Chimpanzee facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Chimpanzees |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Adult female and infant common chimpanzees feeding on Ficus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | |
| Tribe: | |
| Subtribe: |
Panina
|
| Genus: |
Pan
|
Chimpanzees are great apes. They live in Africa. They are one of our closest living relatives in the animal kingdom.
Chimpanzees are fascinating animals that share many things with humans, from how they live in groups to how they use tools.
Contents
- Where do they live?
- What do chimpanzees look like?
- How do chimpanzees live together?
- What do chimpanzees eat?
- How do chimpanzees raise their young?
- How do chimpanzees communicate?
- Are chimpanzees smart?
- Why are chimpanzees important to study?
- Are they in danger?
- Relationship with humans
- Taxonomy
- Interesting facts about chimpanzees
- Related pages
- Images for kids
- See also
Where do they live?
Chimpanzees live in different parts of tropical Africa. You can find them in countries like Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda, and many others. They are very adaptable and can live in different kinds of places, like thick rainforests, drier woodlands, and even areas where forests meet grasslands.
Scientists have identified different groups of chimpanzees living in different areas, sometimes called subspecies. These groups might have slight differences in how they look or behave.
What do chimpanzees look like?
Chimpanzees are covered in coarse black hair, but their faces, fingers, toes, and the palms and soles of their feet are bare. Adult male chimpanzees are usually bigger and heavier than females. Males can weigh between 40 and 70 kilograms (about 88 to 154 pounds), and females weigh between 27 and 50 kilograms (about 60 to 110 pounds). They can stand up to about 150 centimeters (around 4 feet 11 inches) tall.
Chimpanzees have long arms that are longer than their legs, which helps them move around in trees. Their hands have long fingers and short thumbs, and their feet are good at grasping things, like branches. As they get older, some chimpanzees might get bald spots or white or grey patches of hair, especially on their chin.
How do chimpanzees live together?
Chimpanzees are very social animals and live in groups called communities. These communities can have anywhere from about 15 to over 150 members. However, they don't always stay together in one big group. They often travel and look for food in smaller, temporary groups that can change throughout the day. This is called a "fission-fusion" society because the larger group fissions (splits) into smaller ones and then fuses (comes back together).
In chimpanzee communities, males tend to stay in the group they were born into, while females often move to a new community when they become teenagers. Males in a community are often related to each other. There is usually a ranking system among the males, and males are generally dominant over females.
Males work together to protect their territory and the members of their group. They also help search for food. Sometimes, males form friendships or alliances with each other, which can help them move up in the group's ranking. Even though there's a ranking, individual chimpanzees have a lot of freedom to decide who they spend time with.
Chimpanzees can be very protective of their home area. Sometimes, groups of male chimpanzees will patrol the edges of their territory.
What do chimpanzees eat?
Chimpanzees are omnivores, which means they eat both plants and animals. Their favorite food is fruit, especially ripe fruit. But they also eat leaves, seeds, flowers, bark, and other plant parts.
Besides plants, chimpanzees also eat insects like termites and ants, birds and their eggs, and sometimes small mammals. They are known to hunt monkeys, like the red colobus monkey. When they hunt, they sometimes work together as a team. After a successful hunt, they often share the meat with other members of the hunting party and even those who were just watching.
Even though they hunt, most of a chimpanzee's diet comes from plants.
How do chimpanzees raise their young?
Chimpanzees give birth to live young. The gestation period of chimpanzees lasts between six and eight months. Usually only one offspring is produced; they rarely have twins.
Chimpanzee mothers take care of their babies for several years. When a baby chimpanzee is born, it is completely helpless and clings to its mother's belly. As they get a little older, around five or six months, they start riding on their mother's back. They stay very close to their mothers for their first year.
By the time they are about two years old, they can move around on their own and start exploring a little further away from their mothers. They usually stop drinking their mother's milk around four to six years old.
Young chimpanzees stay close to their mothers even after they are weaned. They learn important skills from their mothers and other members of the community. The mother's position in the group can sometimes affect the future position of her offspring. Adolescent male chimpanzees spend time with adult males, learning about hunting and patrolling the territory.
How do chimpanzees communicate?
Chimpanzees use many different ways to communicate with each other, including facial expressions, body postures, and sounds.
Their faces are very expressive. A wide grin can show that they are playing. If they are scared, they might make a "full closed grin." They also use sounds like "pant-hoots," which are loud calls that can help groups stay together and might even show who is important in the group. They also grunt when they are eating or greeting each other. Young chimpanzees might whimper if they are lost or want something.
Chimpanzees also "drum" on tree trunks with their hands and feet to communicate over longer distances, especially when they meet chimpanzees from other communities.
Are chimpanzees smart?
Yes, chimpanzees are very intelligent! They show many signs of being smart, like being able to remember things, work together, and use tools.
They are one of the few animal species that can recognize themselves in a mirror, which suggests they have a sense of self. Scientists have seen chimpanzees using insects to help treat their own wounds and the wounds of other chimpanzees.
Different groups of chimpanzees have their own ways of doing things, like using tools or grooming each other. This is sometimes called culture, as these behaviors are learned and passed down through the group.
Chimpanzees are famous for using tools. They can modify sticks to "fish" for termites or ants from their mounds. They also use stones or branches to crack open nuts. They even use leaves like sponges to soak up water to drink. In some areas, chimpanzees have been seen sharpening sticks to hunt small animals.
Scientists have also tried to teach chimpanzees human languages, like sign language. While there has been some success in teaching them signs, there is still debate about whether they can truly learn and use language in the same way humans do.
Chimpanzees also seem to understand cooperation and can choose good partners to work with to get food rewards. They even show behaviors that look like laughter when they are playing or tickled.
Why are chimpanzees important to study?
Studying chimpanzees helps us learn more about them, their behavior, and how they live. Because they are so closely related to humans, studying chimpanzees can also give us clues about our own evolution and behavior.
Scientists like Jane Goodall have spent many years observing chimpanzees in the wild, which has taught us a huge amount about their complex social lives, their intelligence, and their tool use.
Are they in danger?
Sadly, chimpanzees are considered an endangered species. This means their populations are decreasing, and they face serious threats in the wild.
One of the biggest problems for chimpanzees is losing their habitat. Forests are being cut down for farming, logging, and building roads, which leaves less space for chimpanzees to live and find food.
Another major threat is poaching. Chimpanzees are sometimes hunted for food or captured illegally to be sold as pets.
Diseases can also be a problem for chimpanzees. Because they are so similar to humans, they can catch many of the same illnesses. As human populations grow and move closer to chimpanzee habitats, the risk of spreading diseases between humans and chimpanzees increases.
Efforts are being made to protect chimpanzees and their habitats, including establishing national parks and working to stop illegal hunting.
Relationship with humans
According to a genome study done by the Chimpanzee Sequencing and Analysis Consortium, humans share either 95% or 96% of their DNA with chimpanzees. However, this applies only to single nucleotide polymorphisms, that is, changes in single base pairs only. The full picture is rather different.
24% of the chimpanzee genome does not align with the human genome, and so cannot be directly compared. There are more differences as well, totaling at least 30% differences between chimpanzee and Homo sapiens genomes.
Chimpanzees and humans have a long history of interaction, though not always a good one for the chimpanzees. In the past, chimpanzees were sometimes used in entertainment like circuses or tea parties, but this is now widely seen as harmful to the animals.
Some chimpanzees have also been kept as pets, but this is very dangerous because they are strong and can be unpredictable, especially as they get older.
Scientists have also studied chimpanzees in laboratories to learn more about health and behavior. However, there are many discussions about the ethics of using chimpanzees in research, and many have now been moved to sanctuaries where they can live in more natural settings.
While chimpanzees are generally shy of humans in the wild, interactions can sometimes be dangerous, especially if chimpanzees feel threatened or if humans behave inappropriately. It's important to remember that they are wild animals and should be respected from a safe distance.
Taxonomy
- Genus Pan: Chimpanzees
- Common chimpanzee, Pan troglodytes
- Bonobo or Pygmy (small) chimpanzee, Pan paniscus
Interesting facts about chimpanzees
- In captivity, chimpanzees have been able to learn American Sign Language (ASL) to communicate with caregivers.
- Baby chimpanzees can be identified by their small size and a tuft of white hair on their backside.
- A chimpanzee is about four times stronger than a human of the same size.
- Chimpanzees build a new nest nightly, which means that their bed is always clean.
- Chimps are poor swimmers because they are top-heavy and have a low body fat percentage.
- Chimpanzees have senses similar to the five senses humans have.
- Bonobos and chimpanzees were once thought to be one species.
- Scientists have found that chimps are able to learn and create simple games like a 4-year-old child can create.
- Chimpanzees have been shown to have their own individual personalities.
- Chimpanzees live up to 60 years in the wild.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
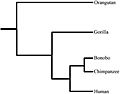
Relationships among apes. The branch lengths are a measure of evolutionary distinctness. Based on genome sequencing by The Chimpanzee Sequencing and Analysis Consortium. Figure from Yousaf et al. 2021, adapted from Prado-Martinez et al. 2013.
-
Mutual grooming, removing lice
-
Adult male eastern chimpanzee snatches a dead bushbuck antelope from a baboon in Gombe Stream National Park
-
Hugo Rheinhold's Affe mit Schädel ("Ape with skull"), c. 1893
-
Ham, the first great ape in space, before being inserted into his Mercury-Redstone 2 capsule on January 31, 1961
-
Feeding station at Gombe, where Jane Goodall used to feed and observe the chimpanzees
See also
 In Spanish: Chimpancé común para niños
In Spanish: Chimpancé común para niños