North Macedonia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Republic of North Macedonia
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Anthem: Денес над Македонија (Macedonian)
"Today over Macedonia" |
|
![Location of North Macedonia (green)on the European continent (dark grey) — [Legend]](/images/thumb/3/35/Location_Macedonia_Europe.png/350px-Location_Macedonia_Europe.png)
Location of North Macedonia (green)
on the European continent (dark grey) — [Legend] |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Skopje 42°0′N 21°26′E / 42.000°N 21.433°E |
| Official languages | |
|
|
| Ethnic groups
(2021)
|
|
| Religion
(2021)
|
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic |
| Gordana Siljanovska-Davkova | |
| Hristijan Mickoski | |
|
• Chairman of the Assembly
|
Afrim Gashi |
| Legislature | Assembly |
| Establishment history | |
|
• Socialist Republic of Macedonia
|
2 August 1944 |
|
• Independence referendum
|
8 September 1991 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
25,436 km2 (9,821 sq mi) (145th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
1.1 |
| Population | |
|
• 2021 census
|
|
|
• Density
|
71.43/km2 (185.0/sq mi) (122nd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2019) | ▼ 30.7 medium |
| HDI (2022) | high · 83rd |
| Currency | Macedonian denar (MKD) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Calling code | +389 |
| ISO 3166 code | MK |
| Internet TLD |
|
North Macedonia ( mass-IH-doh-NEE-ə), officially called the Republic of North Macedonia, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is a landlocked country, meaning it has no coastlines. North Macedonia shares borders with Kosovo, Serbia, Bulgaria, Greece, and Albania.
The country is located in the northern part of the larger geographical region of Macedonia. Skopje is the capital and largest city. About a quarter of the country's 1.83 million people live there. Most people in North Macedonia are ethnic Macedonians, who are a South Slavic people. A large group of Albanians also live there, making up about 25% of the population. Other groups include Turks, Roma, and Serbs.
Contents
History of North Macedonia
The history of this area began with the ancient kingdom of Paeonia. Later, in the 6th century BC, the Persian Empire took control. In the 4th century BC, it became part of the Kingdom of Macedonia. The Roman Republic conquered the region in the 2nd century BC. It then became part of the Roman province of Macedonia.
The area was part of the Byzantine Empire for a long time. However, Slavic tribes often raided and settled there starting in the 6th century AD. Over centuries, different empires like the Bulgarian, Byzantine, and Serbian Empires fought for control. From the mid-14th century until the early 1900s, it was part of the Ottoman Empire.
After the Balkan Wars in 1912 and 1913, the land that is now North Macedonia came under Serbian rule. During World War I, Bulgaria ruled the territory. After the war, it returned to Serbian rule as part of the new Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes.
During World War II, Bulgaria again took control. In 1945, it became a state within communist Yugoslavia. North Macedonia peacefully left Yugoslavia in 1991 after a vote.
The country joined the United Nations (UN) in 1993. For a while, it was known as "the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" (FYROM). This was because of a disagreement with Greece over the name "Macedonia". In 2018, this issue was solved with an agreement. The country officially changed its name to "Republic of North Macedonia" in early 2019.
North Macedonia is also a member of NATO, the Council of Europe, and the WTO. Since 2005, it has been a candidate to join the European Union.
Geography and Climate

North Macedonia covers an area of about 25,713 km2 (9,928 sq mi). It is a landlocked country in the middle of the Balkan peninsula. The country has about 748 km (465 mi) of borders. It shares them with Serbia, Kosovo, Bulgaria, Greece, and Albania.
The country's landscape is mostly rugged. A central valley is formed by the Vardar river. This valley is surrounded by mountain ranges. Three large lakes are found on the southern borders: Lake Ohrid, Lake Prespa, and Dojran Lake. Lake Ohrid is thought to be one of the oldest lakes in the world. The region often experiences earthquakes. A major earthquake in 1963 badly damaged Skopje.
North Macedonia has many beautiful mountains. The highest mountain is Mount Korab, which is 2,764 m (9,068 ft) tall. There are 1,100 large water sources in the country. Rivers flow into three different seas: the Aegean, the Adriatic, and the Black Sea. The Vardar river is the largest and is very important for the country's economy.
There are around fifty ponds and three natural lakes. These are Lake Ohrid, Lake Prespa, and Lake Dojran. North Macedonia also has nine spa towns with natural hot springs.
Climate Zones
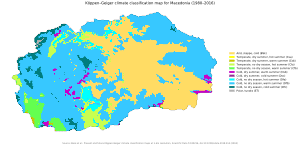
North Macedonia has four distinct seasons. Summers are warm and dry. Winters are moderately cold and snowy. Temperatures can range from −20 °C (−4 °F) in winter to 40 °C (104 °F) in summer.
There are three main climate zones:
- A mildly continental zone in the north.
- A temperate Mediterranean zone in the south.
- A mountainous zone in high-altitude areas.
The warmest places are Demir Kapija and Gevgelija. Here, temperatures often go above 40 °C (104 °F) in July and August. The amount of rainfall changes across the country. It is highest in the western mountains and lowest in the Vardar valley. This varied climate allows for growing many different plants. These include wheat, corn, potatoes, and rice.
Biodiversity and Wildlife
North Macedonia is home to about 3,700 different plant species. Most of these are flowering plants. The country's forests have many animals. These include bears, wild boars, wolves, foxes, and deer. The lynx is a very rare animal found in the western mountains.
North Macedonia has four national parks. These parks protect the country's beautiful nature and wildlife.
| Name | Established | Size | Picture |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mavrovo | 1948 | 731 km2 |  |
| Galičica | 1958 | 227 km2 |  |
| Pelister | 1948 | 125 km2 |  |
| Šar Mountains | 2021 | 244 km2 |  |
Government and Politics

North Macedonia is a parliamentary democracy. This means that the government is chosen by the people through elections. The country has a single-chamber parliament called the Assembly. It also has an independent court system.
The Assembly has 120 members. These members are elected every four years. The President of North Macedonia has a mostly ceremonial role. The real power lies with the Prime Minister. The President is the head of the armed forces. They are elected every five years and can serve a maximum of two terms.
The Assembly is the country's law-making body. It proposes and adopts laws. The Constitution of North Macedonia was put in place after the country became independent in 1991. It sets limits on the power of both local and national governments. The constitution also states that Skopje is the capital. Any citizen aged 18 or older can vote in elections.
The Government holds the executive power. The Prime Minister is the most powerful political person. The Prime Minister chooses the government members. These members are ministers for different areas like economy, finance, and foreign affairs. They serve for four years. The courts handle judicial power. The highest courts are the Supreme Court and the Constitutional Court. Judges are appointed by the Assembly.
Administrative Divisions
North Macedonia is divided into 84 municipalities. Ten of these municipalities make up the City of Skopje, which is the capital. These divisions help manage local government and services.
Economy and Trade
North Macedonia has made many economic changes since it became independent. It has an open economy, meaning it trades a lot with other countries. Trade makes up more than 90% of its GDP (Gross Domestic Product). The country has seen steady, though slow, economic growth.
The government has worked to control inflation, which is when prices go up. They have also tried to attract foreign businesses and help small and medium-sized businesses grow. The government introduced a flat tax system to make the country more attractive for investors. The tax rate was lowered to 10% in 2008.
Unemployment has been a challenge, but it has decreased over time. Many international manufacturing companies have opened offices in North Macedonia. These include companies from the automotive industry.
In terms of what the country produces, manufacturing, mining, and construction make up the largest part of the economy. Trade, transportation, and hotels are also important. Agriculture is a significant sector as well.
North Macedonia trades mostly with the European Union. Germany is its biggest trading partner. Other important partners include Italy, the United States, and Turkey.
Tourism in North Macedonia
Tourism is a big part of North Macedonia's economy. It made up 6.7% of its GDP in 2016. The number of foreign visitors has been increasing. In 2019, over 1.1 million tourists visited the country. Most tourists come from Turkey, Serbia, Greece, Bulgaria, and Poland.
The most popular types of tourism are:
- Lake tourism: There are three large lakes (Ohrid, Prespa, Dojran) and over 50 smaller glacial lakes.
- Mountain tourism: North Macedonia has 16 mountains that are higher than 2,000 meters.
Other types of tourism include rural tourism, ecotourism, city tourism, and cultural tourism. Cultural tourism involves enjoying local food, traditional music, festivals, and historical sites.
Infrastructure and Education
Transport Links
North Macedonia is located in the middle of the Balkan peninsula. This means that important transport routes connecting different parts of Europe pass through it. The main route connects Greece with the rest of Europe through the Vardar valley.
The country has a railway network of 699 km (434 mi). The most important railway line connects Serbia, Skopje, and Greece. There are also plans to build a direct railway line between Skopje and Sofia, Bulgaria. Skopje is the main railway hub.
North Macedonia Post is the state company that handles mail services. It was created in 1992. Water transport is mainly for tourism on Lake Ohrid and Lake Prespa.
North Macedonia has 17 airports. Two of these are international airports: Skopje International Airport and Ohrid St. Paul the Apostle Airport.
Education and Technology
Students can attend one of five state universities. These include the Ss. Cyril and Methodius University of Skopje and the St. Clement of Ohrid University of Bitola. There are also several private universities.
North Macedonia has made great progress in connecting to the internet. A project called Macedonia Connects helped make it the first country in the world with widespread wireless broadband internet. Many schools are now connected to the internet. An internet provider also offers Wi-Fi services in the 11 largest cities. The national library, National and University Library "St. Kliment of Ohrid", is in Skopje.
People and Culture
Population and Ethnic Groups
According to the 2021 census, North Macedonia has a population of 1,836,713 people. The average age of the population is about 40 years. There are slightly more females than males.
The largest ethnic group is the Macedonians. The second largest group is the Albanians, who live mostly in the northwestern part of the country. Other significant groups include Turks and Roma.
Religions in North Macedonia
Religion in North Macedonia (2021) Eastern Orthodoxy (46.1%) Catholicism (0.4%) Other Christian (13.9%) Islam (32.2%) None (0.1%) Others (7.3%)
Eastern Orthodox Christianity is the most common religion in North Macedonia. About 46.1% of the population are Orthodox Christians. Most of them belong to the Macedonian Orthodox Church. Other Christian groups make up 13.9% of the population.
Muslims make up 32.2% of the population. North Macedonia has one of the highest percentages of Muslims in Europe. Most Muslims are Albanians, Turks, Romani, or Bosniaks.
At the end of 2011, there were 1,842 churches and 580 mosques in the country. The Orthodox and Islamic communities have religious schools in Skopje.
The Macedonian Byzantine Catholic Church has about 11,000 members. There is also a small Protestant community.

The Jewish community in North Macedonia is small today. Most of them live in Skopje. Many Macedonian Jews are Sephardic, whose ancestors came from Spain and Portugal in the 15th century.
Languages Spoken
The main official language across North Macedonia is the Macedonian language. Albanian is also an official language at the state level. In towns where at least 20% of the people belong to another ethnic group, their language can also be used for official purposes.
Macedonian is a South Slavic language. It is very similar to Bulgarian and has some similarities with Serbian. The standard Macedonian language was set up after World War II.
Besides Macedonian and Albanian, other languages spoken by many people include Turkish, Romani, Serbian/Bosnian, and Aromanian. Macedonian Sign Language is used by the deaf community.
According to the last census, most citizens speak Macedonian. Albanian is the second most spoken language.
Major Cities
|
Largest cities or towns in North Macedonia
|
||
|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Pop. |
| 1 | Skopje | 526,502 |
| 2 | Kumanovo | 75,051 |
| 3 | Bitola | 69,287 |
| 4 | Prilep | 63,308 |
| 5 | Tetovo | 63,176 |
| 6 | Štip | 42,000 |
| 7 | Veles | 40,664 |
| 8 | Ohrid | 38 818 |
| 9 | Strumica | 33,825 |
| 10 | Gostivar | 32,814 |
Culture and Arts
North Macedonia has a rich culture with strong traditions in art, architecture, poetry, and music. Many old and protected religious sites can be found here. The country hosts annual festivals for poetry, cinema, and music.
Macedonian music has been greatly influenced by Byzantine church music. The country has many well-preserved Byzantine fresco paintings. These date mostly from the 11th to the 16th centuries.
Important cultural events include:
- The Ohrid Summer festival for classical music and drama.
- The Struga Poetry Evenings, which bring together poets from over 50 countries.
- The International Camera Festival in Bitola.
- The Skopje Jazz Festival in Skopje.
The National Opera opened in 1947. Every year, the May Opera Evenings are held in Skopje.
Delicious Cuisine
North Macedonia's food is typical of the Balkans. It shows influences from Mediterranean and Middle Eastern (Ottoman) cooking. There are also some influences from Italian, German, and Eastern European foods. The warm climate helps grow many different vegetables, herbs, and fruits. This makes Macedonian food very diverse.
Macedonian cuisine is known for its dairy products, wines, and local alcoholic drinks like rakija. Tavče gravče (a baked bean dish) and mastika (an alcoholic drink) are considered the national dish and drink. Other popular dishes include Šopska salad, stuffed peppers, and pastrmajlija.
Sports and Recreation
Football, handball, and basketball are the most popular sports in North Macedonia. The North Macedonia national football team plays at the Toše Proeski Arena. In 2020, the national team qualified for UEFA Euro 2020, their first major tournament.
Handball is another important team sport. Macedonian clubs have done well in European competitions. RK Vardar won the Champions League twice. The European Women's Handball Championship was held in North Macedonia in 2008.
The national basketball team has played in the EuroBasket championships. Their best finish was 4th place in 2011. Pero Antić was the first Macedonian basketball player to play in the National Basketball Association (NBA).
In summer, the Ohrid Swimming Marathon takes place on Lake Ohrid. In winter, people can go skiing at the country's winter sports centers. North Macedonia also takes part in the Olympic Games. Magomed Ibragimov won a bronze medal in wrestling at the 2000 Summer Olympics. This was the first medal for the independent country.
Cinema and Media

Filmmaking in North Macedonia dates back over 110 years. The first film was made in 1895 by the Janaki and Milton Manaki. Movies often show the history, culture, and daily life of the Macedonian people. Many Macedonian films have won awards at festivals worldwide.
The first Macedonian feature film was Frosina, released in 1952. In 1994, Milcho Manchevski's film Before the Rain was nominated for an Academy Award for Best International Feature Film. In 2020, the documentary Honeyland was nominated for two Academy Awards.
The oldest newspaper in the country is Nova Makedonija, started in 1944. Other well-known newspapers include Utrinski vesnik and Dnevnik. Macedonian Radio Television is the public TV channel. There are also several popular private TV channels like Sitel and Kanal 5.
Public Holidays
North Macedonia celebrates several public holidays throughout the year:
| Date | English name | Macedonian name | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1–2 January | New Year | Нова Година, Nova Godina | |
| 7 January | Christmas Day (Orthodox) | Прв ден Божиќ, Prv den Božiḱ | |
| April/May | Good Friday (Orthodox) | Велики Петок, Veliki Petok | Orthodox Easter and other Easter dates do not match; see: List of dates for Easter |
| April/May | Easter Sunday (Orthodox) | Прв ден Велигден, Prv den Veligden | |
| April/May | Easter Monday (Orthodox) | Втор ден Велигден, Vtor den Veligden | |
| 1 May | Labour Day | Ден на трудот, Den na trudot | |
| 24 May | Saints Cyril and Methodius Day | Св. Кирил и Методиј, Ден на сèсловенските просветители; Sv. Kiril i Metodij, Den na sèslovenskite prosvetiteli | |
| 2 August | Republic Day | Ден на Републиката, Den na Republikata | Day when the Republic was established in 1944, also Ilinden Uprising in 1903. |
| 8 September | Independence Day | Ден на независноста, Den na nezavisnosta | Day of independence from Yugoslavia |
| 11 October | Day of the Macedonian Uprising | Ден на востанието, Den na vostanieto | Beginning of Anti-fascist war during WWII in 1941 |
| 23 October | Day of the Macedonian Revolutionary Struggle (Holiday) | Ден на македонската револуционерна борба,Den na makedonskata revolucionarna borba | Day when the Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO) was established in 1893. |
| 1 Shawwal | Eid ul-Fitr | Рамазан Бајрам, Ramazan Bajram | moveable, see: Islamic Calendar |
| 8 December | Saint Clement of Ohrid Day | Св. Климент Охридски, Sv. Kliment Ohridski |
National Symbols
- Sun: The official flag of the Republic of North Macedonia, adopted in 1995, shows a yellow sun. It has eight rays that spread out to the edges of a red background.
- Coat of arms: After gaining independence in 1991, North Macedonia kept its coat of arms. It was adopted in 1946. The coat of arms has a wreath of wheat, tobacco, and poppy. These are tied with a ribbon that looks like traditional folk clothing. In the middle, there are mountains, rivers, lakes, and the sun. These symbols represent "the richness of our country, our struggle, and our freedom."
See also
 In Spanish: Macedonia del Norte para niños
In Spanish: Macedonia del Norte para niños