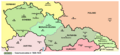
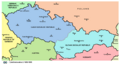
Czechoslovakia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Czechoslovakia
Československo
Česko‑Slovensko |
|||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1918–1939 1945–1992 1939–1945: Government-in-exile |
|||||||||||||||
|
Anthem: ’Kde domov můj’ (Czech)
’Where is my home’ ’Nad Tatrou sa blýska’ (Slovak) ’Lightning Over the Tatras’ |
|||||||||||||||
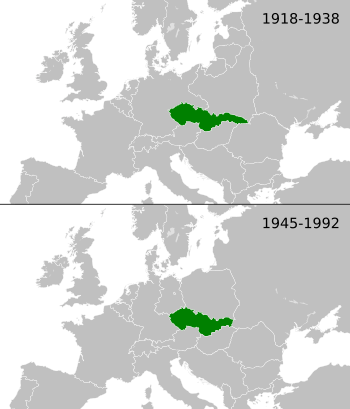
Czechoslovakia during interwar period and Cold War
|
|||||||||||||||
| Capital | Prague (Praha) 50°05′N 14°25′E / 50.083°N 14.417°E |
||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Czech · Slovak · German · Hungarian · Yiddish · Rusyn | ||||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Czechoslovak | ||||||||||||||
| Government | First Czechoslovak Republic (1918–1938) Second Czechoslovak Republic (1938–1939) Third Czechoslovak Republic (1945–1948) Czechoslovak Socialist Republic (1948–1990) Czech and Slovak Federative Republic (1990–1992) |
||||||||||||||
| President | |||||||||||||||
|
• 1918–1935
|
Tomáš G. Masaryk | ||||||||||||||
|
• 1935–1938 · 1945–1948
|
Edvard Beneš | ||||||||||||||
|
• 1938–1939
|
Emil Hácha | ||||||||||||||
| Prime Minister | |||||||||||||||
|
• 1918–1919 (first)
|
Karel Kramář | ||||||||||||||
|
• 1992 (last)
|
Jan Stráský | ||||||||||||||
| Historical era | 20th century | ||||||||||||||
|
• Independence
|
28 October 1918 | ||||||||||||||
|
• German occupation
|
1939 | ||||||||||||||
|
• Liberation
|
9 May 1945 | ||||||||||||||
|
• Coup d'état
|
25 February 1948 | ||||||||||||||
| November–December 1989 | |||||||||||||||
|
• Dissolution
|
31 December 1992 | ||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||
|
• 1921
|
13,607,385 | ||||||||||||||
|
• 1992
|
15,600,000 | ||||||||||||||
| Currency | Czechoslovak koruna | ||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Today part of | ∟ |
||||||||||||||
Czechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a country in Europe. It was formed in 1918 after the end of World War I. Before that, it was part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. The country existed for many years, but it eventually split into two new countries in 1993.
Czechoslovakia was located in Central Europe. Its capital city was Prague, which is now the capital of the Czech Republic. The country was home to different groups of people, mainly Czechs and Slovaks, who spoke their own languages.
Contents
A Brief History of Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia had a very interesting and sometimes difficult history. It went through many changes in its government and borders.
How Czechoslovakia Began
Czechoslovakia became an independent country on October 28, 1918. This happened after Austria-Hungary lost World War I. People in the region wanted their own country where Czechs and Slovaks could live together.

Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk was a very important leader. He became the first president of the new country. He helped set up a democratic government.
World War II and Its Impact
In the late 1930s, Nazi Germany, led by Adolf Hitler, became very powerful. In 1938, Nazi Germany took over parts of Czechoslovakia. By 1939, they had full control and split off Slovakia as a separate state.
During World War II, Czechoslovakia was under German rule. Many people resisted the occupation. After the war ended in 1945, Czechoslovakia became independent again.
The Communist Era
After World War II, the Soviet Union (USSR) became a very strong country. The USSR was a communist country, meaning the government controlled almost everything. It wanted to have influence over countries in Eastern Europe.
In 1948, the Communist Party took control of Czechoslovakia's government. This was a big change. The country became known as the Czechoslovak Socialist Republic. During this time, the government was a dictatorship, meaning people had fewer freedoms.
In 1968, there was a period called the Prague Spring. The government, led by Alexander Dubček, tried to make the country more free. However, the Soviet Union and its allies did not like these changes. They sent their armies to invade Czechoslovakia. This stopped the reforms and brought back strict communist rule.
The Velvet Revolution
In 1989, many countries in Eastern Europe started to move away from communism. In Czechoslovakia, people peacefully protested against the communist government. This event is known as the Velvet Revolution. It was called "Velvet" because it happened without violence.
The Velvet Revolution successfully ended the communist dictatorship. The country began to become a democracy again. Václav Havel became the last president of Czechoslovakia.
The Peaceful Split
After the Velvet Revolution, leaders in Czechoslovakia decided that the Czech and Slovak parts of the country should become separate nations. On January 1, 1993, Czechoslovakia peacefully split into two independent countries: the Czech Republic and Slovakia.
This separation was done without any fighting. Both countries are now members of the European Union.
Official Names of Czechoslovakia
Over its history, Czechoslovakia had several official names. These names often reflected the political changes happening in the country.
- 1918–1920: Republic of Czechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovak State
- 1920–1938: Czechoslovak Republic (ČSR)
- 1938–1939: Czecho-Slovak Republic
- 1945–1960: Czechoslovak Republic (ČSR)
- 1960–1990: Czechoslovak Socialist Republic (ČSSR)
- 1990–1992: Czech and Slovak Federative Republic (ČSFR)
Images for kids
-
A monument to Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk and Milan Rastislav Štefánik
See also
 In Spanish: Checoslovaquia para niños
In Spanish: Checoslovaquia para niños