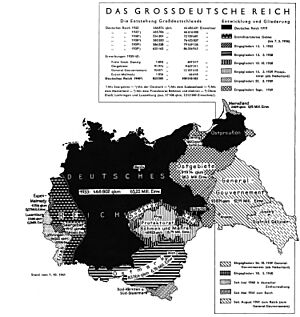
Nazi Germany facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
German Reich (1933–1943)
Deutsches Reich Greater German Reich (1943–1945) Großdeutsches Reich |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1933–1945 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Left: National flag and merchant ensign (1933–1935)
Right: National flag and merchant ensign (1935–1945) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Anthems: Das Lied der Deutschen
("The Song of the Germans") and Horst-Wessel-Lied ("The Horst Wessel Song") |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
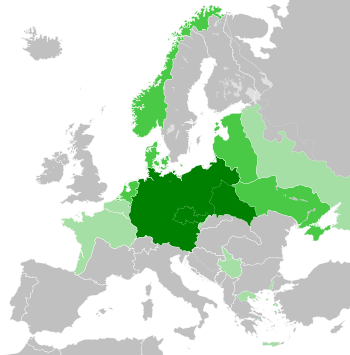
Germany's territorial control at its greatest extent during World War II (late 1942):
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
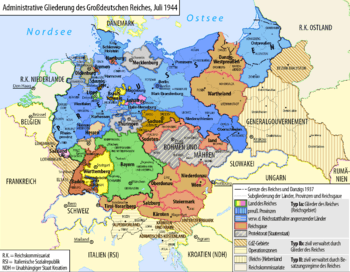
Administrative divisions of Germany, July 1944
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital and largest city
|
Berlin 52°31′N 13°23′E / 52.517°N 13.383°E |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | German | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | 1939 census Majority: 94.5% Christian (Protestant, Roman Catholic) Minorities: 3.5% Gottgläubig 1.5% Irreligious 0.4% Jewish 0.1% Other religions |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | German | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Wehrstaat (Military State) Unitary National Socialist single-party totalitarian military state |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Head of State | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1933–1934
|
Paul von Hindenburg | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1934–1945
|
Adolf Hitler | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1945
|
Karl Dönitz | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chancellor | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1933–1934
|
Adolf Hitler | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1945
|
Joseph Goebbels | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1945
|
Lutz Graf Schwerin von Krosigk | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Legislature | Großdeutscher Reichstag | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• State council
|
Reichsrat (abolished in 1934) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Interwar/World War II | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30 January 1933 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23 March 1933 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 March 1938 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 September 1939 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Death of Hitler
|
30 April 1945 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 May 1945 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23 May 1945 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1939 | 633,786 km2 (244,706 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1940 | 823,505 km2 (317,957 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1939
|
79,375,281 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1940
|
109,518,183 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GDP (PPP) | 1941 estimate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Total
|
$412.000 billion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Reichsmark (ℛℳ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | DE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nazi Germany describes the country of Germany between 1933 and 1945. During this time, Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party were in complete control. They called their rule the Third Reich, meaning "Third Empire". This name suggested they were following the Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and the German Empire (1871–1918). The Nazis even called it the Thousand-Year Reich, but it only lasted 12 years. It ended in May 1945 when the Allied forces defeated Germany. They entered the capital city, Berlin, which brought World War II in Europe to a close.
Contents
History of Nazi Germany
How the Nazis Took Power
On January 30, 1933, Paul von Hindenburg, Germany's President, made Hitler the Chancellor of Germany. The Nazi Party quickly started removing anyone who disagreed with them. They wanted to gain full control. When Hindenburg died in August 1934, Hitler combined the roles of chancellor and president. This made him the dictator. A public vote in 1934 confirmed Hitler as the sole Führer (leader). His word became the highest law in the land.
Economic Changes and Military Growth
During the Great Depression, the Nazis helped Germany's economy recover. They ended widespread unemployment by spending a lot on the military. They also built large public projects, like the Autobahnen (motorways). A huge secret program to build up the military, called rearmament, created the Wehrmacht (armed forces). This return to economic stability made the Nazi government popular.
Germany's Expansion and World War II
Germany began demanding more land. They threatened war if their demands were not met. In 1938, Germany took over Austria in an event called the Anschluss. They then demanded and received the Sudetenland area of Czechoslovakia. Germany signed a non-aggression agreement with the Soviet Union. On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. This started World War II in Europe. Germany, along with Italy and other Axis powers, took control of most of Europe by 1940. They also posed a threat to Great Britain.
Nazi Beliefs and Persecution
Racism, especially against Jewish people, was a core idea of the Nazi government. The Nazis believed that Germanic peoples were a "master race". They thought this group was the purest part of the Aryan race. Many groups were targeted by the Nazis. These included Jews, Romani people, Slavs, homosexuals, and political opponents. Also targeted were Jehovah Witnesses and Freemasons. People who refused to work and other "undesirables" were put in prison, forced to leave the country, or killed. The government also controlled art. They promoted certain styles and banned others.
The End of the War
After Germany's initial success invading the Soviet Union in 1941, the war turned. By 1943, Germany started losing ground. By late 1944, they were pushed back to their 1939 borders. Germany faced heavy bombing from the air. The Axis powers were forced back in Eastern and Southern Europe. After the Allied invasion of France, Germany was defeated. The Soviet Union attacked from the east, and other Allies from the west. Germany surrendered on May 8, 1945. Hitler refused to give up, which caused huge damage to Germany. Many more people died in the final months of the war. After the war, the Allies worked to remove Nazi ideas from Germany. Many Nazi leaders were tried for war crimes at the Nuremberg trials.
Geography and Land Changes
How Germany's Borders Changed
After losing World War I, Germany lost some land. This was part of the Treaty of Versailles. They lost Alsace-Lorraine, Northern Schleswig, and Memel. The Saarland became a special area under French control. Its people would later vote on which country to join. Poland became a separate country and gained access to the sea. This created the Polish Corridor, which separated Prussia from the rest of Germany. Danzig became a free city.
Germany regained the Saarland in 1935 after a vote. In 1938, they took over Austria in the Anschluss. The Munich Agreement of 1938 gave Germany control of the Sudetenland. Six months later, they took the rest of Czechoslovakia. In March 1939, Lithuania gave up the Memel district after Germany threatened invasion.
Between 1939 and 1941, German forces invaded many countries. These included Poland, Denmark, Norway, France, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Belgium, Yugoslavia, Greece, and the Soviet Union. Germany took parts of northern Yugoslavia in April 1941. In 1943, Italy gave Trieste, South Tyrol, and Istria to Germany.
Territories Under German Control
Some conquered areas became part of Germany. Hitler wanted to create a larger German empire. Several areas, like Alsace-Lorraine, were put under the control of a nearby German region called a Gau. In some occupied countries, Germany set up Reichskommissariate. These were like colonial governments. Areas under German rule included the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, the Baltic states, Belarus, and Ukraine. Parts of Belgium and France were controlled by the German military. Belgian Eupen-Malmedy, which was German until 1919, was taken back. Part of Poland was added to Germany. The General Government was set up in central Poland. Denmark, Norway, and the Netherlands had civilian governments. These were mostly run by local people but were under German control. Hitler planned to eventually add many of these areas to Germany. In 1943, Germany occupied Albania and Montenegro. They also set up a government in occupied Serbia in 1941.
Military and Other Forces
The Wehrmacht (Armed Forces)

From 1935 to 1945, Germany's armed forces were called the Wehrmacht. This included the Heer (army), Kriegsmarine (navy), and Luftwaffe (air force). After August 2, 1934, all military members had to swear an oath. They promised to obey Hitler without question. This new oath meant they had to obey Hitler even if his orders were against the law.
SA and SS Groups
The Sturmabteilung (SA), also known as Brownshirts, was the Nazi Party's first military-like group. Formed in 1921, their job was to protect Nazi leaders at events. They also fought against rival political groups in the streets. They took part in violent acts against Jewish people and others. By 1934, the SA had over half a million members. This was much larger than the regular army, which was limited to 100,000 men by the Versailles Treaty.
The SS groups committed many terrible acts against civilians and soldiers. From 1935, the SS led the persecution of Jewish people. They gathered them into special areas called ghettos and into concentration camps. When World War II began, SS Einsatzgruppen units followed the army into Poland and the Soviet Union. From 1941 to 1945, they murdered more than two million people. This included 1.3 million Jewish people. The SS-Totenkopfverbände (death's head units) ran the concentration and extermination camps. Millions more people were murdered in these camps.
In 1931, the SS created an intelligence service called the Sicherheitsdienst (SD). Its job was to find and arrest communists and other political opponents. The SS also started its own businesses. These included housing companies, factories, and publishing houses.
Society and Daily Life
Education Under Nazi Rule
In 1933, new laws forced all Jewish teachers, professors, and officials out of schools. Most teachers had to join the Nationalsozialistischer Lehrerbund (NSLB). University professors had to join the National Socialist German Lecturers League. Teachers had to swear loyalty to Hitler. Those who did not fully support Nazi ideas were often reported and fired. Many teachers left the job because of low pay. This led to larger class sizes.
The government controlled what was taught in schools. They also decided which textbooks could be used. Books that the Nazis did not like were removed from school libraries. From January 1934, teaching Nazi ideas became mandatory. Some students were chosen to become future Nazi leaders. They received special training from age 12 at Adolf Hitler Schools and National Political Institutes of Education.
Primary and secondary education focused on racial biology, population policy, and physical fitness. The school subjects, even math, were changed to focus on race. Military training became a key part of physical education. Physics lessons focused on topics useful for the military, like how bullets fly. Students had to watch all films made by the Propaganda Ministry for schools.
University enrollment dropped a lot during this time. However, more students joined medical schools. This was because Jewish doctors had been forced to leave their jobs, creating openings. From 1934, university students had to attend military training. First-year students also had to work for six months in a labor camp.
The Role of Women and Family
The Nazis had specific ideas about women. They were against the feminist movement. They believed a woman's main role was her husband, family, children, and home. Feminist groups were closed or joined into the National Socialist Women's League. This group taught women about raising children, sewing, and cooking. Women were encouraged to leave their jobs. They were also encouraged to have many children if they were considered "racially suitable."
Women who had many children received awards. A bronze award was given for four children, silver for six, and gold for eight or more. Large families also received money to help with costs. While these efforts increased the birth rate, the number of families with four or more children actually went down slightly. Taking women out of the workforce did not free up jobs for men. This was because women mostly worked in jobs men were not interested in. The Nazis did not want many women working in factories before the war. So, foreign workers were brought in. After the war started, many slave laborers were used. In 1943, Hitler ordered all women under fifty to work for the war effort. Women then moved into farm and factory jobs. By September 1944, 14.9 million women were working in making weapons.
Women were expected to be strong and healthy. The ideal woman was a sturdy peasant woman. She would work the land and have strong children. Women were praised for being athletic and tanned from working outdoors.
Public Health Efforts
Nazi Germany had a strong movement against smoking. Research in 1939 showed a link between smoking and lung cancer. The Reich Health Office tried to limit smoking. They gave lectures and handed out pamphlets. Smoking was banned in many workplaces, on trains, and for military members on duty. The government also worked to control other harmful substances. These included asbestos and pesticides. As part of a general health campaign, water supplies were cleaned. Lead and mercury were removed from products. Women were told to get regular breast cancer screenings.
Control Over Information (Censorship)
The government controlled newspapers and other media. The Reich Press Chamber closed or bought newspapers and publishing companies. By 1939, the Propaganda Ministry directly owned over two-thirds of newspapers and magazines. The Nazi Party's daily newspaper was the Völkischer Beobachter.
The Propaganda Ministry issued many rules each week. These rules said exactly what news should be published and how to present it. Newspapers followed these rules closely, especially about what to leave out. Fewer people read newspapers. This was partly because the quality of news went down. Also, radio became very popular. Towards the end of the war, propaganda became less effective. People found ways to get information from other sources.
Many authors left Germany. Some wrote books criticizing the Nazi government from exile. The government recommended that remaining authors write about German myths. By the end of 1933, over a thousand books were banned by the Nazis. Most were by Jewish authors or featured Jewish characters. Nazi book burnings happened. On May 10, 1933, tens of thousands of books were publicly burned. These books were by many famous people. Books about peace, liberal ideas, or those supporting the previous German government were targeted. Any writings by Jewish authors were also destroyed.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Adolf Hitler became Germany's head of state, with the title of Führer und Reichskanzler, in 1934.
-
Joseph Goebbels, Reich Minister of Public Enlightenment and Propaganda
-
A Nazi propaganda poster proclaiming that Danzig is German
-
German soldiers march near the Arc de Triomphe in Paris, 14 June 1940
-
German refugees in Bedburg, near Kleve, 19 February 1945
-
IG Farben synthetic oil plant under construction at Buna Werke (1941). This plant was part of the complex at Auschwitz concentration camp.
-
(from left) Hitler; Robert Ley, head of the German Labour Front; Ferdinand Porsche, armaments manufacturer; and Hermann Göring, head of the Four Year Plan (1942)
-
Woman with Ostarbeiter badge at the IG Farben plant in Auschwitz
-
Prisoner barracks at Dachau Concentration Camp, where the Nazis established a dedicated clergy barracks for clerical opponents of the regime in 1940
-
A Nazi book burning on 10 May 1933 in Berlin, as books by Jewish and leftist authors are burned
-
Plans for Berlin called for the Volkshalle (People's Hall) and a triumphal arch to be built at either end of a wide boulevard.
-
Leni Riefenstahl (behind cameraman) at the 1936 Summer Olympics
See also
 In Spanish: Alemania nazi para niños
In Spanish: Alemania nazi para niños
 | William M. Jackson |
 | Juan E. Gilbert |
 | Neil deGrasse Tyson |