Federalism facts for kids
Federalism is a way of organizing a country's government. It means that power is shared between a central government (like the main government of a country) and smaller local governments (like states or provinces).
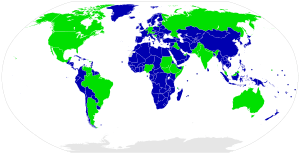
This system helps to balance power. The central government handles big national issues. The local governments manage things that are important to their specific areas. Many countries around the world use federalism, including the United States of America, Canada, Switzerland, and Austria. The European Union also works in a similar way.
Contents
How Federalism Works in Different Countries
Federalism in the United States
In the United States, federalism describes how the power is shared between the national government and the state governments. This relationship has changed over time.
The U.S. Constitution sets out how this power is divided. It doesn't explain federalism in one place. Instead, it talks about the rights and duties of both state and federal governments.
The national government has specific powers listed in the Constitution. These are called enumerated powers. They include things like collecting taxes, declaring war, and managing trade between states and with other countries. The Constitution also gives the national government implied powers. This means it can pass any law that is "necessary and proper" to carry out its listed powers.
After the American Civil War, the national government became much stronger. It started to have more influence on daily life. This happened because it needed to control businesses that operated across state lines. It also worked to protect civil rights and provide social services.
The idea of Dual federalism suggests that the national government and state governments are equal. Each has its own areas of power. However, since the Civil War, national courts often decide what the national government's powers are. There's also a concept called "bi-federalism." This includes Native American governments, which have their own limited powers.
Federalism in Canada
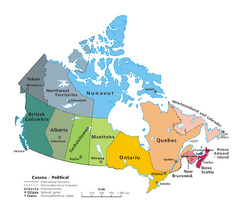
In Canada, federalism means that power is divided between the national parliament and the provincial governments. The Constitution Act, 1867 (formerly the British North America Act) spells out these powers.
Section 91 of the constitution gives powers to the national government. Section 92 gives powers to the provincial governments. If something isn't directly mentioned in the constitution, the national government usually has the power to make laws about it. However, there have been many disagreements between the two levels of government. These often involve who has power over the economy, taxes, and natural resources.
Federalism in Australia
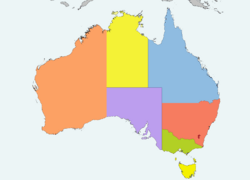
Australia became a federation on January 1, 1901. Before this, the United Kingdom had set up six self-governing colonies on the Australian continent. In the 1890s, these colonies held referendums (votes) to decide if they should unite.
When all colonies voted to join, the Federation of Australia began. This created the Commonwealth of Australia in 1901. Australia's federal system is similar to the United States. However, Australia uses a parliamentary system (like the UK) instead of a presidential system.
Federalism in Brazil
In Brazil, the monarchy ended in 1889. A military coup d'état (a sudden takeover of government) led to a presidential system. This system established federalism in Brazil. Every Brazilian constitution since 1891 has confirmed this system.
The 1988 Brazilian Constitution added something new to federalism. It included municipalities (local city governments) as federal entities. This means Brazilian municipalities have some powers usually given to states in other federal systems.
Federalism in India
The Government of India (also called the Union Government) was created by the Constitution of India. It governs a "federal union" of 29 states and 7 union territories.
India's government has three levels. The Constitution explains what each level of government can do. It first set up a two-level system: the Union Government and the State governments. Later, a third level was added: Panchayats (local village councils) and Municipalities.
The Seventh Schedule of the Indian Constitution divides government powers into three lists:
- Union List: This list includes important national topics like defense, foreign affairs, banking, and currency. Only the Union Government can make laws on these subjects.
- State List: This list contains subjects important to states and local areas, such as police, trade, agriculture, and irrigation. Only State Governments can make laws on these subjects.
- Concurrent List: This list includes topics that both the Union Government and State Governments are interested in. Examples are education, forests, trade unions, and marriage. Both levels of government can make laws on these subjects. If their laws conflict, the law made by the Union Government usually wins.
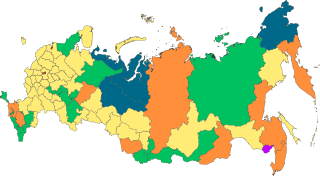
Federalism in the Russian Federation
After the Russian Empire, the government structure changed towards a more independent model. This began with the creation of the USSR. After the Soviet Union broke up, reforms under Boris Yeltsin kept much of the Soviet structure. However, they added more freedom to the way the different republics and regions were governed.
All of Russia's smaller government divisions are called "subjects." Some smaller areas, like the republics, have more independence. This is often because they have a large number of people from a non-Russian ethnic group.
Today, there are 85 federal subjects in Russia.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Federalismo para niños
In Spanish: Federalismo para niños