affordable computer for learning, was launched by the Raspberry Pi Foundation.
Solving Crimes
- 1836: The Marsh test, used to find arsenic poisoning, was invented by James Marsh.
- 1888–1895: Sir Francis Galton developed a way to classify fingerprints. This was a huge step for forensic science (using science to solve crimes).
- 1984: DNA fingerprints were discovered by Alec Jeffreys. This allows scientists to identify people using their unique DNA.
- 1987: The process of DNA profiling was developed by Alec Jeffreys.
- 1995: The world's first national DNA database was created in the UK.
Engineering Marvels
- 1698: The first working steam pump was invented by Thomas Savery.
- 1712: The Atmospheric steam engine, a powerful machine that used steam, was invented by Thomas Newcomen.
- 1781: The Iron Bridge, the first metal bridge ever, was built by Abraham Darby III.
- 1791: The first true gas turbine was invented by John Barber.
- 1800: The first practical screw-cutting lathe, a machine for making precise screws, was developed by Henry Maudslay.
- 1830: The first electric transformer was invented by Michael Faraday.
- 1831: Michael Faraday also invented the first electrical generator, or dynamo.
- 1845: The hydraulic crane was developed by William Armstrong.
- 1862: Plastic was invented by Alexander Parkes.
- 1884: The steam turbine was invented by Charles Algernon Parsons. This powerful engine is used to generate electricity.
- 1885: The compression ignition engine, also known as the diesel engine, was invented by Herbert Akroyd Stuart.
- 1902: Disc brakes, now common in cars, were patented by Frederick W. Lanchester.
- 1904: The vacuum tube (or valve), a key component in early electronics, was invented by John Ambrose Fleming.
- 1940: The cavity magnetron, a vital part of microwave ovens and some radar systems, was improved by John Randall and Harry Boot.
- 1963: High-strength carbon fibre was invented at the Royal Aircraft Establishment. This strong, lightweight material is used in everything from airplanes to sports equipment.
- 2007: The RepRap Project, the first self-replicating 3D Printer, was developed at the University of Bath.
Household Helpers

John Harington, who invented the modern flushing toilet in 1596.
- Before 1596: The modern flushing toilet was invented by John Harington.
- 1780: The first mass-produced toothbrush was made by William Addis.
- 1810: The tin can for food preservation was patented by Peter Durand.
- 1828: The thermosiphon, which is the basis for most modern central heating systems, was invented by Thomas Fowler.
- 1830: The lawn mower was invented by Edwin Beard Budding.
- 1845: The rubber band was patented by Stephen Perry.
- 1878: The incandescent light bulb was invented by Joseph Wilson Swan.
- 1884: The light switch was invented by John Henry Holmes.
- 1901: The first powered vacuum cleaner was invented by Hubert Cecil Booth.
- 1924: The first modern dishwasher was invented by William Howard Livens.
- 1955: The first fully automatic electric kettle was made by Russell Hobbs.
- 1963: The lava lamp was invented by Edward Craven Walker.
- 1983: The "bagless" vacuum cleaner was invented by James Dyson.
Industrial Progress
- 1740: Crucible steel, a very strong type of steel, was developed by Benjamin Huntsman.
- 1746: The lead chamber process, for making large amounts of sulfuric acid, was invented by John Roebuck.
- 1760-1840: The Industrial Revolution saw many pioneers like Isambard Kingdom Brunel, who built amazing bridges and ships.
- 1795: The hydraulic press, a machine that uses liquid pressure to create force, was invented by Joseph Bramah.
- 1824: Portland cement, a key ingredient in concrete, was patented by Joseph Aspdin.
- 1840: The electroplating process, which coats metal objects with a thin layer of another metal, was patented by George Elkington.
- 1850–1855: The Bessemer process for making steel was developed by Henry Bessemer. This made steel much cheaper and easier to produce.
- 1862: The first man-made plastic, called Parkesine, was invented by Alexander Parkes.
- 1912: Stainless steel, which doesn't rust, was invented by Harry Brearley.
- 1933: The first practical polythene (a type of plastic) was discovered by Eric Fawcett and Reginald Gibson.
- 1952: The float glass process, for making high-quality flat glass, was invented by Alastair Pilkington.
Medical Breakthroughs
- 1628: William Harvey correctly described how blood circulates around the body.
- 1711: The first blood pressure measurement was taken by Stephen Hales.
- 1798: The smallpox vaccine, the first successful vaccine ever, was invented by Edward Jenner. This saved countless lives and led to the end of smallpox.
- 1800: The anaesthetic properties of nitrous oxide (laughing gas) were discovered by Humphry Davy.
- 1817: James Parkinson first described the disease that would later be named Parkinson's disease.
- 1850s: John Snow figured out how cholera was spreading, which helped stop outbreaks. He also helped pioneer general anaesthetic.
- 1860 onwards: Modern nursing was pioneered by Florence Nightingale, who improved hospital conditions and patient care.
- 1867: Joseph Lister invented antisepsis in surgery, using chemicals to kill germs and prevent infections during operations.
- 1887: The first practical ECG machine, which measures heart activity, was invented by Augustus Desiré Waller.
- 1912: Vitamins were discovered by Frederick Gowland Hopkins.
- 1937 onwards: Dorothy Crowfoot Hodgkin developed protein crystallography, which helped her figure out the structures of important molecules like penicillin and insulin.
- 1940s: Important research on using penicillin to treat infections was done by Jack Suchet and Sir Alexander Fleming.
- 1949: The first use of diagnostic ultrasound in medicine was by John J. Wild.
- 1949–1950: Harold Ridley developed artificial intraocular lens surgery for cataract patients.
- 1960 onwards: The hip replacement operation was pioneered by John Charnley.
- 1967 onwards: Computed Tomography (CT scans) were invented by Sir Godfrey Hounsfield. CT scans create detailed images of the inside of the body.
- 2014: The "Mom incubator," an inflatable incubator for premature babies, was invented by James Roberts.
Military Innovations
- 1718: The Puckle Gun, a multi-shot gun, was invented by James Puckle.
- 1784: The shrapnel shell, an artillery munition that explodes into many small pieces, was developed by Henry Shrapnel.
- 1830s: The safety fuse for explosives was invented by William Bickford.
- 1866: The first effective self-propelled naval torpedo was invented by Robert Whitehead.
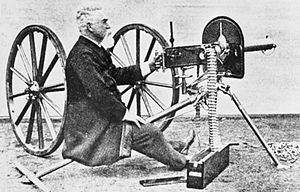
- 1884: The Maxim gun, the first self-powered machine gun, was invented by Sir Hiram Maxim.
- 1906: The Dreadnought battleship, a very powerful type of warship, is credited to Admiral John "Jackie" Fisher.
- 1916: The tank was developed and first used in combat by the British during World War I. Key inventors include Major Walter Gordon Wilson and Sir William Tritton.
- 1917: Dazzle camouflage, a type of ship camouflage that made it hard to tell a ship's direction, was created by Norman Wilkinson.
- 1941–1942: The Bailey bridge, a portable, pre-made bridge, was invented by Donald Bailey.
- 1943: The bouncing bomb, used to attack dams, was invented by Barnes Wallis.
- 1943: H2S radar, which helped planes target bombs, was invented by Alan Blumlein.
- 1960: The Harrier jump jet, an aircraft that can take off and land vertically, was developed by Hawker Aircraft.
- Late 1970s: Stun grenades were developed by the British Army's SAS.
Science Discoveries
Physics
- 1600: William Gilbert realized that the Earth is a giant magnet.
- 1660: Robert Hooke proposed Hooke's Law, which describes how springs stretch.
- 1687: Sir Isaac Newton formulated the Law of universal gravitation and Newton's laws of motion. These laws explain how objects move and how gravity works.
- 1800: Infrared radiation, which we feel as heat, was discovered by Sir William Herschel.
- 1823: The electromagnet was invented by William Sturgeon.
- 1831: Michael Faraday discovered that you could create electric current by changing magnetic fields. This is how most electricity is generated today.
- 1897: The electron, a tiny particle that carries electricity, was discovered by J. J. Thomson.
- 1911: Ernest Rutherford discovered the Rutherford model of the Atom, showing that atoms have a small, dense nucleus.
- 1912: The mass spectrometer, a device for measuring the mass of atoms and molecules, was invented by J. J. Thomson.
- 1932: The Neutron, another particle inside an atom, was discovered by James Chadwick.
- 1935: The possibility of Radar was first proven by Arnold Frederic Wilkins and Robert Watson-Watt.
- 1947: Holography, a way to create 3D images, was invented by Dennis Gabor.
- 1964: The Higgs boson, a fundamental particle that helps explain why other particles have mass, was proposed by Peter Higgs and others.
- 1974: Hawking radiation, a theory about black holes, was predicted by Stephen Hawking.
Chemistry
- 1665: Robert Hooke correctly described combustion (burning), noting that something from the air (oxygen) is used up.
- 1766: Hydrogen, a colorless, odorless gas, was discovered by Henry Cavendish.
- 1775: Oxygen was discovered by Joseph Priestley.
- 1803: John Dalton developed modern atomic theory, explaining that all matter is made of tiny particles called atoms. He is considered the father of modern chemistry.
- 1807-1813: Sir Humphry Davy isolated many elements like sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and identified the elemental nature of chlorine and iodine.
- 1825: Benzene, an important chemical, was isolated and identified by Michael Faraday.
- 1865: John Newlands devised an early version of the Periodic Table, arranging elements by their properties.
- 1868: Helium was discovered in the sun by Norman Lockyer.
- 1894: Argon, a noble gas, was discovered by John Strutt, 3rd Baron Rayleigh and William Ramsay.
- 1898: Morris Travers and Sir William Ramsay discovered xenon, neon, and krypton.
- 1901: Silicone was discovered and named by Frederic Kipping.
- 1913: Henry Moseley introduced the concept of atomic number, which helped organize the periodic table.
- 1959: The first practical hydrogen–oxygen fuel cell, which creates electricity from chemical reactions, was developed by Francis Thomas Bacon.
Biology
- 1665: Cell biology began when Robert Hooke discovered the first cells in cork.
- 1859: Charles Darwin published his theories of evolution by natural selection and sexual selection in On the Origin of Species. This changed how we understand life on Earth.
- 1953: The double-helix structure of DNA (the blueprint of life) was determined by Francis Crick and James Watson.
- 1958: Sir John Gurdon achieved the first cloning of an animal, a frog.
- 1960 onwards: Jane Goodall pioneered research into the behavior of chimpanzees, our closest relatives.
- 1977: DNA sequencing, a way to read the order of DNA, was developed by Frederick Sanger. He won the Nobel Prize twice for his work.
- 1996: Dolly the Sheep was born, the first mammal cloned from an adult cell, by Ian Wilmut and Keith Campbell.
Mathematics and Statistics
- 1630–1632: The slide rule, an early calculator, was invented by William Oughtred.
- 1631: William Oughtred introduced the "x" symbol for multiplication and "sin" and "cos" for trigonometry.
- 1687: Calculus, a powerful branch of mathematics, was developed by Sir Isaac Newton.
- 1854: George Boole proposed Boolean algebra, which is the foundation for all digital logic and computers.
- c. 1880: The Venn diagram, used to show relationships between sets, was devised by John Venn.
Astronomy
- 1609: Thomas Harriot made the first drawing of the Moon through a telescope.
- 1668: The Newtonian telescope was invented by Sir Isaac Newton.
- 1705: Edmond Halley determined that Halley's Comet returns regularly.
- 1781: Sir William Herschel discovered the planet Uranus.
- 1783: The existence of black holes was first proposed by John Michell.
- 1843: The existence and position of Neptune were predicted using only math by John Couch Adams.
- 1967: Pulsars, rapidly spinning neutron stars that emit beams of radiation, were discovered by Antony Hewish and Jocelyn Bell.
Earth Science and Weather
- 1802: Luke Howard developed a system for naming clouds.
- 1815: The first geological map of Great Britain was created by William Smith.
- 1820s: The scientific study of dinosaurs was started by Gideon Mantell.
- 1861: The first weather map was created by Francis Galton.
- 1880: The Seismograph, an instrument for detecting and measuring earthquakes, was invented by John Milne.
Sports and Games
- Before 1299: Bowls (or lawn bowls) can be traced back to 13th-century England.
- Early 16th century: Modern boxing developed from older bare-knuckle fighting.
- 1598: The earliest clear mention of cricket was recorded.
- After 1660: Thoroughbred horseracing developed in England.
- 1744: The earliest description of baseball was found in an English book. The game was likely brought to America by English settlers.
- 1823 or 1824: The invention of Rugby football is credited to William Webb Ellis.
- 1850: The idea for the modern Olympic Games was inspired by William Penny Brookes.
- 1857: Sheffield F.C., the world's first and oldest Association football (soccer) club, was formed.
- 1859–1865: Lawn tennis was invented by Harry Gem and Augurio Perera.
- 1874–1875: Snooker, a cue sport, was invented by the British Army in India.
- 1880s: Table tennis (ping-pong) started in Victorian England as an indoor version of tennis.
- 1896: The dartboard layout used in the game of Darts was designed by Brian Gamlin.
- 1948: The first Paralympic games competition, originally called the Stoke Mandeville Games, was created in England by Ludwig Guttmann.
- 1954: Sir Roger Bannister ran the first sub-four-minute mile in history.
Transportation
Air Travel
- 1799: Sir George Cayley set out the idea of the modern aeroplane with separate systems for lift, thrust, and control. He's often called the "father of aviation".
- 1804: Sir George Cayley designed the first glider to carry a human.
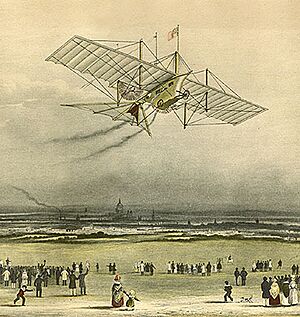
- 1848: The world's first powered flight (30 feet) was achieved in Chard, Somerset, with the Aerial Steam Carriage by John Stringfellow. This was 55 years before the Wright brothers!
- 1929: The turbojet engine was invented by Sir Frank Whittle. This powerful engine made jet airplanes possible.
- 1949: The first commercial jet airliner, the de Havilland Comet, was designed and built by de Havilland.
- 1960: VTOL (Vertical Take-Off and Landing) aircraft, like the Harrier jump jet, which can take off and land straight up, were invented by Gordon Lewis and his team.
- 1965: Concorde, the world's first supersonic commercial aircraft, was a joint project with British and French teams.
Railways

The London Underground, which opened in 1863.
- 1825: The Stockton and Darlington Railway, the world's first working steam passenger railway, opened.
- 1830: The Liverpool and Manchester Railway, the first inter-city steam railway, opened.
- 1802: The first full-scale railway steam locomotive was built by Richard Trevithick.
- 1814: The first successful locomotive with flanged-wheels (which keep trains on the tracks) was built by George Stephenson.
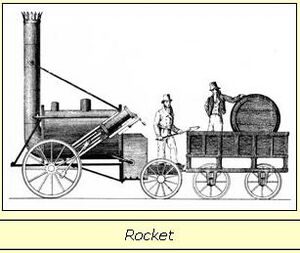
- 1829: Stephenson's Rocket, built by George Stephenson and his son Robert Stephenson, brought together many new ideas to create the most advanced locomotive of its time.
- 1863: The London Underground, the world's oldest underground railway, opened. It was also the first underground railway to use electric trains.
- Late 1940s: Maglev, which uses magnets to make trains float above the tracks, was invented by Eric Laithwaite.
Roads
- 1804: The seat belt was invented by Sir George Cayley.
- 1834: The Hansom cab, a type of horse-drawn carriage, was invented by Joseph Hansom.
- 1868: The first traffic lights (which were manually operated and gas-lit) were installed outside London's Houses of Parliament. They were invented by John Peake Knight.
- 1885: The first successful safety bicycle, "the Rover," was developed by John Kemp Starley. This bicycle looked much more like modern bikes.
- 1901: Tarmac, a material used for roads, was patented by Edgar Purnell Hooley.
- 1934: The Cat's eye, a safety device used in road marking to guide drivers at night, was invented by Percy Shaw.
- 1997: The ThrustSSC, a jet-powered car designed and built in England, set the world Land Speed Record at 1,228 km/h (763 mph).
Sea Travel
- 1578: The first design for a submersible (a small, submarine-like vehicle) with reliable information was by William Bourne.
- 1691: A diving bell that allowed people to stay underwater for a long time was designed by Edmond Halley.
- 1835: The screw propeller, which pushes ships through water, was invented and patented by Francis Pettit Smith.
- 1843: The SS Great Britain, the first steam-powered passenger ship with an iron hull and a screw propeller, was launched. It was designed by Isambard Kingdom Brunel.
- 1876: The Plimsoll Line, a mark on ships showing how much cargo they can safely carry, was devised by Samuel Plimsoll.
- 1912: The world's first patent for an underwater echo ranging device (sonar) was filed by Lewis Fry Richardson after the sinking of the Titanic.
- 1955: The hovercraft, a vehicle that travels over land or water on a cushion of air, was invented by Sir Christopher Cockerell.
Other Cool Inventions
- Early 17th century: The closely cut "English" Lawn became popular, showing off wealth.
- 1762: The Sandwich was invented by John Montagu, the 4th Earl of Sandwich.
- 1767: The carbonated soft drink was invented by Joseph Priestley.
- 1768–1770: The modern circus was invented by Philip Astley.
- 1798: The Marine Police Force, one of the oldest police forces, was formed by John Harriott and Patrick Colquhoun.
- 1821: The world's first modern nature reserve was established by Charles Waterton.
- 1824: The rubber balloon was invented by Michael Faraday.
- 1826: The first effective friction match was invented by John Walker.
- 1829: The Metropolitan Police Force (London police) was founded by Sir Robert Peel.
- 1844: The YMCA (Young Men's Christian Association) was founded in London by Sir George Williams.
- 1846: The Christmas cracker was invented by London confectioner Thomas J. Smith.
- 1851: The Prime meridian (the zero line of longitude) was established at Greenwich.
- 1860: Linoleum, a type of floor covering, was invented by Frederick Walton.
- 1865: The Salvation Army, a Christian church and charity, was founded by William Booth.
- 1897: Plasticine, a modeling clay, was invented by William Harbutt.
- 1901: The Meccano construction system (a model building toy) was invented by Frank Hornby.
- 1907: The scout movement was created by Lord Baden-Powell.
- 1913: The crossword puzzle was invented by Arthur Wynne.
- 1946: Toy building bricks (like Lego) were invented and patented by Hilary (Harry) Fisher Page.
|

All content from Kiddle encyclopedia articles (including the article images and facts) can be freely used under Attribution-ShareAlike license, unless stated otherwise. Cite this article:
List of English inventions and discoveries Facts for Kids. Kiddle Encyclopedia.