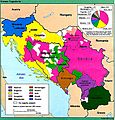
Yugoslavia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Yugoslavia
Југославија
Jugoslavija |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1918–1941 1945–1992 1941–1945: Government-in-exile |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Anthem: "Himna Kraljevine Jugoslavije" (1919–1941)
"Hej, Slaveni" (1945–1992) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
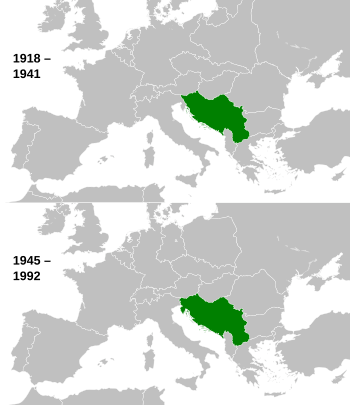
Yugoslavia during Interwar period and the Cold War
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital and largest city
|
Belgrade 44°49′N 20°27′E / 44.817°N 20.450°E |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Official languages | Serbo-Croatian Macedonian Slovene |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Yugoslav | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy (1918–1941) Socialist republic (1945–1990) Federal republic (1990–1992) Details
Unitary constitutional monarchy
(1918–1929, 1931–1939) Unitary absolute monarchy under a royal dictatorship (1929–1931) Federal constitutional monarchy (1939–1941) Government-in-exile (1941–1945) Provisional socialist government presiding over liberated territories (1943–1945) Federal Marxist–Leninist one-party authoritarian dictatorship (1945–1948) Federal Titoist one-party benevolent dictatorship (1948–1980) Federal Titoist one-party socialist republic (1980–1990) Federal parliamentary constitutional republic (1990–1992) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | 20th century | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Creation
|
1 December 1918 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 April 1941 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 October 1945 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29 November 1945 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27 April 1992 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Yugoslav dinar | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Calling code | 38 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Internet TLD | .yu | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Yugoslavia was a country in Europe, located mostly on the Balkan Peninsula. Its name means "Land of the Southern Slavs." The Slavs are a group of people who came from what is now Poland around the 7th century.
Yugoslavia existed in different forms between 1918 and 2006. From 1918 to 1928, it was called the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes. After 1928, it became the Kingdom of Yugoslavia until World War II.
After World War II, it was renamed the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. This country was made up of six republics: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Slovenia. Serbia also had two special areas called autonomous provinces: Vojvodina in the north and Kosovo near Albania.
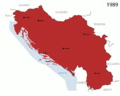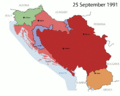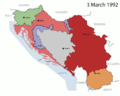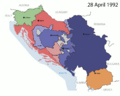
In the early 1990s, the country began to break apart. Slovenia and Croatia became independent in 1991. North Macedonia and Bosnia and Herzegovina followed in 1992. This led to the end of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. Serbia and Montenegro were the last two republics to stay together. In 1992, they formed a new country called the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (FRY), which finally ended in 2006.
Template:TOC limit=3
Contents
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia (1918-1941)
In 1903, a new king named Peter I came to power in Serbia. This made Serbia more focused on its own national identity. Tensions grew with Austria-Hungary when it took over Bosnia in 1908. During this time, Serbia expanded its borders, taking Kosovo and North Macedonia from the Ottoman Empire.
Many Serbian nationalists wanted to create a single country for all Slavs in the Balkans. In June 1914, a Bosnian Serb named Gavrilo Princip killed Austrian Archduke Franz Ferdinand in Sarajevo, Bosnia. This event helped start World War I.
Yugoslavia was formed in 1918, right after World War I ended. Most of its northern lands came from Austria-Hungary, which broke apart during the war. Serbia had already gained southern lands from the Ottoman Empire in the Balkan Wars (1912-1913). The king of Serbia became the king of all Yugoslavia.
For its first ten years, the country was known as the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes. It officially started using the name 'Yugoslavia' in 1929. The Kingdom was invaded by the Axis powers in 1941 during World War II and quickly fell. A new government was planned in 1943, but the idea of a king was soon removed.
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (1945-1992)
After World War II, a new communist government took power in 1945. It was led by Josip Tito from then until 1980. The country changed its name to the SFR Yugoslavia in 1963. It was made up of six separate Socialist Republics: SR Croatia, SR Bosnia and Herzegovina, SR Macedonia, SR Montenegro, SR Serbia, and SR Slovenia.
The SFR Yugoslavia was different from other socialist countries during the Cold War. It chose to stay neutral and not join either side. Yugoslavia was the only socialist country that allowed its people and tourists to travel freely. It also kept good relationships with Western countries.
Yugoslavia was not friends with the Soviet Union after a disagreement between Tito and Stalin. In 1968, when the Soviet Union sent troops into Czechoslovakia to stop its leader from making the country more open, Tito offered to help the Czechoslovak leader.
In the 1970s and 1980s, the different parts of Yugoslavia started to disagree more. Josip Tito had ruled Yugoslavia very strongly, stopping any groups that wanted the country to break up. His government made sure the six republics stayed together. When he passed away in 1980, the new leaders were less strict. This allowed feelings of nationalism to grow in the republics.
The breakup of Yugoslavia was caused by many things. These included growing nationalism, money problems, and issues between different ethnic groups. The Socialist state officially ended in 1992 during the Yugoslav Wars. Serbia and Montenegro decided to stay together as the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.
The Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (1992-2006)
After the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia broke apart, only Serbia and Montenegro wanted to remain united. They formed the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia in 1992. This country was led by Slobodan Milosevic from 1996 to 2000.
For most of its existence, the country was involved in what were called the Yugoslav Wars. These wars included terrible acts of violence. In 1999, NATO forces bombed the country during the Kosovo War.
By the late 1990s, more and more people wanted their regions to become independent. In 2003, the country changed its name from Yugoslavia to a state union called Serbia and Montenegro. Finally, in 2006, Serbia and Montenegro became independent countries. This was the official end of all parts of Yugoslavia.
Today, the lands that were once Yugoslavia are now these independent countries:
- Slovenia
- Croatia
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Montenegro
- Serbia
- North Macedonia
- Kosovo (some countries recognize it as independent, but the UN does not yet)
Images for kids
-
Marshal Josip Broz Tito
See also
 In Spanish: Yugoslavia para niños
In Spanish: Yugoslavia para niños