French Third Republic facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
French Republic
République française
|
|||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1870–1940 | |||||||||||||||
|
Motto: Liberté, égalité, fraternité
("Liberty, equality, fraternity") |
|||||||||||||||
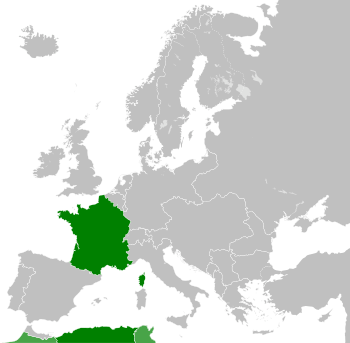
The French Republic in 1914
|
|||||||||||||||
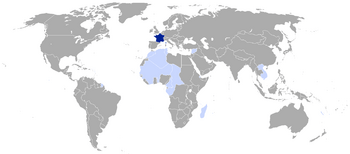
Territories and colonies of the French Republic at the end of 1939
Dark blue: Metropolitan territory Light blue: Colonies, mandates, and protectorates |
|||||||||||||||
| Capital | Paris | ||||||||||||||
| Common languages | French (official), several others | ||||||||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism Calvinism Lutheranism Judaism |
||||||||||||||
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic | ||||||||||||||
| President | |||||||||||||||
|
• 1871–1873 (first)
|
Adolphe Thiers | ||||||||||||||
|
• 1932–1940 (last)
|
Albert Lebrun | ||||||||||||||
| President of the Council of Ministers | |||||||||||||||
|
• 1870–1871 (first)
|
Louis Jules Trochu | ||||||||||||||
|
• 1940 (last)
|
Philippe Pétain | ||||||||||||||
| Legislature | Parliament | ||||||||||||||
| Senate | |||||||||||||||
| Chamber of Deputies | |||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||
|
• Proclamation by Leon Gambetta
|
4 September 1870 | ||||||||||||||
|
• Vichy France established
|
10 July 1940 | ||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||
|
• 1870
|
36,100,000 | ||||||||||||||
| Currency | French Franc | ||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||||||
The French Third Republic (French: La Troisième République) was a period in France when the country was a republic. This meant it was led by elected officials, not a king or emperor. It lasted for 70 years, from 1870 to 1940. This government was created after the Second French Empire collapsed during the Franco-Prussian War. It ended when Nazi Germany defeated France in World War II, leading to a new government called Vichy France.
Contents
The Start of the Third Republic
The Third Republic began on September 4, 1870. This happened during the Franco-Prussian War, a conflict between France and a group of German states led by Prussia. France suffered a major defeat, and its emperor, Napoleon III, was captured.
When news of the emperor's capture reached Paris, people were very upset. They demanded a new government. So, a group of leaders declared that France was now a republic again. This new government had to quickly try to defend France from the invading Prussian army.
What Life Was Like in the Third Republic
The Third Republic brought many important changes to France. It was a time of growth and new ideas. The government worked to make France a modern and fair country.
Education for Everyone
One big change was in education. The government made schooling free for all children. It also became compulsory, meaning children had to go to school. Schools were made secular, which means they were not controlled by the church. This helped more children, especially girls, get an education.
Freedom and Rights
During this period, people gained more freedoms. The government allowed greater freedom of the press, so newspapers could write more freely. People also got the right to form trade unions. This meant workers could join together to ask for better conditions.
The Dreyfus Affair
Not everything was easy. A famous event called the Dreyfus Affair showed some of the problems in French society. It was a scandal where a Jewish army captain, Alfred Dreyfus, was wrongly accused of being a spy. This event divided France and showed how important justice and fairness were.

Separation of Church and State
In 1905, a very important law was passed. It formally separated the Church from the State. This meant the government no longer supported or controlled religious groups. This law aimed to ensure religious freedom for everyone in France.
France and the World
The Third Republic was also a time when France expanded its influence around the world. It built a large colonial empire.
Building an Empire
France gained control over many territories in Africa and Asia. These colonies provided resources and new markets for French goods. However, this expansion also led to conflicts and often involved taking over lands from local people.
Alliances and World War I
As tensions grew in Europe, France formed alliances with other countries. It joined with Britain and Russia to create the Triple Entente. This alliance was important when World War I began in 1914. France played a major role in the war. It suffered many casualties, but eventually, the Triple Entente won.
After the Great War
After World War I, France helped write the Treaty of Versailles, which officially ended the war. France also occupied parts of Germany's Rhineland for a time. This was to ensure Germany paid for the war damages.
The End of the Republic
The Third Republic faced many challenges in the 1930s, including economic problems and political instability.
The Rise of Nazism
The biggest threat came from Nazi Germany under Adolf Hitler. In 1939, World War II began. Germany quickly invaded France in 1940. The French army, despite its efforts, was defeated.
Collapse and New Government
On July 10, 1940, the French Parliament voted to give special powers to Philippe Pétain, a World War I hero. This vote effectively ended the Third Republic and led to the creation of Vichy France, a new government that cooperated with Nazi Germany. This marked the end of an important era in French history.
Images for kids
-
The Representatives of Foreign Powers Coming to Greet the Republic as a Sign of Peace, a 1907 painting by Henri Rousseau.
See also
 In Spanish: Tercera República francesa para niños
In Spanish: Tercera República francesa para niños