Cameroon facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Republic of Cameroon
République du Cameroun (French)
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Anthem:
"Ô Cameroun, berceau de nos ancêtres" (French) "O Cameroon, Cradle of Our Forefathers" |
|
 |
|
| Capital | Yaoundé 3°52′N 11°31′E / 3.867°N 11.517°E |
| Largest city | Douala |
| Official languages | English • French |
| Ethnic groups
(2022)
|
|
| Religion
(2022)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Cameroonian |
| Government | Unitary dominant-party presidential republic under a dictatorship |
| Paul Biya | |
| Joseph Ngute | |
|
• President of Senate
|
Marcel Niat Njifenji |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| National Assembly | |
| Independence
from France and the United Kingdom
|
|
|
• Independence from France
|
1 January 1960 |
|
• Independence from the United Kingdom
|
1 October 1961 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
475,442 km2 (183,569 sq mi) (53rd) |
|
• Water (%)
|
0.57 |
| Population | |
|
• 2024 estimate
|
30,966,105 (52nd) |
|
• Density
|
39.7/km2 (102.8/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2021) | ▼ 42.2 medium |
| HDI (2022) | medium · 151st |
| Currency | Central African CFA franc (XAF) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (WAT) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy yyyy/mm/dd |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +237 |
| ISO 3166 code | CM |
| Internet TLD | .cm |
Cameroon, officially known as the Republic of Cameroon, is a country located in Central Africa. Its capital city is Yaoundé, and its largest city is Douala. About 30 million people live in Cameroon. The country's president is Paul Biya. People in Cameroon speak nearly 250 different languages, but the two official languages are French and English.
Contents
History of Cameroon
The land that is now Cameroon has been home to people for a very long time. Early groups included the Sao civilisation near Lake Chad and the Baka hunter-gatherers in the southeastern rainforest.
European Arrival and Colonial Rule
In the 15th century, Portuguese explorers arrived at the coast. They named the area Rio dos Camarões, meaning "Shrimp River." This name later became "Cameroon" in English. In the 1800s, Fulani soldiers created the Adamawa Emirate in the north. Many other groups in the west and northwest also formed strong kingdoms.
Cameroon became a German colony in 1884 and was called Kamerun. After World War I, Germany lost control. The country was then divided between France and the United Kingdom. They ruled Cameroon as "mandates" from the League of Nations. France took about four-fifths of the land, and the UK took one-fifth.
Independence and Modern Cameroon
A political party called the Union of the Peoples of Cameroon (UPC) wanted Cameroon to be independent. However, France banned the party in the 1950s, which led to fighting.
In 1960, the part of Cameroon ruled by France became independent. It was named the Republic of Cameroun, and Ahmadou Ahidjo became its first president. In 1961, the southern part of British Cameroons joined with it. They formed the Federal Republic of Cameroon. This federation ended in 1972. The country was then renamed the United Republic of Cameroon. In 1984, President Paul Biya changed the name back to the Republic of Cameroon.
Geography of Cameroon
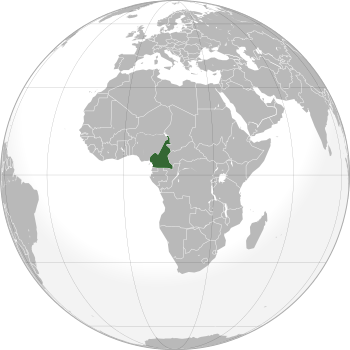
Cameroon is the 53rd largest country in the world, covering about 475,442 square kilometers (183,569 square miles). It is located in Central Africa on the Bight of Bonny, which is part of the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean. Cameroon is found between 1° and 13°N latitude and 8° and 17°E longitude.
People often call Cameroon "Africa in miniature." This is because it has almost all the main climates and types of land found across the continent. You can find coasts, deserts, mountains, rainforests, and savannas here. Cameroon shares borders with Nigeria and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south.
Geographic Zones
Cameroon has five main geographic zones:
- Coastal Plain: This area is very hot and humid, with thick forests. It includes some of the wettest places on Earth.
- South Cameroon Plateau: This area is higher than the coast and is covered by equatorial rainforests.
- Cameroon Range: This is a chain of mountains and hills, including Mount Cameroon, which is the country's highest point at 4,095 meters (13,435 feet). This region has fertile soils, especially near the volcano. Some crater lakes are found here. In 1986, one of these, Lake Nyos, released a cloud of carbon dioxide gas, sadly causing many deaths.
- Adamawa Plateau: This grassy, rugged plateau separates the north and south of the country. It has a mild climate with good rainfall.
- Northern Lowland Region: This dry area extends to Lake Chad. It has savanna scrub and grass, with little rainfall and high temperatures.
Rivers and Waterways
Cameroon has four main river systems. In the south, rivers like the Ntem, Nyong, Sanaga, and Wouri flow into the Gulf of Guinea. The Dja and Kadéï rivers flow southeast into the Congo River. In northern Cameroon, the Bénoué River flows north and west into the Niger. The Logone flows north into Lake Chad, which Cameroon shares with three other countries.
Wildlife of Cameroon
Cameroon is known for its rich biodiversity, meaning it has a huge variety of plants and animals. It has the second-highest concentration of different species in Africa. About 43% of Cameroon's land is covered by forests.
To protect its amazing wildlife, Cameroon has over 20 protected areas. These include national parks, zoos, and forest reserves. The first protected areas were set up in the northern region in 1932. These efforts have helped increase the protected land from about 4% to 12% of the country's total area.
Cameroon is home to 8,260 plant species (156 found nowhere else), 409 mammal species (14 found nowhere else), 690 bird species (8 found nowhere else), 250 reptile species, and 200 amphibian species. Important protected areas include the Mbam Djerem National Park, Benoue National Park, Korup National Park, Takamanda National Park, and the Kagwene Gorilla Sanctuary. The country is also important for many marine and freshwater animals like crabs, snails, fish, and birds.
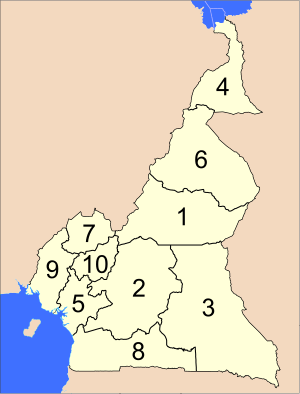
Regions of Cameroon
Cameroon's government divides the country into 10 regions. The president appoints a governor to lead each region. These regions were called provinces until 2008.
The regions are further divided into 58 smaller areas called divisions. These are led by officers appointed by the president.
|
Major Cities
Here are some of the largest cities in Cameroon:
| Ranking | Name | Population |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Douala | 2,000,000 |
| 2. | Yaoundé | 1,600,000 |
| 3. | Garoua | 450,000 |
| 4. | Bafoussam | 350,000 |
| 5. | Maroua | 327,000 |
| 6. | Bamenda | 299,600 |
| 7. | Ngaoundéré | 185,700 |
Culture of Cameroon
Cameroon has a rich and varied culture, influenced by its many different ethnic groups and its history.
Music and Dance
Music and dance are very important in Cameroonian life. They are part of ceremonies, festivals, social gatherings, and even storytelling. Traditional dances often have special steps and might be danced only by men or women. The dances can be for fun or for religious reasons.
Traditionally, music is passed down by listening and repeating. Often, a group of singers will echo a main singer. Music can be made with simple hand claps and foot stomps. People also use instruments like bells, clappers, drums, flutes, horns, rattles, and xylophones. The types of instruments used depend on the ethnic group and region.
Some popular music styles include ambasse bey, assiko, mangambeu, and tsamassi. Nigerian music has also influenced Cameroonian artists. One of the most famous African songs ever, "Sweet Mother" by Prince Nico Mbarga, is a highlife hit.
The two most popular music styles are makossa and bikutsi. Makossa started in Douala and mixes folk music with other styles like highlife and soul. Artists like Manu Dibango and Francis Bebey made makossa famous around the world in the 1970s and 1980s. Bikutsi began as war music among the Ewondo people. Artists like Anne-Marie Nzié turned it into popular dance music.
Holidays
The most important national holiday in Cameroon is National Day, also called Unity Day. It celebrates the country coming together. Important religious holidays include Assumption Day and Ascension Day.
Cuisine
Cameroonian food is different across the country, but a big, one-course dinner is common. A typical meal often includes a starchy food like cocoyams, maize, cassava (manioc), millet, plantains, potatoes, rice, or yams. These are often pounded into a dough-like food called fufu. This is served with a sauce, soup, or stew made from greens, groundnuts, palm oil, or other ingredients. Meat and fish are popular but can be expensive. Chicken is often saved for special events. Dishes are usually spicy, using salt, red pepper sauce, and seasoning cubes.
People often use forks and spoons, but traditionally, food is eaten with the right hand. Breakfast might be leftovers, bread, and fruit with coffee or tea. Snacks are also popular, especially in bigger towns, where you can buy them from street vendors.
Fashion
Cameroon's many different people also mean many different fashion styles. The climate, religious beliefs, ethnic groups, and influences from other countries all play a part in what people wear. Some well-known Cameroonian clothes include Pagnes (wraps worn by women), Chechia (a traditional hat), and Gandura (a male outfit).
Wrappers and loincloths are widely used by both women and men. Their use changes depending on the region. For example, you might see more styles influenced by the Fulani people in the north, and by the Igbo and Yoruba people in the south and west. Imane Ayissi is a famous Cameroonian fashion designer who is known around the world.
Local Arts and Crafts
Traditional arts and crafts are made all over Cameroon. They are used for selling, decorating, and religious purposes. Wood carvings and sculptures are very common. The good quality clay in the western highlands is used to make pottery and ceramics. Other crafts include basket weaving, beadworking, working with brass and bronze, carving and painting calabashes, embroidery, and leather working.
Traditional homes are built using local materials. They can range from simple wood-and-leaf shelters used by nomadic groups to rectangular mud-and-thatch homes in the south. However, homes made with materials like cement and tin are becoming more common.
Literature and Films
Cameroonian literature often focuses on both European and African ideas. Writers from the colonial time, like Louis-Marie Pouka, wrote about fitting into European culture. After World War II, writers such as Mongo Beti and Ferdinand Oyono looked at and criticized colonialism.
Soon after independence, filmmakers like Jean-Paul Ngassa and Thérèse Sita-Bella explored similar topics. In the 1960s, writers like Mongo Beti and Ferdinand Léopold Oyono wrote about life after colonialism, problems with development in Africa, and finding African identity again. In the mid-1970s, filmmakers like Jean-Pierre Dikongué Pipa and Daniel Kamwa showed the differences between traditional and modern society. Over the next two decades, literature and films focused more on purely Cameroonian themes.
Sports
Cameroon strongly supports sports. Traditional sports include canoe racing and wrestling. Hundreds of runners take part in the 40 km (25 mi) Mount Cameroon Race of Hope every year. Cameroon is one of the few tropical countries that has competed in the Winter Olympics.
Football (soccer) is the most popular sport in Cameroon. There are many amateur football clubs, often organized by ethnic groups or company sponsors. The national team has been one of the most successful in Africa. They did very well in the 1982 and 1990 FIFA World Cups. Cameroon has won the African Cup of Nations five times and a gold medal at the 2000 Olympics.
Cameroon hosted the Africa Women Cup of Nations in 2016, the 2020 African Nations Championship, and the 2021 Africa Cup of Nations. The women's football team is called the "Indomitable Lionesses." They are also very successful internationally, though they haven't won a major trophy yet.
Cricket is also growing in Cameroon, with the Cameroon Cricket Federation taking part in international matches. Cameroon has produced several National Basketball Association (NBA) players, including Pascal Siakam and Joel Embiid. The former UFC Heavyweight Champion, Francis Ngannou, is also from Cameroon.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Former president Ahmadou Ahidjo ruled from 1960 until 1982.
-
Paul Biya has ruled the country since 1982.
-
Our Lady of Victories Cathedral, catholic church in Yaoundé
See also
 In Spanish: Camerún para niños
In Spanish: Camerún para niños
 | Valerie Thomas |
 | Frederick McKinley Jones |
 | George Edward Alcorn Jr. |
 | Thomas Mensah |